Abstract
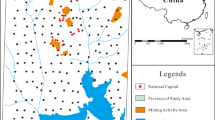
Heavy metal contamination in the soil around a water source is a particularly serious issue, because these heavy metals can be transferred into the water source and can pose significant human health risks through the contamination of drinking water or farmland irrigation water. In this paper, we collected surface soil samples from the area surrounding the Fenhe Reservoir. The concentrations of As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, and Zn were determined and the potential ecological risks posed by the heavy metals were quantitatively evaluated. The primary inputs for As, Ni, and Zn were natural sources, whereas the other elements were derived from mainly anthropogenic sources. Hg displays more serious environmental impacts than the other heavy metals. The upper reaches of the reservoir, located in the northwest, display a higher potential ecological risk.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birke M, Rauch U (2000) Urban geochemistry: investigations in the Berlin metropolitan area. Environ Geochem Health 22(3):233–248
Chen X, Xia XH, Zhao Y, Zhang P (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 181:640–646
Gurhan YM, Semiha I (2008) Multivariate analyses to determine the origin of potentially harmful heavy metals in beach and dune sediments from Kizkalesi coast, Turkey. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81(1):57–68
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Li XY, Liu LJ, Wang YG et al (2013) Heavy metal contamination of urban soil in an old industrial city in Northeast China. Geoderma 192:50–58
Lin Y (2002) Multivariate geostatistical methods to identify and map spatial variations of soil heavy metals. Environ Geol 42(1):1–10
McMartin I, Henderson P, Plouffe A, Knight R (2002) Comparison of Cu–Hg–Ni–Pb concentration in soils adjacent to anthropogenic point sources: examples from four Canadian sites. Geochem Explor Environ Anal 2(1):57–73
Micó C, Recatalá L, Peris M, Sánchez J (2006) Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soil of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 65(5):863–872
Muge A, Filiz K, Muhammet D, Tolga GL (2013) Heavy metal concentrations in surficial and core sediments from Izmir bay: an assessment of contamination and comparison against sediment quality benchmarks. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91(1):69–75
Rizo OD, Morell DF, López JOA et al (2013) Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban topsoils from Las Tunas city, Cuba. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91(1):29–35
SEPA (State Environmental Protection Administration of China) (2008) Environmental quality standard for soils, GB15618-2008
Shi RG, Lv JG, Cai YM et al (2010) Levels, spatial distribution and possible sources of heavy metals contamination of suburban soils in Tianjin, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85(3):287–290
Suresh G, Sutharsan P, Ramasamy V, Venkatachalapathy R (2012) Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:117–124
Wang XJ, Lai JQ, Kong H et al (2008) Analysis of the geochemical distribution characteristics of heavy metal elements in soil in Taiyuan basin and Taiyuan city (in Chinese). Earth Environ 36(1):72–80
Zahra A, Hashmi MZ, Malik RN, Ahmed Z (2014) Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah—feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake reservoir, Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 470–471:925–933
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 41271513.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Liu, G., Shi, W. et al. Soil Heavy Metal Contamination and Risk Assessment Around the Fenhe Reservoir, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93, 182–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1304-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1304-8