Abstract
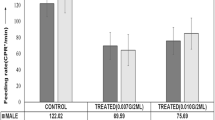
Bisphenol A (BPA), 4-nonylphenol (4-NP) and 4-tert-octylphenol (4-tert-OP) are the endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) that has been shown to exert both toxic and biological effects on living organisms. The present study investigated effects of environmentally relevant concentrations of BPA, 4-NP and 4-tert-OP (0.1, 1 and 10 mg/L) on the fecundity of fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. In the all exposure groups of BPA, 4-NP and 4-tert-OP, it was found a statistically significant decrease in mean fecundity as compared to the control groups (p < 0.05).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner M (1989) Drosophila a laboratory handbook. New York Press, Cold Harbor Spring
Atlı E, Ünlü H (2007) The effects of microwave frequency electromagnetic fields on the fecundity of Drosophila melanogaster. Turkish J Biol 31:1–5
Atlı E, Ünlü H (2008) Bisfenol A’nın Drosophila melanogaster’in canlı kalma oranı üzerine olan etkisi. Poster session presented at: XIX. National Biology Congress, Karadeniz Technical University, Turkey
Atlı E, Ünlü H (2009) Akut nonilfenol uygulamasının Drosophila melanogaster’in gelişimi üzerine toksik etkisinin incelenmesi. Poster session presented at: 7th congress of the Turkish society of toxicology, METU, Turkey
Baldwin WS, Graham SE, Shea D, LeBlanc GA (1997) Metabolic androgenization of female Daphnia magna by the xenoestrogen 4-nonylphenol. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1905–1911
Bettinetti R, Provini A (2002) Toxicity of 4-nonylphenol to Tubifex tubifex and Chironomus riparius in 28-Day Whole Sediment Tests. Ecotox Environ Saf 53:113–121
Cakal Arslan O, Parlak H (2007) Embryotoxic effects of nonylphenol and octylphenol in sea urchin Arbacia lixula. Ecotoxicology 16(6):439–444
Comber MHI, Williams TD, Stewart KM (1993) Effects of nonylphenol on Daphnia magna. Water Res 27:273–276
deFur PL, Crane M, Ingersoll C, Tattersfield L (1999) Endocrine disruption in invertebrates: Endocrinology, testing, and assessment. In: Proceedings of the workshops on endocrine disruption in invertebrates. SETAC Press, The Netherlands. Pensacola, FL
Forbes VE, Warbritton R, Aufderheide J, Van Der Hoeven N, Caspers N (2008) Effects of bisphenol a on fecundity, egg hatchability, and juvenile growth of Marisa cornuarıetis. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(11):2332–2340
Forget-Leray J, Landriau I, Minier C, Leboulenger F (2005) Impact of endocrine toxicants on survival, development, and reproduction of the esturine copepod Eurytemora affinis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 60:288–294
Fukuhori N, Kitano M, Kimura H (2005) Toxic effects of bisphenol A on sexual and asexual reproduction in Hydra oligactis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:495–500
Kahl MD, Makynen EA, Kosian PA, Ankley GT (1997) Toxicity of 4-nonylphenol in a life-cycle test with the midge Chironomus tentans. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 38:155–160
Krebs RA, Feder ME (1998) Hsp 70 and larval thermotolerance in Drosophila melanogaster: how much is enough and when is more too much? J Insect Physiol 44:1091–1101
Krebs RA, Loeschcke V (1994) Response to environmental change: Genetic variation and fitness in Drosophila buzzatii following temperature stress. In: Loeschcke V, Tomiuk J, Jain SK (eds) Conservation Genetics. Birkauser, Basel, pp 309–321
Lemos MFL, Van Gestel CAM, Soares AMVM (2010) Reproductive toxicity of the endocrine disrupters vinclozolin and bisphenol A in the terrestrial isopod Porcellio scaber (Latreille 1804). Chemosphere 78:907–913
Marcial HS, Hagiwara A, Snell TW (2003) Estrogenic compounds affect development of harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(12):3025–3030
Mihaich EM, Friederich U, Carpers N, Hall AT, Klecka GM, Dimond SS, Staples CA, Ortego LS, Hentges SG (2009) Acute and chronic toxicity testing of bisphenol A with aquatic invertebrates and plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1392–1399
Morrow G, Tanguay RM (2003) Heat shock proteins and aging in Drosophila melanogaster. Semin Cell Dev Biol 14:291–299
Obata T, Kubota S (2000) Formation of hydroxyl radicals by environmental estrogen-like chemicals in rat striatum. Neurosci Lett 296:41–44
Oehlmann J, Schulte-Oehlmann U, Tillmann M, Markert B (2000) Effects of endocrine distruptors on prosobranch snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda) in the laboratory. Part I: Bisphenol A and octylphenol as xeno-estrogens. Ecotoxicology 9:383–397
Preston BL, Snell TW, Robetson TL, Dingmann BJ (2000) Use of freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus in screening assay for potential endocrine disrupters. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2923–2928
Pyza E, Mak P, Kramarz P, Laskowski R (1997) Heat shock proteins (hsp70) as biomarkers in ecotoxicological studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 38:244–251
Rauschenbach IY, Sukhanova MZ, Hirashima A, Sutsugu E, Kuano E (2000) Role of ecdysteroid system in the regulation of Drosophila reproduction under environmental stress. Doklady Biol Sci 375:641–643
Reiter LT, Potocki L, Chien S, Gribskov M, Bier E (2001) A systematic analysis of human disease-associated gene sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res 11(6):1114–1125
Rhee JS, Raisuddin S, Lee KW, Seo JS, Ki JS, Kim IC, Park HG, Lee JS (2009) Heat shock protein (Hsp) gene responses of the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus to environmental toxicants. Comp Biochem Physiol 149:104–112
Roy D, Palangt M, Chen CW, Thomas RD, Colerangle J, Atkinson A, Yan ZJ (1997) Biochemical and molecular changes at the cellular level in response to exposure to environmental estrogen-like chemicals. J Toxicol Environ Health 50:1–29
Segner H, Caroll K, Fenske M, Janssen CR, Maack G, Pascoe D, Schafers C, Vandenbergh GF, Watts M, Wenzel A (2003) Identification of endocrine-disrupting effects in aquatic vertebrates and invertebrates: report from the European IDEA Project. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54:302–314
Shurin JB, Dodson SI (1997) Sublethal toxic effects of cyanobacteria and nonylphenol on environmental sex determination and development in Daphnia. Environ Toxicol Chem 16(6):1269–1276
Snyder MJ, Mulder EP (2001) Environmental endocrine disruption in decapod crustacean larvae: hormone titers, cytochrome P450, and stress protein responses to heptachlor exposure. Aqua Toxicol 55:177–190
Sonnenschein C, Soto AM (1998) An updated review of environmental estrogen and androgen mimics and antagonists. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 65(1–6):143–150
Widarto TH, Krogh PH, Forbes VE (2007) Nonylphenol stimulates fecundity but not population growth rate (λ) of Folsomia candida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 67:369–377
Xu LC, Sun H, Chen JF, Bian Q, Qian J, Song L, Wang XR (2005) Evaluation of androgen receptor transcriptional activities of bisphenol A, octylphenol and nonylphenol in vitro. Toxicology 216:197–203
Yesilada E (1999) Genotoxic activity of vinasse and its effect on fecundity and longevity of Drosophila melanogaster. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 63:560–566
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank The Scientific & Technological Researh Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atli, E. The Effects of Three Selected Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals on the Fecundity of Fruit Fly, Drosophila melanogaster . Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91, 433–437 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1083-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1083-7