Abstract
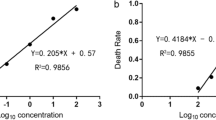
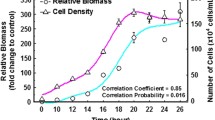
The toxicity of Cr3+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ to Tetrahymena growth metabolism was studied by microcalorimetry at 28°C, and the growth constant (k), peak time (T) and generation times (T G) were calculated. The metal ion concentrations that resulted in 50 % inhibition (IC 50) of population growth were obtained through the dynamic parameters. The results indicated that the order of toxicity was Cd2+ > Cr3+ > Cu2+. Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry results suggested that the metal ions affected the permeability of the cell membrane. Observations of the Cd-exposed organisms by scanning electron microscopy revealed damage to the cell membrane in the form of an altered surface appearance. The cells suffered serious damage after sufficient acting time. Attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectra revealed that amide groups and PO2 − of the phospholipid phospho-diester, both located in the hydrophobic end of the outer layer of the cell membrane, were most readily affected.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blinova I, Ivask A, Heinlaan M, Mortimer M, Kahru (2010) A ecotoxicity of nanoparticles of CuO and ZnO in natural water. Environ Pollut 158:41–47
Cumar SKM, Nagaraja B (2011) Environmental impact of leachate characteristics on water quality. Environ Monit Assess 178(1–4):499–505
Fang LC, Cai P, Li PX, Wu HY, Liang W (2010) Microcalorimetric and potentiometric titration studies on the adsorption of copper by P. putida and B. thuringiensis and their composites with minerals. J Hazard Mater 181:1031–1038
Gokkus O, Oguz M (2011) Investigation of color and COD removal by Fenton reagent from aqueous solutions containing acid and reactive dyestuffs. Desalin Water Treat 26(1–3):160–164
Gonzalez CB, Alonso AJ, Rodas GM (2011) Heavy metal chemical fractionation and immobilization in lightweight aggregates produced from mining and industrial waste. Int J Environ Sci Tech 8(4):667–676
Husaini SN, Zaidi JH, Matiullah (2011) Evaluation of toxic metals in the industrial effluents and their segregation through peanut husk fence for pollution abatement. J Radioanal Nucl Ch 289(1):203–211
Iqbal MA, Chaudhry MN, Zaib S, Vaqas M, Imran M (2011) Accumulation of heavy metals in the agricultural soils close to the industrial drains/areas. Asian J of Chem 23(2):913–916
Kaonga CC, Kumwenda J, Mapoma HT (2010) Accumulation of lead, cadmium, manganese, copper and zinc by sludge worms; Tubifex tubifex in sewage sludge. Int J Environ Sci Tech 7(1):119–126
Kiwi J, Nadtochenko V (2005) Evidence for the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of the bacterial wall membrane at theTiO2 interface by ATR-FTIR and laser kinetic spectroscopy. Langmuir 21:4631–4641
Kong WJ, Zhao YL, Xiao XH (2009) Action of palmatine on Tetrahymena thermophila BF5 growth investigated by microcalorimetry. J Hazard Mater 168:609–613
Li X, Zhang T, Min XM (2010) Toxicity of aromatic compounds to Tetrahymena estimated by microcalorimetry and QSAR. Aquat Toxicol 98:322–327
Liu P, Liu Y, Lu ZX, Zhu JC, Dong JX, Pang DW, Shen P, Qu SS (2004) Study on biological effect of La3+ on Escherichia coli by atomic force microscopy. J Inorg Biochem 98:68–72
Liu P, Zhang WY, Li X, Chen XY, Zhang CC (2007) Microcalorimetric study on the toxic effect of Pb2+ to Tetrahymena. Biol Trace Elem Res 119:175–182
Melo MR, Flores NR, Murrieta SV, Tovar AR, Zúñiga AG, Hernández OF, Mendoza AP, Pérez NO, Dorantes AR (2011) Comparative plant growth promoting traits and distribution of rhizobacteria associated with heavy metals in contaminated soils. Int J Environ Sci Tech 8(4):807–816
Mihaljevic Z, Ternjej I, Stankovic I et al (2011) Assessment of genotoxic potency of sulfate-rich surface waters on medicinal leech and human leukocytes using different versions of the Comet assay. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 74(5):1416–1426
Qin CQ, Zhou B, Zeng LT, Liu Y, Du YM (2004) The physicochemical properties and antitumor activity of cellulase-treated chitosan. Food Chem 84:107–115
Sogut OO, Yildirim EK, Akgun M (2011) The treatment of wastewaters by supercritical water oxidation. Desalin Water Treat 26(1–3):131–138
Twagilimana L, Bohatier J, Groliere CA, Bonnemoy F, Sargos D (1998) A new low-cost microbiotest with the Protozoan Spirostomum teres: culture conditions and assessment of sensitivity of the ciliate to 14 pure chemicals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 41:231–244
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2009ZX07106-003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Li, X., Lu, Y. et al. Acute Toxicity of Heavy Metals to Tetrahymena in an In Vitro Experiment and Envelope Damage Study. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91, 62–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1004-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1004-9