Abstract
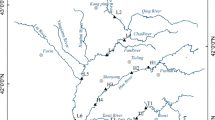
This study was carried out to estimate the potential toxicity of 8 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and 5 organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in sediments in the Ebro River Basin (20 sampling points) according to different methodologies. Detection limit (DL) concentrations were used for compounds reported below the DL (worst-case scenario). The majority of PAH concentrations were found to be below their method detection limit. DL concentrations for OCPs were above the threshold values set by one guideline. In such cases, no toxicity assessment was carried out. It should be noted that no sediment is expected to cause adverse effects on the benthic species living in these sediments according to the methodologies applied.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Toro DM, Mcgrath JA (2000) Technical basis for narcotic chemicals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon criteria. II. Mixtures and sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(8):1971–1982
Di Toro DM, Mcgrath JA, Hansen DJ (2000) Technical basis for narcotic chemicals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon criteria. I. Water and tissue. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(8):1951–1970
Hernandez S, Franco C, Herrera C (2008) Carbono orgánico y materia orgánica en sedimentos superficiales de la Bahía Concepción. Ciencia…Ahora 21 (In Spanish)
Hu W, Wang T, Khim J, Luo W, Jiao W, Lu Y, Naile J, Chen C, Zhang X, Giesy J (2010) HCH and DDT in sediments from marine and adjacent riverine areas of North Bohai Sea, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 59:71–79
Hung CC, Gong GC, Ko FC, Chen HY, Hsu ML, Wu JM, Peng SC, Nan FH, Yeager KM, Santschi PH (2010) Relationships between persistent organic pollutants and carbonaceous materials in aquatic sediments of Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 60(7):1010–1017
Lacorte S, Raldua D, Martinez E, Navarro A, Diez S, Bayona JM, Barcelo D (2006) Pilot survey of a broad range of priority pollutants in sediment and fish from the Ebro river basin (NE Spain). Environ Pollut 140(3):471–482
Long ER, Ingersoll CG, MacDonald DD (2006) Calculation and uses of mean sediment quality guideline quotients: a critical review. Environ Sci Technol 40:1726–1736
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Martinez-Llado X, Gibert O, Marti V, Diez S, Romo J, Bayona JM, de Pablo J (2007) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and tributyltin (TBT) in Barcelona harbour sediments and their impact on benthic communities. Environ Pollut 149(1):104–113
McGrath JA, Paquin PR, Di Toro D (2002) Use of the SEM and AVS approach in predicting metal toxicity in sediments. Fact sheet on environmental risk assessment. Published by the International Council on Mining and Metals (ICMM). No. 10. London, UK
Navarro-Ortega A, Tauler R, Lacorte S, Barcelo D (2010) Occurrence and transport of PAHs, pesticides and alkylphenols in sediment samples along the Ebro River Basin. J Hydrol 383(1–2):5–17
Ololade IA (2010) Prediction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons toxicity using equilibrium partitioning approach and narcosis model. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:238–242
Persaud DR, Jaagumagi R, Hayton A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediments in Ontario. Standards Development Branch. Ontario Ministry of Environment and Energy. Toronto, Canada
Tang ZW, Yang ZF, Shen ZY, Niu JF, Liao RF (2007) Distribution and sources of organochlorine pesticides in sediments from typical catchment of the Yangtze River, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53:303–312
U.S.EPA (2003a) Procedures for the derivation of equilibrium partitioning sediment benchmarks (ESBs) for the protection of benthic organisms: PAH mixtures. EPA-600-R-02 013. Office of Research and Development. Washington, DC 20460
U.S.EPA (2003b) Procedures for the derivation of equilibrium partitioning sediment benchmarks (ESBs) for the protection of benthic organisms: Endrin. EPA-600-R-02-009. Office of Research and Development. Washington, DC 20460
U.S.EPA (2003c) Procedures for the derivation of equilibrium partitioning sediment benchmarks (ESBs) for the protection of benthic organisms: Dieldrin. EPA-600-R-02-010. Office of Research and Development. Washington, DC 20460
Vidal DE, Bay SM (2005) Comparison of sediment quality guideline performance for predicting sediment toxicity in southern California. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(12):3173–3182
Wang JZ, Nie YF, Luo XL, Zeng EY (2008) Occurrence and phase distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta, China. In: 15th international conference on marine pollution and ecotoxicology. Mar Pollut Bull 57(6–12):767–774
Wong CS, Capel PD, Nowell LH (2000) Organochlorine pesticides and PCBs in stream sediment and aquatic biota – initial results from the National Water-Quality Assessment Program, 1992–1995. US Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 00-4053, Sacramento, California
Zhang Z, Huang J, Yu G, Hong H (2004) Occurrence of PAHs, PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in the Tonghui River of Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 130:249–261
Acknowledgments
The authors of this study wish to acknowledge the partnership project between the University of Zaragoza and the Ebro Hydrographical Confederation and MICINN-FEDER funding through CTM2008-01876/TECNO project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veses, O., Mosteo, R., Ormad, M.P. et al. Potential Toxicity of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Organochlorine Pesticides in Sediments from the Ebro River Basin in Spain. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88, 644–650 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-011-0519-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-011-0519-1