Abstract
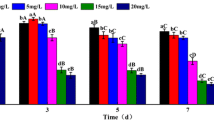
Allelochemical ethyl 2-methyl acetoacetate (EMA) can significantly inhibit the growth of bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa. In order to assess the implication of the damage of EMA on the algal photosynthetic apparatus, the effects of EMA on the algal ultrastructure and pigment composition were investigated. At initial exposure time to EMA (0–40 h), algal allophycocyanin, phycoerythrin and carotenoid degraded firstly; chlorophyll a increased, especially by 47% in the algae exposed to 2 mg L−1 of EMA; phycocyanin was not significantly affected; lipid bodies increased remarkably. After 40 h of EMA exposure, chlorophyll a decreased gradually, especially by 45% in the algae exposed to 4 mg L−1 of EMA; lipid bodies greatly reduced but cyanophycin granules accumulated; thylakoid structures were dissolved or disappeared with the presence of numerous vacuoles. These results showed that all ophycocyanin, phycoerythrin and carotenoid were more sensitive to EMA than other pigments, the cells of M. aeruginosa was stressed by EMA with the occurrence of cyanophycin granules and the photosynthesis pigments and ultrastructure of M. aeruginosa were quickly destroyed by EMA with exposure time increasing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelson JN, Simon MI (1988) Phycobiliproteins in cyanobacteria. In: Lester P, Alexander NG (eds) Method in enzymology. Academic Press, London, p 167
Allen MM, Hutchison F, Weathers PJ (1980) Cyanophycin granule polypeptide formation and degradation in the cyanobacterium Aphanocapsa 6308. J Bacteriol 141:687–693
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Bryant DA (1996) The molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Kluwer Academic publishers, Amsterdam, pp 559–579
Chen JZ, Liu ZL, Ren GJ, Li PF, Jiang YW (2004) Control of Microcystis aeruginosa TH01109 with batangas mandarin skin and dwarf banana peel. Water SA 30(2):279–282
Einhellig FA (1995a) Allelopathy: current status and future goals. In: Inderjit, Dakshini KMM, Einhellig FA (eds) Allelopathy: organisms, processes, and application. American Chemical Society, Washington DC, pp 1–24
Einhellig FA (1995b) Mechanism of action of allelochemicals in allelopathy. In: Inderjit Dakshini KMM, Einhellig FA (eds) Allelopathy: organisms, processes, and application. American Chemical Society, Washington DC, pp 96–116
Eullaffroy P, Vernet G (2003) The F684/F735 chlorophyll fluorescence ratio: a potential tool for rapid detection and determination of herbicide phytotoxicity in algae. Water Res 37(9):1983–1990
Gerasimenko LM, Pusheva MA, Goryunova SV (1972) Developmental cycle of and ultrastructure of Cyanidium caldarium. Microbiology 41:324–326
Goodwin TW (1971) Biosynthesis by chloroplasts. In: Gibbs M (ed) Structure and function of chloroplasts. Springer, Berlin, pp 215–276
Grobe CW, Murphy TM (1998) Solar ultraviolet-B radiation effects on growth and pigment composition of the intertidal alga Ulva expansa (Setch.) S.&G. (Chlorophyta). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 225:39–51
Hong Y, Hu HY, Xie X, Li FM (2008) Responses of enzymatic antioxidants and non-enzymatic antioxidants in cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to allelochemical ethyl 2-methyl acetoacetate (EMA) isolated from reed (Phragmites communis). J Plant Physiol 165(12):1264–1273
Huang JJ, Kolodny NH, Redfearn JT, Allen MM (2002) The acid stress response of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp strain PCC 6308. Arch Microbiol 177(6):486–493
Li FM, Hu HY (2005) Isolation and characterization of a novel antialgal allelochemical from Phragmites communis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):6545–6553
Nakai S, Yamada S, Hosomi M (2005) Anti-cyanobacterial fatty acids released from Myriophyllum spicatum. Hydrobiologia 543:71–78
Nakai S, Zhou S, Hosomi M, Tominaga M (2006) Allelopathic growth inhibition of cyanobacteria by reed. Allelopathy J 18(2):277–285
Padgett MP, Krogmann DW (1987) Large scale preparation of pure phycobiliproteins. Photosynth Res 11:225–235
Pan G, Zhang MM, Chen H, Zou H, Yan H (2006) Removal of cyanobacterial blooms in Taihu Lake using local soils. I. Equilibrium and kinetic screening on the flocculation of Microcystis aeruginosa using commercially available clays and minerals. Environ Pollut 141(2):195–200
Papageorgiou GC (1996) The photosynthesis of cyanobacteria (blue bacteria) from the perspective of signal analysis of chlorophyll alpha fluorescence. J Sci Ind Res India 55(8–9):596–617
Pollio A, Pinto G, Ligrone R, Aliotta G (1993) Effects of the potential allelochemical α-asarone on growth, physiology and ultrastructure of two unicellular green algae. J Appl Phycol 5:395–403
Romanowska-Duda Z, Mankiewicz J, Tarczynska M, Walter Z, Zalewski M (2002) The effect of toxic cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) on water plants and animal cells. Pol J Environ Stud 11(5):561–566
Sarcina M, Tobin MJ, Mullineaux CW (2001) Diffusion of phycobilisomes on the thylakoid membranes of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus 7942 – Effects of phycobilisome size, temperature, and membrane lipid composition. J Biol Chem 276(50):46830–46834
Stransky H, Hager A (1970) Das carotenoidimuster and die Verbreitung des lichtinduzierten Xanthophyllcyclus in Verschiedenen Algenklassen. IV. Cyanophyceae and Rhodophyceae. Arch Mikrobiol 72:84–96
Wu JT, Kuo-Huang LL, Lee J (1998) Algicidal effect of Peridinium bipes on Microcystis aeruginosa. Curr Microbiol 37(4):257–261
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Beijing Forestry University Young Scientist Fund (No. BLX2008025), National Natural Science Foundation of China-Japan Science and Technology Agency (NSFC-JST) Joint Project (No. 50721140017), Support Project (Nansi Lake) (No. 2006BAC10B03) and National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 50825801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, Y., Huang, JJ. & Hu, HY. Effects of a Novel Allelochemical Ethyl 2-Methyl Acetoacetate (EMA) on the Ultrastructure and Pigment Composition of Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa . Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83, 502–508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9795-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9795-4