Abstract
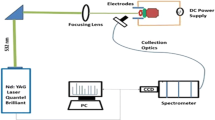
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) System was developed locally for determination of toxic metals in liquid samples and the system was tested for analysis of waste water collected from dairy products processing plant. The plasma was generated by focusing a pulsed Nd: YAG laser at 1064 nm on waste water samples. Optimal experimental conditions were evaluated for improving the sensitivity of our LIBS system through parametric dependence investigations. The Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) results were then compared with the results obtained using standard analytical technique such as Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission Spectroscopy (ICP). The evaluation of the potential and capabilities of LIBS as a rapid tool for liquid sample analysis are discussed in brief.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colao F, Fantoni R, Lazic V, Paolini A, Fabbri F, Ori GG, Marinangeli L, Baliva A (2004) Investigation of LIBS feasibility for in situ planetary exploration: an analysis on Martian rock analogues. Planet Space Sci 52:117–123
Evans EH, Day JA, Price WJ, Smith CM, Sutton K, Tyson JF (2004) Atomic spectrometry update. Advances in atomic emission, absorption and fluorescence and related techniques. J Anal At Spectrom 19:775–778
Fichet P, Menut D, Brennetot R, Vors E, Rivoallan A (2003) Analysis by LIBS of complex solids, liquids and powders with an Echelle Spectrometer. Appl Opts 42:6029–6035
Gondal MA (1997) Laser photo acoustic spectrometer for remote monitoring of atmospheric pollutants. Appl Opts 36:3195–3201
Gondal MA, Hussain T (2006) Determination of poisonous metals in wastewater collected from paint manufacturing plant using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy Talanta (On line available under ref # doi:10.1016/j.talanta)
Gondal MA, Mastromarino J (2000) LIDAR system for environmental studies. Talanta 53: 147–154
Gondal MA, Mastromarino J, Klein UK (2002) Laser Doppler velocimeter for remote measurements of pollutant water and aerosols discharges. Opts Lasers Eng 38:589–600
Gondal MA, Hussain T, Yamani ZH, Baig MA (2006) Detection of heavy metals in Arabian crude oil residue using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. TALANTA 69:1072–1078
Radziemski LJ, Cremers DA (1989) Laser induced plasmas and applications. Marcel Dekker, New York
Royal Commission, Jubail Industrial City, Saudi-Arabian Environmental Regulation Standards, September (1999) and American Public Health Association, Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water 18th edn (1992) American public Health Association, Washington, DC
Sallé B, Cremers DA, Maurice S, Wiens RC (2005) Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for space exploration applications: Influence of the ambient pressure on the calibration curves prepared from soil and clay samples. Spectrochim Acta Part B 60:479–490
Stratis DN, Eland KL, Angel SM (2000) Enhancement of aluminum, titanium and iron in glass using pre-ablation spark dual-pulse LIBS. Appl Spectrosc 54:1719–1726
Striganove A, Sventitski N (1968) Table of spectral lines of neutral and ionized atoms. Plenum, New York
US EPA R&D Report (1992) Risk reduction engineering laboratory cincinnati OH 45268 EPA/600/S-92/005
Wainner RT, Harmon RS, Miziolek AW, McNesby KL, French PD (2001) Analysis of environmental lead contamination: comparison of LIBS field and laboratory instruments. Spectrochim Acta Part B 56:777–793
Winefordner JD, Gornushkin IB, Pappas D, Matveev OI, Smith BW (2000) Novel uses of lasers in atomic spectroscopy: plenary lecture. J Anal At Spectrom 15:1161–1189
Acknowledgments
The support by the Physics Departments and King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals is gratefully acknowledged. One of the author (T.H.) is thankful to National University of Science and Technology and Government of Pakistan for finacial support for his Ph.D work. He is also thankful to KFUPM for its hospitality and permission to work at its research facilties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, T., Gondal, M.A. Detection of Toxic Metals in Waste Water from Dairy Products Plant Using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80, 561–565 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9418-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9418-5