Abstract
Purpose
Nationwide data have been lacking on drug abuse (DA)-associated mortality. We do not know the degree to which this excess mortality results from the characteristics of drug-abusing individuals or from the effects of DA itself.
Method
DA was assessed from medical, criminal, and prescribed drug registries. Relative pairs discordant for DA were obtained from the Multi-Generation and Twin Registers. Mortality was obtained from the Swedish Mortality registry.
Results
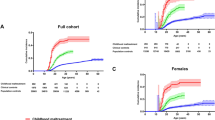
We examined all individuals born in Sweden 1955–1980 (n = 2,696,253), 75,061 of whom developed DA. The mortality hazard ratio (mHR) (95% CIs) for DA was 11.36 (95% CIs, 11.07–11.66), substantially higher in non-medical (18.15, 17.51–18.82) than medical causes (8.05, 7.77–8.35) and stronger in women (12.13, 11.52–12.77) than in men (11.14, 10.82–11.47). Comorbid smoking and alcohol use disorder explained only a small proportion of the excess DA-associated mortality. Co-relative analyses demonstrated substantial familial confounding in the DA–mortality association with the strongest direct effects seen in middle and late-middle ages. The mHR was highest for opiate abusers (24.57, 23.46–25.73), followed by sedatives (14.19, 13.11–15.36), cocaine/stimulants (12.01, 11.36–12.69), and cannabis (10.93, 9.94–12.03).
Conclusion
The association between registry-ascertained DA and premature mortality is very strong and results from both non-medical and medical causes. This excess mortality arises both indirectly—from characteristics of drug-abusing persons—and directly from the effects of DA. Excess mortality of opiate abuse was substantially higher than that observed for all other drug classes. These results have implications for interventions seeking to reduce the large burden of DA-associated premature mortality.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Degenhardt L, Hall W (2012) Extent of illicit drug use and dependence, and their contribution to the global burden of disease. Lancet 379(9810):55–70
Degenhardt L, Whiteford HA, Ferrari AJ, Baxter AJ, Charlson FJ, Hall WD, Freedman G, Burstein R, Johns N, Engell RE, Flaxman A, Murray CJ, Vos T (2013) Global burden of disease attributable to illicit drug use and dependence: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 382(9904):1564–1574
Patel V, Chisholm D, Dua T, Laxminarayan R, Medina-Mora ME (2015) Mental, neurological, and substance use disorders, 3rd edn. World Bank Group, Washington, D.C.
Larm P, Hodgins S, Larsson A, Samuelson YM, Tengstrom A (2008) Long-term outcomes of adolescents treated for substance misuse. Drug Alcohol Depend 96(1–2):79–89
Bargagli AM, Hickman M, Davoli M, Perucci CA, Schifano P, Buster M, Brugal T, Vicente J (2006) Drug-related mortality and its impact on adult mortality in eight European countries. Eur J Public Health 16(2):198–202
Degenhardt L, Singleton J, Calabria B, McLaren J, Kerr T, Mehta S, Kirk G, Hall WD (2011) Mortality among cocaine users: a systematic review of cohort studies. Drug Alcohol Depend 113(2–3):88–95
Degenhardt L, Bucello C, Mathers B, Briegleb C, Ali H, Hickman M, McLaren J (2011) Mortality among regular or dependent users of heroin and other opioids: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Addiction 106(1):32–51
Perucci CA, Bargagli AM, Davoli M, Sperati A, Hartnoll R, Vicente J (2000) Mortality of drug users in the EU: coordination of implementation of new cohort studies, follow-up and analysis of existing cohorts and development of new methods and outputs. Report No.: EMCDDA Scientific report: EMCDDA CT.99.EP.07/CT.00.EP.13. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). Lisboa
Ridolfo B, Stevenson C (2001) The Quantification of drug-caused mortality and morbidity in Australia, 1998. Canberra, AIHW. Drug Statistics Series no. 7. Cat. no. PHE 29. 6-1-2016
Lindblad R, Hu L, Oden N, Wakim P, Rosa C, VanVeldhuisen P (2016) Mortality rates among substance use disorder participants in clinical trials: pooled analysis of twenty-two clinical trials within the National Drug Abuse Treatment Clinical Trials Network. J Subst Abuse Treat 70:73–80
Mokdad AH, Marks JS, Stroup DF, Gerberding JL (2004) Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. JAMA 291(10):1238–1245
Case A, Deaton A (2015) Rising morbidity and mortality in midlife among white non-Hispanic Americans in the 21st century. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(49):15078–15083
Singleton J, Degenhardt L, Hall W, Zabransky T (2009) Mortality among amphetamine users: a systematic review of cohort studies. Drug Alcohol Depend 105(1–2):1–8
Calabria B, Degenhardt L, Hall W, Lynskey M (2010) Does cannabis use increase the risk of death? Systematic review of epidemiological evidence on adverse effects of cannabis use. Drug Alcohol Rev 29(3):318–330
Lopez-Quintero C, Roth KB, Eaton WW, Wu LT, Cottler LB, Bruce M, Anthony JC (2015) Mortality among heroin users and users of other internationally regulated drugs: a 27-year follow-up of users in the Epidemiologic Catchment Area Program household samples. Drug Alcohol Depend 156:104–111
Bargagli AM, Sperati A, Davoli M, Forastiere F, Perucci CA (2001) Mortality among problem drug users in Rome: an 18-year follow-up study, 1980–1997. Addiction 96(10):1455–1463
Rodriguez DF, Carrera MR, Navarro M, Koob GF, Weiss F (1997) Activation of corticotropin-releasing factor in the limbic system during cannabinoid withdrawal. Science 276(5321):2050–2054
Fergusson DM, Horwood LJ (2000) Cannabis use and dependence in a New Zealand birth cohort. N Z Med J 113(1109):156–158
Agrawal A, Jacobson KC, Prescott CA, Kendler KS (2004) A twin study of personality and illicit drug use and abuse/dependence. Twin Res 7(1):72–81
Grant BF, Goldstein RB, Saha TD, Chou SP, Jung J, Zhang H, Pickering RP, Ruan WJ, Smith SM, Huang B, Hasin DS (2015) Epidemiology of DSM-5 alcohol use disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry 72(8):757–766
Akaike H (1987) Factor analysis and AIC. Psychometrika 52:317–332
Ljungquist B, Berg S, Lanke J, McClearn GE, Pedersen NL (1998) The effect of genetic factors for longevity: a comparison of identical and fraternal twins in the Swedish Twin Registry. J Gerontol Med Sci 53A(6):M441–M446
Kendler KS, Ohlsson H, Sundquist J, Sundquist K (2016) Alcohol use disorder and mortality across the lifespan: a longitudinal cohort and co-relative analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 73(6):575–581
SAS Institute I (2011) SAS/STAT User’s Guide, version 9.3. SAS Institute Inc, SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Onyeka IN, Beynon CM, Hannila ML, Tiihonen J, Fohr J, Tuomola P, Kuikanmaki O, Tasa N, Paasolainen M, Kauhanen J (2014) Patterns and 14-year trends in mortality among illicit drug users in Finland: the HUUTI study. Int J Drug Policy 25(6):1047–1053
Cottler LB, Hu H, Smallwood BA, Anthony JC, Wu LT, Eaton WW (2016) Nonmedical opioid pain relievers and all-cause mortality: a 27-year follow-up from the epidemiologic catchment area study. Am J Public Health 106(3):509–516
Oyefeso A, Ghodse H, Clancy C, Corkery J, Goldfinch R (1999) Drug abuse-related mortality: a study of teenage addicts over a 20-year period. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 34(8):437–441
Fugelstad A, Annell A, Rajs J, Agren G (1997) Mortality and causes and manner of death among drug addicts in Stockholm during the period 1981–1992. Acta Psychiatr Scand 96(3):169–175
Mathers BM, Degenhardt L, Bucello C, Lemon J, Wiessing L, Hickman M (2013) Mortality among people who inject drugs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull World Health Organ 91(2):102–123
Mathers BM, Degenhardt L, Phillips B, Wiessing L, Hickman M, Strathdee SA, Wodak A, Panda S, Tyndall M, Toufik A, Mattick RP (2008) Global epidemiology of injecting drug use and HIV among people who inject drugs: a systematic review. Lancet 372(9651):1733–1745
Kringlen E, Torgersen S, Cramer V (2001) A Norwegian psychiatric epidemiological study. Am J Psychiatry 158(7):1091–1098
Rounsaville BJ, Kosten TR, Weissman MM, Prusoff B, Pauls D, Anton SF, Merikangas K (1991) Psychiatric disorders in relatives of probands with opiate addiction. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48(1):33–42
Merikangas KR, Stolar M, Stevens DE, Goulet J, Preisig MA, Fenton B, Zhang H, O’Malley SS, Rounsaville BJ (1998) Familial transmission of substance use disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55(11):973–979
Bierut LJ, Dinwiddie SH, Begleiter H, Crowe RR, Hesselbrock V, Nurnberger JI Jr, Porjesz B, Schuckit MA, Reich T (1998) Familial transmission of substance dependence: alcohol, marijuana, cocaine, and habitual smoking: a report from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55(11):982–988
Acknowledgements
This Project was supported by Grant R01DA030005 from the National Institutes of Health, the Swedish Research Council (K2012-70X-15428-08-3), the Swedish Research Council for Health, Working Life and Welfare (In Swedish: Forte; Reg. no.: 2013-1836), the Swedish Research Council (2012-2378; 2014-10134) and FORTE (2014-0804) as well as ALF funding from Region Skåne awarded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical standards
The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committees on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. We secured ethical approval for this study from the Regional Ethical Review Board of Lund University (No. 2008/409).
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kendler, K.S., Ohlsson, H., Sundquist, K. et al. Drug abuse-associated mortality across the lifespan: a population-based longitudinal cohort and co-relative analysis. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 52, 877–886 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-017-1398-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-017-1398-5