Abstract
Purpose
Immigrants have heightened risks of psychotic disorders, and it is proposed that migration influences symptom profiles. The purpose of this study was to investigate if either migration experience and/or visible minority status affected symptom profiles, using a cross-culturally validated five-factor model of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS), in patients with broadly defined psychotic disorders.
Methods
PANSS was assessed in a large catchment area based sample of patients with psychotic disorders verified with the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (n = 1,081). Symptom profiles based on Wallwork et al. five-factor model were compared for Norwegians (73 %), white immigrants (10.5 %), and visible minority groups (16.5 %).
Results
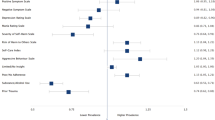
Visible minorities were significantly younger, had less education, more often a schizophrenia diagnosis and higher PANSS positive, negative and disorganized/concrete factor scores than Norwegians and white immigrants. After controlling for confounders only the items “Delusions” and “Difficulty in abstract thinking” differed between groups. Multivariate analyses indicated that these items were not associated with immigration per se, but rather belonging to a visible minority.
Conclusion
We found mostly similarities in psychotic symptoms between immigrants and Norwegians when using a cross-culturally validated five-factor model of the PANSS. Immigration did not directly influence psychotic symptom profiles but visible minority groups had higher levels of “Delusions” and “Difficulty in abstract thinking”, both symptoms that are partially context dependent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coid JW, Kirkbride JB, Barker D, Cowden F, Stamps R, Yang M, Jones PB (2008) Raised incidence rates of all psychoses among migrant groups: findings from the. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65(11):1250–1258. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.65.11.1250
Cantor-Graae E, Selten J (2005) Schizophrenia and migration: a meta-analysis and review. Am J Psychiatry 162(1):12–24. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.1.12
Bourque F, van der Ven E, Malla A (2011) A meta-analysis of the risk for psychotic disorders among first- and second-generation immigrants. Psychol Med 41(5):897–910. doi:10.1017/S0033291710001406
Selten JP, Slaets JP, Kahn RS (1997) Schizophrenia in surinamese and dutch antillean immigrants to The Netherlands: evidence of an increased incidence. Psychol Med 27(4):807–811. doi:10.1017/S0033291797005199
Selten JP, Sijben N (1994) First admission rates for schizophrenia in immigrants to The Netherlands. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 29(2):71–77. doi:10.1007/BF00805625
Bhugra D, Leff J, Mallett R, Der G, Corridan B, Rudge S (1997) Incidence and outcome of schizophrenia in whites, African-Caribbeans and Asians in London. Psychol Med 27(4):791–798. doi:10.1017/S0033291797005369
Bolden L, Wicks MN (2005) Length of stay, admission types, psychiatric diagnoses, and the implications of stigma in African Americans in the nationwide inpatient sample. Issues Ment Health Nurs 26(10):1043–1059. doi:10.1080/01612840500280703
Schofield P, Ashworth M, Jones R (2011) Ethnic isolation and psychosis: re-examining the ethnic density effect. Psychol Med (41):1263–1269. doi:10.1017/S0033291710001649
Das-Munshi J, Becares L, Boydell JE, Dewey ME, Morgan C, Stansfeld SA, Prince MJ (2012) Ethnic density as a buffer for psychotic experiences: findings from a national survey (EMPIRIC). Br J Psychiatry 201(4):282–290. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.111.102376
van Os J (2012) Psychotic experiences: disadvantaged and different from the norm. Br J Psychiatry 201(4):258–259. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.112.110262
Veling W (2013) Ethnic minority position and risk for psychotic disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry 26(2):166–171. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e32835d9e43
Bresnahan M, Begg MD, Brown A, Schaefer C, Sohler N, Insel B, Vella L, Susser E (2007) Race and risk of schizophrenia in a US birth cohort: another example of health disparity? Int J Epidemiol 36(4):751–758. doi:10.1093/ije/dym041
Amad A, Guardia D, Salleron J, Thomas P, Roelandt JL, Vaiva G (2013) Increased prevalence of psychotic disorders among third-generation migrants: results from the French Mental Health in General Population survey. Schizophr Res. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2013.03.011
Schrier AC, van de Wetering BJM, Mulder PGH, Selten JP (2001) Point prevalence of schizophrenia in immigrant groups in Rotterdam: data from outpatient facilities. European Psychiatry 16(3):162–166. doi:10.1016/S0924-9338(01)00558-2
Anglin DM, Malaspina D (2008) Racial and ethnic effects on psychotic psychiatric diagnostic changes from admission to discharge: a retrospective chart review. J Clin Psychiatry 69(3):464–469
Schaffer A, Cairney J, Cheung A, Veldhuizen S, Kurdyak P, Levitt A (2009) Differences in prevalence and treatment of bipolar disorder among immigrants: results from an epidemiologic survey. Can J Psychiatry 54(11):734–742
Berg AO, Melle I, Rossberg JI, Romm KL, Larsson S, Lagerberg TV, Andreassen OA, Hauff E (2011) Perceived discrimination is associated with severity of positive and depression/anxiety symptoms in immigrants with psychosis: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 11(1):77. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-11-77
Janssen I, Hanssen M, Bak M, Bijl RV, De Graaf R, Vollebergh W, McKenzie K, van Os J (2003) Discrimination and delusional ideation. Br J Psychiatry 182(1):71–76
Haasen C, Yagdiran O, Mass R, Krausz M (2001) Schizophrenic disorders among Turkish migrants in Germany. A controlled clinical study. Psychopathology 34(4):203–208. doi:10.1159/000049308
Veling W, Selten JP, Mackenbach JP, Hoek HW (2007) Symptoms at first contact for psychotic disorder: comparison between native Dutch and ethnic minorities. Schizophr Res 95(1–3):30–38. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2007.06.024
Harvey I, Williams M, McGuffin P, Toone BK (1990) The functional psychoses in Afro-Caribbeans. Br J Psychiatry 157:515–522. doi:10.1192/bjp.157.4.515
Sohler NL, Bromet EJ (2003) Does racial bias influence psychiatric diagnoses assigned at first hospitalization? Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 38(8):463–472. doi:10.1007/s00127-003-0653-0
Kennedy N, Boydell J, van Os J, Murray RM (2004) Ethnic differences in first clinical presentation of bipolar disorder: results. J Affect Disord 83(2–3):161–168. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2004.06.006
Dassori AM, Miller AL, Velligan D, Saldana D, Diamond P, Mahurin R (1998) Ethnicity and negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Cult Divers Ment Health 4(1):65–69. doi:10.1037/1099-9809.4.1.65
Van Der Ven E, Bourque F, Joober R, Selten JP, Malla AK (2012) Comparing the clinical presentation of first-episode psychosis across different migrant and ethnic minority groups in Montreal, Quebec. Can J Psychiatry 57(5):300–308
Chang N, Newman J, D’Antonio E, McKelvey J, Serper M (2011) Ethnicity and symptom expression in patients with acute schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 185(3):453–455. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2010.07.019
Harrison G, Amin S, Singh SP, Croudace T, Jones P (1999) Outcome of psychosis in people of African-Caribbean family origin. Population-based first-episode study. Br J Psychiatry 175:43–49. doi:10.1192/bjp.175.1.43
Perron BE, Fries LE, Kilbourne AM, Vaughn MG, Bauer MS (2010) Racial/Ethnic group differences in bipolar symptomatology in a community sample of persons with bipolar I disorder. J Nerv Ment Dis 198(1):16–21. doi:10.1097/NMD.0b013e3181c818c5
Li H, Eack SM, Montrose DM, Miewald JM, Keshavan M (2011) Longitudinal treatment outcome of African American and Caucasian patients with first episode psychosis. Asian J Psychiatr 4(4):266–271. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2011.08.004
Perera R, Owens DG, Johnstone EC (1991) Disabilities and circumstances of schizophrenic patients—a follow-up study. Ethnic aspects. A Comparison of three matched groups. Br J Psychiatry Suppl (13):40–2, 44–6
Birchwood M, Cochrane R, Macmillan F, Copestake S, Kucharska J, Carriss M (1992) The influence of ethnicity and family structure on relapse in first-episode schizophrenia. A comparison of Asian, Afro-Caribbean, and white patients. Br J Psychiatry 161:783–790. doi:10.1192/bjp.161.6.783
Douzenis A, Apostolopoulos A, Seretis D, Rizos EN, Christodoulou C, Lykouras L (2011) The effect of ethnicity on prescribing practice and treatment outcome in inpatients suffering from schizophrenia in Greece. BMC Psychiatry 11:66. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-11-66
Bae SW, Brekke JS (2002) Characteristics of Korean-Americans with schizophrenia: a cross-ethnic comparison with African-Americans, Latinos, and Euro-Americans. Schizophr Bull 28(4):703–717
van der Gaag M, Cuijpers A, Hoffman T, Remijsen M, Hijman R, de Haan L, van Meijel B, van Harten PN, Valmaggia L, de Hert M, Wiersma D (2006) The five-factor model of the positive and negative syndrome scale I: confirmatory factor analysis fails to confirm 25 published five-factor solutions. Schizophr Res 85(1–3):273–279. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2006.04.001
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13(2):261–276. doi:10.1093/schbul/13.2.261
Elmsley RA, Roberts MC, Rataemane S, Pretorius J, Oosthuizen PP, Turner J, Niehaus DJ, Keyter N, Stein DJ (2002) Ethnicity and treatment response in schizophrenia: a comparison of 3 ethnic groups. J Clin Psychiatry 63(1):9–14. doi:10.4088/JCP.v63n0103
Ng CH, Chong SA, Lambert T, Fan A, Hackett L, Mahendran R, Subramaniam M, Schweitzer I (2005) An inter-ethnic comparison study of clozapine dosage, clinical response and plasma levels. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 20(3):163–168. doi:10.1097/00004850-200505000-00007
Lempesi H, Ploumpidis D, Kontaxakis V, Havaki-Kontaxaki B, Konstantakopoulos G, Gonidakis F, Papadimitriou G (2009) Clinical symptoms and social functioning among immigrant and Greek patients with schizophrenia: a comparative study. Psychiatriki 20(4):319–328
Lim CS, Subramaniam M, Poon LY, Chong SA, Verma S (2011) Cross-ethnic differences in severity of symptomatology of individuals with first-episode schizophrenia spectrum disorder. Early Interv Psychiatry 5(3):242–248. doi:10.1111/j.1751-7893.2011.00260.x
Wallwork RS, Fortgang R, Hashimoto R, Weinberger DR, Dickinson D (2012) Searching for a consensus five-factor model of the positive and negative syndrome scale for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 137(1–3):246–250. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2012.01.031
WMA (2008) World medical association declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects, 59th edn. World Medical Association, Seoul
Ventura J, Liberman RP, Green MF, Shaner A, Mintz J (1998) Training and quality assurance with the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (SCID-I/P). Psychiatry Res 79(2):163–173. doi:10.1016/S0165-1781(98)00038-9
Pedersen G, Hagtvet KA, Karterud S (2007) Generalizability studies of the global assessment of functioning-split version. Compr Psychiatry 48(1):88–94. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2006.03.008
Langeveld J, Andreassen OA, Auestad B, Faerden A, Hauge LJ, Joa I, Johannessen JO, Melle I, Rund BR, Rossberg JI, Simonsen E, Vaglum P, Larsen TK (2012) Is there an optimal factor structure of the positive and negative syndrome scale in patients with first-episode psychosis? Scand J Psychol. doi:10.1111/sjop.12017
van der Gaag M, Hoffman T, Remijsen M, Hijman R, de Haan L, van Meijel B, van Harten PN, Valmaggia L, de Hert M, Cuijpers A, Wiersma D (2006) The five-factor model of the positive and negative syndrome scale II: a ten-fold cross-validation of a revised model. Schizophr Res 85(1–3):280–287. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2006.03.021
Daugstad G (ed) (2006) Innvandring og innvandrere 2006. Statistisk Sentralbyrå, Oslo-Kongsvinger
Rezai, Maclagan LC, Donovan LR, Tu JV (2013) Classification of Canadian immigrants into visible minority groups using country of birth and mother tongue. Open.Med 7(4):e85–e93
Henriksen K, Østby L, Ellingsen DE (2010) Innvandring og innvandrere, vol 2010. Statistics Norway, Oslo
Ratcliff K, Farhall J, Shawyer F (2011) Auditory hallucinations: a review of assessment tools. Clin Psychol Psychother 18(6):524–534. doi:10.1002/cpp.729
Afuwape SA, Johnson S, Craig TJ, Miles H, Leese M, Mohan R, Thornicroft G (2006) Ethnic differences among a community cohort of individuals with dual diagnosis in South London. J Mental Health 15(5):551–567. doi:10.1080/09638230600900140
Kelly DL, Dixon LB, Kreyenbuhl JA, Medoff D, Lehman AF, Love RC, Brown CH, Conley RR (2006) Clozapine utilization and outcomes by race in a public mental health system: 1994-2000. J Clin Psychiatry 67(9):1404–1411. doi:10.4088/JCP.v67n0911
Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel RR (2005) What does the PANSS mean? Schizophr Res 79(2–3):231–238
Reininghaus U, Craig TK, Fisher HL, Hutchinson G, Fearon P, Morgan K, Dazzan P, Doody GA, Jones PB, Murray RM, Morgan C (2010) Ethnic identity, perceptions of disadvantage, and psychosis: findings from the AESOP study. Schizophr Res 124(1–3):43–48. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2010.08.038
Bhugra D, Leff J, Mallett R, Morgan C, Zhao JH (2010) The culture and identity schedule - a measure of cultural affiliation: acculturation, marginalization and schizophrenia. Int J Soc Psychiatry. doi:10.1177/0020764009358024
Veling W, Selten JP, Susser E, Laan W, Mackenbach JP, Hoek HW (2007) Discrimination and the incidence of psychotic disorders among ethnic minorities in The Netherlands. Int J Epidemiol 36(4):761–768. doi:10.1093/ije/dym085
Karlsen S, Nazroo JY, McKenzie K, Bhui K, Weich S (2005) Racism, psychosis and common mental disorder among ethnic minority groups in England. Psychol Med 35(12):1795–1803. doi:10.1017/S0033291705005830
Verdoux H, Husky M, Tournier M, Sorbara F, Swendsen JD (2003) Social environments and daily life occurence of psychotic symptoms: an experience sampling test in a non-clinical population. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 38(11):654–661. doi:10.1007/s00127-003-0702-8
Allardyce J, Boydell J (2006) Review: the Wider Social Environment and Schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 32(4):592–598. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbl008
Arnold LM, Keck PE, Collins J, Wilson R, Fleck DE, Corey KB, Amicone J, Adebimpe VR, Strakowski SM (2004) Ethnicity and first-rank symptoms in patients with psychosis. Schizophr Res 67(2–3):207–212. doi:10.1016/s0920-9964(02)00497-8
Veling W, Selten JP, Mackenbach JP, Hoek HW (2007) Symptoms at first contact for psychotic disorder: comparison between native Dutch and ethnic minorities. Schizophr Res 95:30–38. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2007.06.024
Barrio C, Yamada A-M, Atuel H, Hough RL, Yee S, Berthot B, Russo PA (2003) A tri-ethnic examination of symptom expression on the positive and negative syndrome scale in schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Schizophr Res 60(2–3):259–269. doi:10.1016/S0920-9964%2802%2900223-2
Saha S, Scott JG, Varghese D, McGrath JJ (2011) Socio-economic disadvantage and delusional-like experiences: a nationwide population-based study. Eur Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2011.09.004
Mark TL, Palmer LA, Russo PA, Vasey J (2003) Examination of treatment pattern differences by race. Ment Health Serv Res 5(4):241–250. doi:10.1023/A:1026281118990
Fasfous AF, Hidalgo-Ruzzante N, Vilar-López R, Catena-Martínez A, Pérez-García M (2013) Cultural differences in neuropsychological abilities required to perform intelligence tasks. Arch Clinical Neuropsychol 28(8):784–790. doi:10.1093/arclin/act074
Klingberg S, Wittorf A, Wiedemann G (2006) Disorganization and cognitive impairment in schizophrenia: independent symptom dimensions? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256(8):532–540. doi:10.1007/s00406-006-0704-0
Mercado CL, Johannesen JK, Bell MD (2011) Thought disorder severity in compromised, deteriorated, and preserved intellectual course of schizophrenia. J Nerv Ment Dis 199(2):111–116. doi:10.1097/NMD.0b013e3182083bae
Park DC, Huang C-M (2010) Culture wires the brain: a cognitive neuroscience perspective. Perspect Psychol Sci 5(4):391–400. doi:10.1177/1745691610374591
Flynn JR (1987) Massive IQ gains in 14 nations: what IQ tests really measure. Psychol Bull 101(2):171–191. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.101.2.171
APA (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, D.C
Cermolacce M, Sass L, Parnas J (2010) What is bizarre in bizarre delusions? A critical review. Schizophr Bull 36(4):667–679. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbq001
Nerhus M, Berg AO, Haram M, Kvitland LR, Andreassen OA, Melle I (2013) Migrant background and ethnic minority status as predictors for duration of untreated psychosis. Early Interv Psychiatry. doi:10.1111/eip.12106
Ayazi T, Bøgwald K (2008) Innvandreres bruk av poliklinisk psykiatrisk tjeneste. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 2(128):162–165
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the participants in the TOP study and the clinicians collaborating in patient recruitment for their contribution. We would also like to thank Thomas Bjella, Eivind Bakken, and Ragnhild Storli. Funding for this study was provided by the Kristian Gerhard Jebsen Foundation, the Research Council of Norway (Grants #181831, 147787/320, 167153/V50) and the Regional Health Authority for South-Eastern Norway Health Authority (Grants #2010-074 and #2006-258). Neither had any role in study design, data collection, analysis and interpretation, writing of the report, or the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berg, A.O., Andreassen, O.A., Aminoff, S.R. et al. The impact of immigration and visible minority status on psychosis symptom profile. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 49, 1747–1757 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-014-0897-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-014-0897-x