Abstract
Introduction
The influence of sociodemographics and clinical factors on the quality of life (qol) of an individual with schizophrenia is being widely studied, particularly in developed countries. The de-institutionalization process that is taking course in Brazil, to a less symptoms-focused approach, makes necessary the assessment of the qol of these patients living in the community.
Objectives
To evaluate factors related to the qol in patients diagnosed with schizophrenia or schizo-affective disorder, and who are users of one of the two municipal community mental health services of a Rio de Janeiro district, Brazil.
Material and methods
A cross-sectional study was carried out. Selected patients were interviewed with Brazilian versions of Lancashire Quality of Life Profile, Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale and Calgary Depression Scale for Schizophrenia.
Results
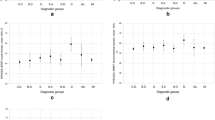
A total of 136 patients participated in the study. Most of them were single and lived with their relatives, had low educational level, were unemployed and had low income. A great number of the interviewed did not have any social contact outside the family and leisure activity, except watching television and/or listening to the radio. Finances and work situation had the lowest satisfaction level. Educational level, presence of positive and depressive symptoms, hospital admissions were negatively associated with qol. For those receiving state benefit, perceived qol increased with age. These predictors explained more than 42% of the total subjective qol score variance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Centro de Atenção Psicossocial Ernesto Nazareth.
Posto de Atendimento Médico Newton Alves Cardoso.
Fourth Edition of Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders from American Psychiatric Association (apud [6]).
Points whose residuals are so large that they indicate that either the model or the response are erroneous.
Points that affect the model parameters.
Income have been adjusted in function of currency rates (US$ average quotation from 2003 to 2004) and the standard of living (purchasing power parities from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development).
References
Oliver J, Huxley P, Bridges K, Mohamed H (1996) Quality of life and mental health services. Routledge, London, New York
The WHOQOL Group (1998) Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment. Psychol Med 28:551–558
The WHOQOL Group (1998) The World Health Organization Quality of Life Assessment (WHOQOL): development and general psychometric properties. Soc Sci Med 46:1569–1585
Lehman AF (1983) The well-being of chronic mental patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 40:369–373
World Health Organization/Pan American Health Organization (2001) O Peso dos Transtornos Mentais e Comportamentais. In: Relatório Sobre a Saúde no Mundo – Saúde Mental: Nova Concepção, Nova Esperança. World Health Organization, Geneve
Kaplan HI, Sadock BJ (2001) Chapter 12. 7th ed. William & Wilkins, Baltimore
Katschnig H (2000) Schizophrenia and quality of life. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 407:33–37
Katschnig H (1997) How useful is the concept of quality of life in psychiatry? Curr Opin Psychiatry 10:337–345
Warner R, de Girolamo G, Belelli G, Bologna C, Fioritti A, Rosini G (1998) The quality of life of people with schizophrenia in Boulder, Colorado, and Bologna, Italy. Schizophr Bull 24:559–568
Gaite L, Vazquez-Barquero JL, Borra C, Ballesteros J, Schene A, Welcher B et al (2002) Quality of life in patients with schizophrenia in five European countries: the EPSILON study. Acta Psychiatr Scand 105:283–292
Armazém de Dados do Rio de Janeiro (2004) In:http://www.armazemdedados.rio.rj.gov.br. Instituto Municipal de Urbanismo Pereira Passos – Prefeitura da Cidade do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro
Coppini RZ (2001) Perfil de qualidade de vida – Lancashire. Thesis, UNIFESP – Escola Paulista de Medicina
Romano F, Elkis H (1996) Tradução e adaptação de um instrumento de avaliação psicopatológica das psicoses: a escala breve de avaliação psiquiátrica – versão ancorada (BPRS-A). Jornal Brasileiro de Psiquiatria 45:43–49
Bressan RA, Chaves AC, Shirakawa I, de Mari J (1998) Validity study of the Brazilian version of the Calgary Depression Scale for Schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 32:41–49
Lauritsen JM, Bruus M, Myatt M (2004) EpiData 3.02. In: http://www.epidata.dk EpiData Association, Odense
The Comprehensive R Archive Network (2003) R-2.0.1. In:http://cran.r-project.org/ The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Roder-Wanner UU, Oliver JP, Priebe S (1997) Does quality of life differ in schizophrenic women and men? An empirical study. Int J Soc Psychiatry 43:129–143
Bengtsson-Tops A, Hansson L (1999) Subjective quality of life in schizophrenic patients living in the community. Relationship to clinical and social characteristics. Eur Psychiatry 14:256–263
Doyle M, Flanagan S, Browne S, Clarke M, Lydon D, Larkin C et al. (1999) Subjective and external assessments of quality of life in schizophrenia: relationship to insight. Acta Psychiatr Scand 99:466–472
Corrigan PW, Buican B (1995) The construct validity of subjective quality of life for the severely mentally ill. J Nerv Ment Dis 183:281–285
Ruggeri M, Gater R, Bisoffi G, Barbui C, Tansella M (2002) Determinants of subjective quality of life in patients attending community-based mental health services. The South-Verona Outcome Project 5. Acta Psychiatr Scand 105:131–140
Packer S, Husted J, Cohen S, Tomlinson G (1997) Psychopathology and quality of life in schizophrenia. J Psychiatry Neurosci 22:231–234
Reine G, Lancon C, Di Tucci S, Sapin C, Auquier P (2003) Depression and subjective quality of life in chronic phase schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand 108:297–303
Hofer A, Kemmler G, Eder U, Edlinger M, Hummer M, Fleischhacker WW (2004) Quality of life in schizophrenia: the impact of psychopathology, attitude toward medication, and side effects. J Clin Psychiatry 65:932–939
Roy MA, Maziade M, Labbe A, Merette C (2001) Male gender is associated with deficit schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 47:141–147
Gur RE, Petty RG, Turetsky BI, Gur RC (1996) Schizophrenia throughout life: sex differences in severity and profile of symptoms. Schizophr Res 21:1–12
Bardenstein KK, McGlashan TH (1990) Gender differences in affective, schizoaffective, and schizophrenic disorders. A review. Schizophr Res 3:159–172
Mintz AR, Dobson KS, Romney DM (2003) Insight in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 61:75–88
Chan S, Yu Iu W (2004) Quality of life of clients with schizophrenia. J Adv Nurs 45:72–83
Skantze K, Malm U, Dencker SJ, May PR, Corrigan P (1992) Comparison of quality of life with standard of living in schizophrenic out-patients. Br J Psychiatry 161:797–801
Rossler W, Salize HJ, Cucchiaro G, Reinhard I, Kernig C (1999) Does the place of treatment influence the quality of life of schizophrenics? Acta Psychiatr Scand 100:142–148
Carpiniello B, Lai GL, Pariante CM, Carta MG, Rudas N (1997) Symptoms, standards of living and subjective quality of life: a comparative study of schizophrenic and depressed out- patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand 96:235–241
Duno R, Pousa E, Domenech C, Diez A, Ruiz A, Guillamat R (2001) Subjective quality of life in schizophrenic outpatients in a Catalan urban site. J Nerv Ment Dis 189:685–690
Bow-Thomas CC, Velligan DI, Miller AL, Olsen J (1999) Predicting quality of life from symptomatology in schizophrenia at exacerbation and stabilization. Psychiatry Res 86:131–142
UK700 Group (1999) Predictors of quality of life in people with severe mental illness. Study methodology with baseline analysis in the UK700 trial. Br J Psychiatry 175:426–432
Dickerson FB, Ringel NB, Parente F (1998) Subjective quality of life in out-patients with schizophrenia: clinical and utilization correlates. Acta Psychiatr Scand 98:124–127
Franz M, Lis S, Pluddemann K, Gallhofer B (1997) Conventional versus atypical neuroleptics: subjective quality of life in schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry 170:422–425
Huppert JD, Weiss KA, Lim R, Pratt S, Smith TE (2001) Quality of life in schizophrenia: contributions of anxiety and depression. Schizophr Res 51:171–180
Norman RM, Malla AK, McLean T, Voruganti LP, Cortese L, McIntosh E et al (2000) The relationship of symptoms and level of functioning in schizophrenia to general wellbeing and the Quality of Life Scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand 102:303–309
Browne S, Roe M, Lane A, Gervin M, Morris M, Kinsella A, et al. (1996) Quality of life in schizophrenia: relationship to sociodemographic factors, symptomatology and tardive dyskinesia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 94:118–124
Lehman AF, Ward NC, Linn LS (1982) Chronic mental patients: the quality of life issue. Am J Psychiatry 139:1271–1276
Evans S, Huxley P, Priebe S (2000) A comparison of the quality of life of severely mentally ill people in UK & German samples. Int J Soc Psychiatry 46:47–56
Steinert T, Wiebe C, Gebhardt RP (1999) Aggressive behavior against self and others among first-admission patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatr Serv 50:85–90
Postrado LT, Lehman AF (1995) Quality of life and clinical predictors of rehospitalization of persons with severe mental illness. Psychiatr Serv 46:1161–1165
Fagundes HM (1999) Os CAPS de Campo Grande e Santa Cruz e a consolidação da rede de atenção psicossocial na cidade do Rio de Janeiro. In: Cadernos IPUB. Instituto de Psiquiatria da UFRJ, Rio de Janeiro
Larsen EB, Gerlach J (1996) Subjective experience of treatment, side-effects, mental state and quality of life in chronic schizophrenic out-patients treated with depot neuroleptics. Acta Psychiatr Scand 93:381–388
Junginger J (1996) Psychosis and violence: the case for a content analysis of psychotic experience. Schizophr Bull 22:91–103
Junginger J (1995) Command hallucinations and the prediction of dangerousness. Psychiatr Serv 46:911–914
Acknowledgements
We thank the assistance of the users, carers and clinical staff of the two services. Special thanks are due to Dr Elizabete Possidente, Dr Norma Gamarra and Dr Sérgio Neves for their contribution during data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Souza, L.A., Coutinho, E.S.F. The quality of life of people with schizophrenia living in community in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Soc Psychiat Epidemiol 41, 347–356 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-006-0042-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-006-0042-6