Abstract
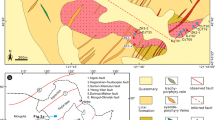
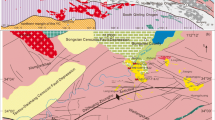
The Chengchao and Jinshandian deposits in the southeast Hubei Province are the two largest skarn Fe deposits in the Middle–Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt (MLYRVMB), China. They are characterized by NW-striking orebodies that are developed along the contacts between the Late Mesozoic granitoid and Triassic carbonate and clastic rocks. New sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe and laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry zircon U–Pb dating of the mineralization-related quartz diorite and granite at Chengchao yield ages of 129 ± 2 and 127 ± 2 Ma, respectively, and those at Jinshandian of 127 ± 2 and 133 ± 1 Ma, respectively. These results are interpreted as the crystallization age of these intrusions. Hydrothermal phlogopite samples from the skarn ores at Chengchao and Jinshandian have the plateau 40Ar–39Ar ages of 132.6 ± 1.4 and 131.6 ± 1.2 Ma, respectively. These results confirm that both intrusions and associated skarn Fe mineralization were formed contemporaneously in the middle Early Cretaceous time. New zircon U–Pb and phlogopite 40Ar–39Ar ages in this study, when combined with available precise geochronological data, demonstrate that there were two discontinuous igneous events, corresponding to two episodes of skarn Fe-bearing mineralization in the southeast Hubei Province: (1) 140–136 Ma diorites and quartz diorites and 141–137 Ma skarn Cu–Fe or Fe–Cu deposits and (2) 133–127 Ma quartz diorites and granites and 133–132 Ma skarn Fe deposits. This scenario is similar to that proposed for the entire MLYRVMB. The intrusions related to skarn Fe deposits show obviously petrological and geochemical differences from those related to skarn Cu–Fe or Fe–Cu deposits. The former are quartz diorite and diorite in petrology and have similar adakitic geochemical signatures and in equilibrium with a garnet-rich residue, whereas the latter are petrologically granite and quartz diorite that are distinguishable from adakitic rocks and in equilibrium with a plagioclase residue. These features indicated that two episodes of magmatism and the formation of skarn Fe-bearing deposits in the southeast Hubei Province, MLYRVMB, might be associated lithosphere thinning induced by asthenosphere upwelling during the Late Mesozoic.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen T (2002) Correction of common Pb in U–Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem Geol 192:59–79
Black LP, Gulson BL (1978) The age of the Mud Tank Carbonatite, Strangways Range, Northern Territory. BMR J Aust Geol Geophys 3:227–232
Black LP, Kamo SL, Allen CM, Aleinikoff JN, Davis DW, Korsch RJ, Foudoulis C (2003) Temorai: a new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U–Pb geochemistry. Chem Geol 200:155–170
Brown PE, Hagemann SG (1995) MacFlincor and its application to fluids in Archean lode-gold deposits. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:3943–3952
Boynton WV (1984) Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed) Rare earth element geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 63–114
Chang YF, Liu XP, Wu CY (1991) The copper–iron belt of the lower and middle reaches of the Changjiang River. Geological, Beijing, pp 1–234, In Chinese with English abstract
Chen HX (1993) Relationship of the Triassic evaporates beds with the mineralization of iron ores in Chengchao, southeastern Hubei Province. Bull Inst Geomechanics CAGS 15:163–177, In Chinese with English abstract
Chen JF, Yan J, Xie Z, Xu X, Xing F (2001) Nd and Sr isotopic compositions of igneous rocks from the lower Yangtze region in eastern China: constraints on sources. Phys Chem Earth (A) 26:719–731
Dalrymple GB, Lamphere MA (1971) 40Ar/39Ar technique of K–Ar dating: a comparison with the conventional technique. Earth Planet Sci Lett 12:300–308
Defant MJ, Drummond MS (1990) Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 347:662–665
DePaolo DJ, Daley EE (2000) Neodymium isotopes in basalts of the southwest basin and range and lithospheric thinning during continental extension. Chem Geol 169:157–185
Dodson MH (1973) Cooling temperature in cooling geochronological and petrological systems. Contrib Mineral Petrol 40:259–274
Fan Y, Zhou TF, Yuan F, Qian CC, Lu SM, Cooke D (2008) LA-ICPMS zircon U–Pb ages of the A–type granites in the Lu–Zong (Lujiang–Zongyang) area and their geological significances. Acta Petrol Sin 24:1715–1724, In Chinese with English abstract
Fu Q, Li LT, Kuang QG, Zhao ZX (2008) Gravity and magnetic abnormally and resource potential prediction in the Jinshandian mine, eastern Hubei Province. Geol Prospecting 44(3):60–64, In Chinese with English abstract
Giletti B (1974) Studies in diffusion I, argon in phlogopite mica. In: Hoffman AW, Giletti BJ, Yonder HS (eds) Geochemical transport and kinetics. Carnegie Institute of Washington, Washington, DC, pp 107–115
Griffin WL, Belousova EA, Shee SR, Pearson NJ, O’Reilly SY (2004) Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton: U–Pb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons. Precambrian Res 131:231–282
Hoskin PWO, Black LP (2000) Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon. J Metamorph Geol 18:423–439
Hou KJ, Yuan SD (2010) Zircon U–Pb age and Hf isotopic composition of the volcanic and sub-volcanic rocks in the Ningwu basin and their geological applications. Acta Petrol Sin 26:888–902, In Chinese with English abstract
Hou ZQ, Pan XF, Yang ZM, Qu XM (2007) Porphyry Cu–(Mo–Au) deposits not related to oceanic-slab subduction: examples from Chinese porphyry deposits in continental settings. Geoscience 21:332–351, In Chinese with English abstract
Institute of Mineral Resources Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (IMRCAGS) (2005) Description about diagram of China’s iron ore deposit resources (scale of 1:5 million). Geological Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–54, In Chinese
Ishihara S (1977) The magnetite-series and ilmenite-series granitic rocks. Min Geol 27:293–305
Jackson SE, Pearson NJ, Griffin WL, Belousova EA (2004) The application of laser ablation–inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry to in situ U–Pb zircon geochronology. Chem Geol 211:47–69
Jahn BM, Wu FY, Lo CH, Tsai CH (1999) Crust–mantle interaction induced by deep subduction of the continental crust: geochemical and Sr–Nd isotopic evidence from post-collisional mafic–ultramafic intrusions of the northern Dabie complex, central China. Chem Geol 157:119–146
Li JW, Zhao XF, Zhou MF, Vasconcelos P, Ma CQ, Deng XD, Zhao YX, Wu G (2008) Origin of the Tongshankou porphyry–skarn Cu–Mo deposit, eastern Yangtze craton, Eastern China: geochronological, geochemical, and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic constraints. Miner Deposita 43:319–336
Li JW, Zhao XF, Zhou MF, Ma CQ, de Souza ZS, Vasconcelos P (2009) Late Mesozoic magmatism from the Daye region, eastern China: U–Pb ages, petrogenesis, and geodynamic implications. Contrib Mineral Petrol 157:383–409
Li JW, Deng XD, Zhou MF, Liu YS, Zhao XF, Guo JL (2010a) Laser ablation ICP–MS titanite U–Th–Pb dating of hydrothermal ore deposits: a case study of the Tonglushan Cu–Fe–Au skarn deposit, SE Hubei Province, China. Chem Geol 270:56–67
Li XH, Li WX, Wang XC, Li QL, Liu Y, Tang GQ, Gao YY, Wu FY (2010b) SIMS U–Pb zircon geochronology of porphyry Cu–Au–(Mo) deposits in the Yangtze River metallogenic belt, eastern China: magmatic response to early Cretaceous lithospheric extension. Lithos 119:427–438
Ling MX, Wang FY, Ding X, Hu YH, Zartman RE, Xiong XL, Sun WD (2009) Cretaceous ridge subduction along the Lower Yangtze River belt, Eastern China. Econ Geol 104:303–321
Ludwig KR (2003) User’s manual for Isoplot 3.00: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication 4
Ma CQ, Yang KG, Tang ZH, Li ZT (1994) Magma-dynamics of granitoids—theory method and a case study of the eastern Hubei granitoids. China University of Geosciences, Beijing, pp 1–260, In Chinese with English abstract
Ma CQ, Yang KG, Ming HL, Lin GC (2003) The timing of tectonic transition from compression to extension in Dabie orogen: evidences from Mesozoic granites. Sci China (D) 33:817–827, In Chinese
Mao JW, Wang YT, Lehmann B, Yu JJ, Du AD, Mei YX, Li YF, Zang WS, Stein HJ, Zhou TF (2006) Molybdenite Re–Os and albite 40Ar/39Ar dating of Cu–Au–Mo and magnetite porphyry systems in the Yangtze River valley and metallogenic implications. Ore Geol Rev 29:307–324
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Pirajno F, Ye HS, Wang YB, Li YF, Xiang JF, Zhao HJ (2010) Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous granitoid magmatism in Eastern Qinling, central-eastern China: SHRIMP zircon U–Pb ages and tectonic implications. Aust J Earth Sci 57:51–78
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Duan C, Pirajno F, Ishiyama D, Chen YC (2011) A tectono-genetic model for porphyry–skarn Cu–Au–Mo–Fe and magnetite-apatite deposits along Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley, Eastern China. Ore Geol Rev (in press)
Ni RS, Wu QC, Yue WZ (1998) The evolution and mineralization of terrestrial basins from the lower Yangtze region. Shanghai Science and Technology Literature, Shanghai, pp 1–118, In Chinese
Pan Y, Dong P (1999) The lower Changjiang (Yangzi/Yangtze River) metallogenic belt, East China: intrusion- and wall rock-hosted Cu–Fe–Au, Mo, Zn, Pb, Ag deposits. Ore Geol Rev 15:177–242
Patiño Douce AE, Beard JS (1995) Dehydration-melting of biotite gneiss and quartz amphibolite from 3 to 15 kbar. J Petrol 36:707–738
Pei RF, Hong DW (1995) The granites of South China and their metallogeny. Episodes 18:77–86
Peng JT, Zhou MF, Hu RZ, Shen NP, Yuan SD, Bi XW, Du AD, Qu WJ (2006) Precise molybdenite Re–Os and mica Ar–Ar dating of the Mesozoic Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, central Nanling district, South China. Miner Deposita 41:661–669
Rapp RP, Watson EB (1995) Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8–32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust–mantle recycling. J Petrol 36:891–931
Shu QA, Chen PL, Cheng JR (1992) Geology of iron–copper deposits in Eastern Hubei Province, China. Metallurgic Industry, Beijing, pp 1–510, In Chinese
Steiger RH, Jager E (1977) Subcommission on geochronology: convention on the use of decay constants in geo- and cosmo-chronology. Earth Planet Sci Lett 36:359–362
Sun WD, Xie Z, Chen JF, Zhang X, Chai Z, Du A, Zhao J, Zhang C, Zhou T (2003) Os–Os dating of copper and molybdenum deposits along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Econ Geol 98:175–180
Tang YC, Wu CY, Chu GZ, Xing FM, Wang YM, Cao FY, Chang YF (1998) Geology of copper–gold polymetallic deposits in the along Changjiang area of Anhui province. Geological, Beijing, pp 1–351, In Chinese with English abstract
Wang L, Hu MA, Zhang WS (2009) Structural ore-controlling characteristic and prospecting direction in Chengchao iron deposit in Southeast Hubei. Metal Mine 4:74–77, In Chinese with English abstract
Wang Q, Zhao ZH, Xu JF, Li XH, Bao ZW, Xiong XL, Liu YM (2003) Petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Yanshanian adakite-like rocks in the Eastern Yangtze Block. Sci China (D) 46(supp):164–176
Wang Q, Zhao ZH, Bao ZW, Xu JF, Liu W, Li CF, Bai ZH, Xiong XL (2004) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Tongshankou and Yinzu adakitic intrusive rocks and the associated porphyry copper–molybdenum mineralization in southeast Hubei, East China. Resour Geol 54:137–152
Wang Q, Wyman DA, Xu JF, Zhao ZH, Jian P, Xiong XL, Bao ZW, Li CF, Bai ZH (2006) Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakitic and shoshonitic igneous rocks in the Luzong area, Anhui Province (eastern China): implications for geodynamics and Cu–Au mineralization. Lithos 89:424–446
Wang SS (1983) Dating of the Chinese K–Ar standard sample (Fangshan biotite, ZBH-25) by using the 40Ar/39Ar method. Sci Geol Sin 4:315–321, In Chinese with English abstract
Wang Y (2006) The onset of the Tan–Lu fault movement in eastern China: constraints from zircon (SHRIMP) and 40Ar/39Ar dating. Terra Nova 18:423–431
Wang YJ (2007) Review of China iron deposit prospecting. Jiangsu Geol 31:161–164, In Chinese with English abstract
Wang YX, Li LP (1994) The relationship between strata and genesis of skarn-type ore deposits in view of paleohydrogeologic analysis: with an example from the Zhangfushan iron deposit, eastern Hubei. Miner Resour Geol 8(1):63–68, In Chinese with English abstract
Williams IS (1998) U–Th–Pb geochronology by ion microprobe. Rev Econ Geol 7:1–35
Xia JL, Hu MA, Xu BJ, Zhang WS, Yang Z, Wang L (2009) Geochemistry constraint on the ore-forming materials of the Chengchao iron deposit, Hubei Province. Geosciences 23:285–291, in Chinese with English abstract
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Zhou SD, Ye HS, Yan QR, Zhang ZS (2006) SHRIMP zircon U–Pb dating for volcanic rocks of the Dasi Formation in southeast Hubei Province, middle–lower reaches of the Yangtze River and its implications. Chin Sci Bull 51:3000–3009
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li LR, Qu WJ, Pirajno F, Du AD (2007) Re–Os molybdenite and Ar–Ar phlogopite dating of Cu–Fe–Au–Mo (W) deposits in southeastern Hubei, China. Miner Petrol 90:249–270
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Li LR, Beirlein F (2008a) Geochemistry and Nd–Sr isotopic studies of late Mesozoic granitoids in the southeastern Hubei province, middle–lower Yangtze River belt, Eastern China: petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Lithos 104:216–230
Xie GQ, Li RL, Jiang GH, Zhao CS, Hou KJ (2008b) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic granitoids in southeastern Hubei Province and constrains on the timing of lithospheric thinning, middle–lower reaches of the Yangtze River, Eastern China. Acta Petrol Sin 24:1703–1714, In Chinese with English abstract
Xie, GQ (2009) Geochronology and genesis of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks and its relation to skarn Cu–Fe–Au deposits in southeastern Hubei Province, Middle–Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, Eastern China. The report of Post-doctoral Fellowship in China University of Geosciences, Beijing, pp 1–183, In Chinese with English abstract
Xie GQ, Mao JW, Zhao HJ, Wei KT, Jin SG, Pan HJ, Ke YF (2011) Timing of skarn deposit formation of the Tonglushan ore district, southeastern Hubei Province, Middle–Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt and its implications. Ore Geol Rev doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.05.005
Xiong XL, Adam J, Green TH (2005) Rutile stability and rutile/melt HFSE partitioning during partial melting of hydrous basalt: implications for TTG genesis. Chem Geol 218:339–359
Xu G, Lin X (2000) Geology and geochemistry of the Changlongshan skarn iron deposit, Anhui Province, China. Ore Geol Rev 16:91–106
Xu HJ, Ma CQ, Ye K (2007) Early cretaceous granitoids and their implications for the collapse of the Dabie orogen, eastern China: SHRIMP zircon U–Pb dating and geochemistry. Chem Geol 240:238–259
Xu XS, Suzuki K, Liu L, Wang DZ (2010) Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Late Mesozoic granites in the NE Yangtze Block, China: further insights from the Jiuhuashan–Qingyang complex. Geol Mag 147:219–232
Xu ZG (1985) Genesis of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in eastern China as discussed in light of the characteristics of the structural stress field. Acta Geol Sin 59:109–126, In Chinese with English abstract
Yao PH, Wang KN, Du CL, Lin ZT, Song X (1993) Records of China’s iron ore deposits. Metallurgic Industry, Beijing, pp 1–662, In Chinese
Yuan SD, Hou KJ, Liu M (2010) Timing of mineralization and geodynamic framework of iron–oxide–apatite deposits in Ningwu Cretaceous Basin in the Middle–Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River, China: constraints from Ar–Ar dating on phlogopites. Acta Petrol Sin 30:797–808, In Chinese with English abstract
Zhai YS, Yao SZ, Lin XD, Zhou XN, Wan TF, Jin FQ, Zhou ZG (1992) Fe–Cu–Au metallogeny of the Middle–Lower Changjiang region. Geological, Beijing, pp 1–235, In Chinese
Zhai YS, Xiong YY, Yao SZ, Liu XD (1996) Metallogeny of copper and iron deposits in the Eastern Yangtze Craton, east-central China. Ore Geol Rev 11:229–248
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Qian Q, Yang JH, Wang YL, Zhao TP, Guo GJ (2001) The characteristics and tectonic–metallogenic significances of the adakites in Yanshan period from eastern China. Acta Petrol Sin 17:236–244, In Chinese with English abstract
Zhang Q, Jian P, Liu DY, Wang YL, Qian Q, Wang Y, Xue H (2003) SHRIMP dating of volcanic rocks from Ningwu area and its geological implications. Sci China (D) 46:830–837
Zhang Q, Jin WJ, Li CD, Wang YL (2010) Revisiting the new classification of granitic rocks based on whole rock Sr and Yb contents: index. Acta Petrol Sin 26:985–1015, In Chinese with English abstract
Zhang SZ, Lin XD, Yao SZ (1985) Zonal distribution of altered mineralization in Zhangfushan skarn iron ore deposit of ore magmatic–hydrothermal transitional type, Hubei Province. Earth Sci 10(4):45–51, In Chinese with English abstract
Zhang WX, Liu MX, Xu BJ (1995) On gold-bearing nature of complex rocks in Jinshandian—applying trace analysis of gold to heavy sand. Earth Sci 20(2):156–158, In Chinese with English abstract
Zhao HJ, Mao JW, Xiang JF, Zhou ZH, Wei KT, Ke YF (2010) Mineralogy and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic compositions of quartz diorite from the Tonglushan deposit, Hubei Province. Acta Petrol Sin 26:768–784, In Chinese with English abstract
Zhou TF, Yuan F, Yue SC, Liu XC, Zhang X, Fan Y (2007) Geochemistry and evolution of ore-forming fluids of the Yueshan Cu-Au skarn- and vein-type deposits, Anhui Province, South China. Ore Geol Rev 31:279–303
Zhou TF, Fan Y, Yuan F, Lu SM, Shang SG, David C, Sebastien M, Zhao GC (2008) Geochronology of the volcanic rocks in the Luzong (Lujiang–Zongyang) basin and its significance. Sci China (D) 51:1470–1482
Zhou XM, Sun T, Shen WZ, Shu LS, Niu YL (2006) Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: a response to tectonic evolution. Episodes 29:26–33
Zhou XR, Ren J (1994) Mesozoic granites in the Middle–Lower reaches of Yangtze River. Geological, Beijing, pp 1–119, In Chinese
Acknowledgments
We thank Wei Shikun, Xiong Jizhuan, Hu Qinglu, Wei Ketao, Jin Shangguang, Ke Yufu, and local geologists from the Chengchao and Jinshandian mine for providing invaluable assistance and constructive discussions during our field investigations. Constructive comments by Professor Mei-fu Zhou significantly improved the earlier draft, and we are grateful to two anonymous journal reviewers, Editors Romer R, Lehmann B and Tecson Jeyel for critical reviews and helpful comments, which greatly improved the manuscript. This work was supported jointly by the National Special Research Programs for Non-Profit Trades (Sponsored by MLR, 200911007-18), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program; 2007CB411407 and 2007CB411405), the Basic Scientific Research Operation Cost of State-Leveled Public Welfare Scientific Research Courtyard (K0902), the National Science Foundation of China (40972054), the Geological Survey of China Geological Survey Project (1212011120994), and State Key Laboratory of Ore Deposit Geochemistry, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences China (201005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: R. L. Romer
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, G., Mao, J., Zhao, H. et al. Zircon U–Pb and phlogopite 40Ar–39Ar age of the Chengchao and Jinshandian skarn Fe deposits, southeast Hubei Province, Middle–Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt, China. Miner Deposita 47, 633–652 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-011-0367-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-011-0367-2