Abstract
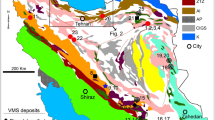
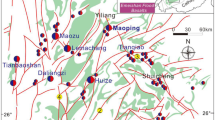
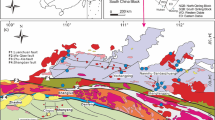
The Changba Pb-Zn SEDEX deposit occurs in the Middle Devonian sequence of the Anjiaca Formation of the Western Qinling Hercynian Orogen in the Gansu Province, China. The Changba-II orebody is hosted in biotite quartz schist and is the largest of 143 stratiform orebodies that are hosted either in biotite quartz schist or marble. The Changba-II comprises two types of mineralization: a bedded facies and an underlying breccia lens. The bedded section exhibits three sulfide sub-facies zoned from bottom to top: 1) banded sphalerite intercalated with quartz albitite; 2) interbedded massive pyrite and sphalerite ore; and 3) banded sphalerite ore intercalated with banded baritite. Major metallic minerals are sphalerite, pyrite, galena, with minor arsenopyrite, pyrrhotite, boulangerite, and rare chalcopyrite. The bedded sulfides are underlain by a lens of brecciated and albitized biotite-quartz schists cemented by sulfides and tourmaline.
Massive and bedded sulfide δ34S values range from 8.1 to 29.3‰, whereas barite δ34S values range from 20.8 to 31.5‰. Disseminated pyrite in footwall schists has δ34S values ranging from 8.1 to 10.6‰, and increase to values ranging from 11.1 to 14.7‰ in the hangingwall. The lower δ34S values for massive and bedded sulfides are interpreted to be derived from progressive bacterial sulfate reduction (BSR) of Devonian seawater in a sulfate-restricted sub-basin. The higher δ34S values for massive and bedded sulfides could be a product of quantitative BSR but this is incompatible with barite being more abundant above the bedded sulfides. Instead, it is more likely that thermochemical sulfate reduction of seawater sulfate or of evaporite was the source of heavy hydrothermal sulfur. Heavy hydrothermal sulfur was injected into a sulfate-restricted sub-basin where it mixed with low δ34S BSR sulfide to form the massive and bedded sulfides. The REE patterns of sulfide layers and associated quartz albitite and baritite are similar to those of the host biotite quartz schists, suggesting that the hydrothermal fluids leached REE from the underlying rocks. Pb isotope ratios in galena form an array between the Upper Crust and the Mantle reservoir curves, which indicates that the lead is derived from upper crustal rocks comprising mafic igneous units. The Sr87/Sr86 ratio of 0.7101 for carbonate within the sulfide layers also suggests that Sr is derived from the mixing of Sr leached from upper crustal rocks with Middle Devonian seawater Sr. A Rb-Sr isochron age of 389.4 ± 6.4 Ma for sulfide layers and the interbedded hydrothermal sediments is consistent with the age of host Mid-Devonian strata. Ar39/Ar40 plateau age at 352.8 ± 3.5 Ma and Ar39-Ar40 isochron age of 346.6 ± 6.4 Ma for albite in the quartz albitite intercalated with sulfide layers indicate either albite formation after the sulfides or thermal resetting of the Rb-Sr system at about 350 Ma, the age of collision between the North China and Yangtze cratons.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D, Höy, T (2000) Fragmental sedimentary rocks of the Aldridge Formation, Purcell Supergroup, British Columbia.In: Lydon JW, Höy T, Slack JF, Knapp ME (eds.) The geological environment of the Sullivan deposit, British Columbia. Geological Association of Canada, Mineral Deposit Division Special Publication No. 1, pp 259–271
Burke, WH, Denison, RE, Hetherington, EA, Koepnick, RB, Nelson, HF, Otto, JB (1982) Variation of seawater 87Sr / 86Sr through out Phanerozoic time. Geology, 10, 516 – 519
Claypool, GE, Holser, WT, Kaplan, IR, Sakai, H, Zak, I (1980) The age curves of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation. Chem. Geol. 28:199 – 260
Courtois, C, Treuil, M (1977) Distribution des terres rares et de quelques éléments en trace dans les sédiments récents des fosses de la Mer Rouge, Chem. Geol. 20:57 – 72
Doe, BR, Zartman, RE (1979) Plumbotectonics, the Phanerozoic. In: Barnes, HL (ed.) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits, 2nd Edition. John Willy & Sons, NY, p. 22–70
Du, D-H (1986) Devonian System in the Qinling-Bashan district, Shaanxi, China (in Chinese): Xi’an Jiaotong University Publishing House, Xi’an, 358 p.
Gao, S, Zhang, B-R, Li, Z-J, Xie, Q-, Gu, X-M, Zhang, H-F, Ouyang, J-P and Gao, C-L (1995) Chemical composition of the continental crust in the Qinling Orogenic Belt and its adjacent North China and Yangtze Cratons. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56:3933 – 3950
Godwin, CI, Sinclair, AJ (1982) Average lead isotope growth curves for shale-hosted zinc-lead deposits, Canadian Cordillera. Econ. Geol. 77:675 – 690
Goodfellow, WD, Lydon, JW, Turner, RJW (1993) Geology and genesis of stratiform sediment-hosted (Sedex) zinc-lead-silver sulfide deposits. In: Kirkham, RV, Sinclair, WD, Thorpe, RI, Dule, JM (eds.) Mineral Deposit Modeling: Geological Association of Canada, Special Paper 40, p. 201 – 251
Goodfellow, WD, Rhodes, D (1990) Geological setting, geochemistry and origin of the Tom stratiform Zn-Pb-Ag-barite deposits. In: Abbott, JG, Turner, RHW (eds.) Mineral deposits of the Northern Canadian Cordillera: International Association on the Genesis of Ore Deposits, 8th Symposium, Ottawa, Ont., Field Trip 14 Guidebook, p. 177 – 244
Hamilton, JM, Bishop, DP, Morris, HC, Owens, OE (1982) Geology of the Sullivan orebody, Kimberley, B.C., Canada. In: Hutchinson RW, Spence CD, Franklin JM (eds.) Precambrian sulphide deposits, H.S. Robinson Memorial Volume, Geological Association of Canada, Special Paper 25, pp 597–666
Hannak, W (1981) Genesis of the Rammelsberg ore deposit near Goslar/Upper Harz, Federal Republic of Germany. In: Wolf, KH (ed.) Handbook of Strata-Bound and Stratiform Ore Deposits. 9, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam, p. 551 – 642
He, D-R (1987) Preliminary metallogenic analysis of the Devonian stratabound deposits in the Qinling Orogenic belt. Northwest Economic Geology 5 : 1 – 24
Henderson, P (1984) Rare earth element geochemistry. In: Henderson, P (ed.) Development in geochemistry, 2nd, Amsterdam, Elsevier, 510 p.
Large, D, Walcher, E (1999) The Rammelsberg massive sulphide Cu-Zn-Pb-Ba-deposit, Germany: an example of sediment-hosted, massive sulphide mineralisation. Mineralium Deposita 34:522 – 538
Large, DE (1983) Sediment-hosted massive sulfide lead-zinc deposits: An empirical model. In: Sangster, DF (ed.) Sediment-hosted stratiform lead-zinc deposits, Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Handbook, p. 1–30
Liu B (1990) Devonian sedimentary environment and evolution of the sedimentary basin in Zashui-Zhen’an District, East Qinling Mountains, China (in Chinese, with English abstract). Acta Sedimentologica Sinica 9:35 – 56
Lydon JW (1996) Sedimentary exhalative sulfides (Sedex). In: Eckstrand, OR Synclair, WD, Thorpe, RI (eds.) Geology of Canadian Mineral Deposit Types, Geological Survey of Canada, Geology of Canada 8:130 – 152.
Lydon JW, Höy T, Slack JF, Knapp ME (2000) The geological environment of the Sullivan deposit, British Columbia. Geological Association of Canada Mineral Deposit Division, Special Publication 1, 834 p.
Meng, Q-R, Zhang, G-W (2000) Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, central China. Tectonophysics 323:183 – 196
Moore, DW, Young, LE, Modene, JS, Plahuta, JT (1986) Geological setting and genesis of the Red Dog zinc-lead-silver deposit, Western Brooks Range, Alaska. Econ. Geol. 81:1696 – 1727
Ohmoto, H (1992) Biogeochemistry of sulfur and mechanisms of sulfide-sulfate mineralization in Archean oceans. In: Schidlowski M, Golubic S, Kimberley MM, McKirdy DM, Trudinger PA. (eds.) Early organic evolution implications for mineral and energy resources, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 491 – 559
Qi, S-J, Li, Y (1993) Lead-zinc metallogenic belt of Devonian System in Qinling Mountains (in Chinese, with English abstract), Geol. Publ. House, Beijing, 240 p.
Shang, R-Y, Yan, Z (1988) Granite of Mt. Qinling & Dabashan (in Chinese with English abstract). China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan, 281 p.
Slack, J. F., Turner, R. J. W., and Ware, P. L. G., 1998, Boron-rich mud volcanoes of the Black Sea region: Modern analogues to ancient sea-floor tourmalinites associated with Sullivan-type Pb-Zn deposits? Geology 26:439–442
Taylor BE, Beaudoin G (2000) Sulphur isotope stratigraphy of the Sullivan Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, B.C.: Evidence for hydrothermal sulphur, and bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction, in Lydon JW, Höy T, Slack JF, Knapp ME (eds) The geological environment of the Sullivan deposit, British Columbia. Geological Association of Canada, Mineral Deposit Division, Special Publication 1:696–719.
Turner, RJW (1990) Jason stratiform Zn-Pb-barite deposit, Selwyn Basin, Canada (NTS 105-O-1): Geological setting, hydrothermal facies and genesis. In: Abbott JG, Turner RJW (eds.) Mineral deposits of the northern Canadian Cordillera, Yukon-northeastern British Columbia: International Association on the Genesis of Ore Deposits, 8th Symposium, Ottawa, Ont., Field Trip 14 Guidebook, p. p 137–177
Turner, RJW (1992) Formation of Phanerozoic stratiform sediment-hosted zinc-lead deposits: Evidence for the critical role of ocean anoxia. Chem. Geol. 99:165 – 188
Wang, H-Z (1982), Tectonic development of the margin area on both sides of the ancient ocean in Eastern Qinling (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Geol. Sinica. 26:56 – 79
Wang, J-L (1984) On the lead-zinc deposits in the Xicheng district, Gansu Province (in Chinese with English abstract), China. Gansu Publishing House, Lanzhou, 126 p.
Wang, J-L (1996) Qinling type lead-zinc metallogenic belt of Devonian system in Qinling Mountains (Chinese with English abstract). Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Xu, Z-Q (1988) Formation, deformation, evolution and plate dynamics of eastern Qinling composite mountain chain, China (in Chinese, with English abstract). Environmental Science Publishing House, Beijing, 174 p.
Yang, Z-H (1991) Structure, lithofacies and mineralization of the marginal transform fault basin (in Chinese, with English abstract), Science Press, Beijing, 186 p.
Zartman, R.E. and Doe, B.R. (1981) Plumbotectonics- The model. Tectonophysics, 75:135–162
Zeng, Y-F (1992) Devonian sedimentary basin type and major feature in the south China (in Chinese, with English abstract). Acta Sedimentologica Sinica 11: 14-21
Zhang, G-W (1988) Formation and evolution of the Qinling orogenic belt (in Chinese with English abstract). Northwestern Univ. Press, Xi’an, 192 p.
Zhang, G-W (1993) Reconfirmed to basic tectonics of the Qinling orogenic belt, growth of the Asia (Chinese with English abstract). Seismological Pub. House, Beijing
Zhang, Z-Q, Liu, D-Y, Fu, G-M (1994) Isotope age study of metamorphic sequences of North Qinling Belt (in Chinese with English abstract). Geol. Publ. House, Beijing, 190 p.
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by the Open Geochemical Lab of the China Academy of Sciences of China, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada and Université Laval (Québec, Canada). G.M. thanks Shaojun Zhong for his guidance and support. The Changba Mine of the Baiyin Non Ferrous Metals Corporation (BNMC) is thanked for access to the mines and their valuable materials. Comments by two anonymous reviewers, Dr. Karen Kelley, and Dr. R. Goldfarb and L. Meinert significantly improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: E. Frimmel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, G., Beaudoin, G., Qi, S. et al. Geology and geochemistry of the Changba SEDEX Pb-Zn deposit, Qinling orogenic belt, China. Miner Deposita 39, 380–395 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-004-0416-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-004-0416-1