Abstract
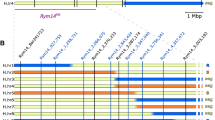
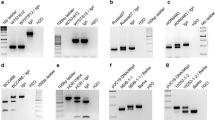
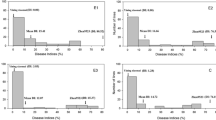
The genetic structure of the rym5 locus was studied in a population comprising 391 doubled-haploid lines that were evaluated for resistance to two strains of Barley Yellow Mosaic Virus (BaYMV-1, 2) and to Barley Mild Mosaic Virus (BaMMV). The absence of recombinants that are able to differentiate between the reaction to these different bymoviruses provides evidence that rym5 is a complex locus, which is either composed of several closely linked genes or of an allelic series of a single gene. For marker-assisted introgression of this locus into adapted barley germplasm, a CAPS (cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence) and a microsatellite marker were developed that flank the gene at distances of 0.8 and 1.3% recombination, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 19 June 1998 / Accepted: 24 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graner, A., Streng, S., Kellermann, A. et al. Molecular mapping and genetic fine-structure of the rym5 locus encoding resistance to different strains of the Barley Yellow Mosaic Virus Complex. Theor Appl Genet 98, 285–290 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051070
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051070