Abstract
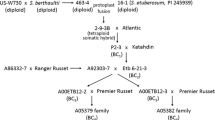
Bulked segregant analysis and high-resolution mapping were used to pinpoint the position of the Lv gene for resistance to Leveillula taurica in tomato. Mapping in an F2, corresponding to more than 3800 gametes, indicates that Lv is positioned within the 0.84-cM interval defined by the RFLP markers CT121 and CT129, with the closest marker, CT121, being only 0.16 cM from the gene. The tight linkage of these markers demonstrates their usefulness in marker-assisted breeding for Lv, and the high-resolution map provides a starting a starting point for positional cloning of this resistance gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 February 1997 / Accepted: 21 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chunwongse, J., Doganlar, S., Crossman, C. et al. High-resolution genetic map of the Lv resistance locus in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 95, 220–223 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050551
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050551