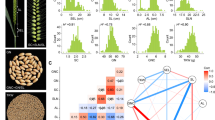
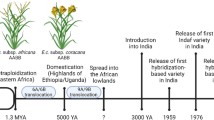
Abstract
Key message
Genome differentiation has shaped the divergence in element concentration between rice subspecies and contributed to the correlation among trace minerals in the rice grain.
Abstract
The balance between trace minerals in rice, a staple food for more than half of the world’s population, is crucial for human health. However, the genetic basis underlying the correlation between trace minerals has not been fully elucidated. To address this issue, we first quantified the concentrations of 11 trace minerals in the grains of a diversity panel of 575 rice cultivars. We found that eight elements were accumulated at significantly different levels between the indica and japonica subspecies, and we also observed significant correlation patterns among a number of elements. Further, using a genome-wide association study, we identified a total of 96 significant association loci (SALs). The differentiation of the major-effect SALs along with the different number of high-concentration alleles present in the two subspecies shaped the different element performance in indica and japonica varieties. Only a few SALs located in clusters and the majority of SALs showed subspecies/subgroup differentiation, indicating that the correlations between elements in the diversity panel were mainly caused by genome differentiation instead of shared genetic basis. The genetic architecture unveiled in this study will facilitate improvement in breeding for trace mineral content.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T, Taguchi-Shiobara F, Kojima Y, Ebitani T, Kuramata M, Yamamoto T, Yano M, Ishikawa S (2011) Detection of a QTL for accumulating Cd in rice that enables efficient Cd phytoextraction from soil. Breed Sci 61:43–51
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K (2009) Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res 19:1655–1664
Andresen E, Peiter E, Kupper H (2018) Trace metal metabolism in plants. J Exp Bot 69:909–954
Bashir K, Nozoye T, Ishimaru Y, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa NK (2013) Exploiting new tools for iron bio-fortification of rice. Biotechnol Adv 31:1624–1633
Bashir K, Rasheed S, Kobayashi T, Seki M, Nishizawa NK (2016) Regulating subcellular metal homeostasis: the key to crop improvement. Frontiers Plant Sci 7:1192
Bates D (2014) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using the lme4 package in R. J Stat Softw. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Browning BL, Browning SR (2009) A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype-phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals. Am J Hum Genet 84:210–223
Buckler ES, Holland JB, Bradbury PJ, Acharya CB, Brown PJ, Browne C, Ersoz E, Flint-Garcia S, Garcia A et al (2009) The genetic architecture of maize flowering time. Science 325:714–718
Bughio N, Yamaguchi H, Nishizawa NK, Nakanishi H, Mori S (2002) Cloning an iron-regulated metal transporter from rice. J Exp Bot 53:1677–1682
Chen Z, Fujii Y, Yamaji N, Masuda S, Takemoto Y, Kamiya T, Yusuyin Y, Iwasaki K, Kato S et al (2013) Mn tolerance in rice is mediated by MTP8.1, a member of the cation diffusion facilitator family. J Exp Bot 64:4375–4387
Civan P, Craig H, Cox CJ, Brown TA (2015) Three geographically separate domestications of Asian rice. Nat Plants 1:15164
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT et al (2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27:2156–2158
Deng F, Yamaji N, Xia J, Ma JF (2013) A member of the heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA5 is involved in xylem loading of copper in rice. Plant Physiol 163:1353–1362
Descalsota GIL, Swamy BPM, Zaw H, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Amparado A, Mauleon R, Chadha-Mohanty P, Arocena EC, Raghavan C et al (2018) Genome-wide association mapping in a rice MAGIC plus population detects QTLs and genes useful for biofortification. Frontiers Plant Sci 9:1347
Descalsota-Empleo GI, Amparado A, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Tesoro F, Stangoulis J, Reinke R, Swamy BPM (2019) Genetic mapping of QTL for agronomic traits and grain mineral elements in rice. Crop J 7:560–572
Fang C, Ma Y, Wu S, Liu Z, Wang Z, Yang R, Hu G, Zhou Z, Yu H et al (2017) Genome-wide association studies dissect the genetic networks underlying agronomical traits in soybean. Genome Biol 18:161
Garcia-Oliveira AL, Tan L, Fu Y, Sun C (2009) Genetic identification of quantitative trait loci for contents of mineral nutrients in rice grain. J Integr Plant Biol 51:84–92
Hu BL, Huang DR, Xiao YQ, Fan YY, Chen DZ, Zhuang JY (2016a) Mapping QTLs for mineral element contents in brown and milled rice using an Oryza sativa × O. rufipogon backcross inbred line population. Cereal Res Commun 44:57–68
Hu Y, Cheng H, Tao S (2016b) The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in China: a critical review. Environ Int 92–93:515–532
Huang XY, Salt DE (2016) Plant ionomics: from elemental profiling to environmental adaptation. Mol Plant 9:787–797
Huang X, Wei X, Sang T, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhao Y, Li C, Zhu C, Lu T et al (2010) Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat Genet 42:961–967
Huang X, Kurata N, Wei X, Wang ZX, Wang A, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu K, Lu H et al (2012) A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature 490:497–501
Huang Y, Sun C, Min J, Chen Y, Tong C, Bao J (2015) Association mapping of quantitative trait loci for mineral element contents in whole grain rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem 63:10885–10892
Huang XY, Deng F, Yamaji N, Pinson SR, Fujii-Kashino M, Danku J, Douglas A, Guerinot ML, Salt DE et al (2016a) A heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA4 prevents copper accumulation in rice grain. Nat Commun 7:12138
Huang Y, Tong C, Xu F, Chen Y, Zhang C, Bao J (2016b) Variation in mineral elements in grains of 20 brown rice accessions in two environments. Food Chem 192:873–878
Huang DR, Fan YY, Hu BL, Xiao YQ, Chen DZ, Zhuang JY (2018) Assessment and genetic analysis of heavy metal content in rice grain using an Oryza sativa x O. rufipogon backcross inbred line population. J Sci Food Agric 98:1339–1345
Ishikawa S, Abe T, Kuramata M, Yamaguchi M, Ando T, Yamamoto T, Yano M (2010) A major quantitative trait locus for increasing cadmium-specific concentration in rice grain is located on the short arm of chromosome 7. J Exp Bot 61:923–934
Ishikawa S, Ishimaru Y, Igura M, Kuramata M, Abe T, Senoura T, Hase Y, Arao T, Nishizawa NK et al (2012) Ion-beam irradiation, gene identification, and marker-assisted breeding in the development of low-cadmium rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:19166–19171
Ishimaru Y, Masuda H, Bashir K, Inoue H, Tsukamoto T, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Aoki N, Hirose T et al (2010) Rice metal-nicotianamine transporter, OsYSL2, is required for the long-distance transport of iron and manganese. Plant J 62:379–390
Kashiwagi T, Shindoh K, Hirotsu N, Ishimaru K (2009) Evidence for separate translocation pathways in determining cadmium accumulation in grain and aerial plant parts in rice. BMC Plant Biol 9:8
Kawahara Y, de la Bastide M, Hamilton JP, Kanamori H, McCombie WR, Ouyang S, Schwartz DC, Tanaka T, Wu J et al (2013) Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice (N Y) 6:4
Lahner B, Gong J, Mahmoudian M, Smith EL, Abid KB, Rogers EE, Guerinot ML, Harper JF, Ward JM et al (2003) Genomic scale profiling of nutrient and trace elements in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21:1215–1221
Letunic I, Bork P (2016) Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W242–245
Li H (2011) A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 27:2987–2993
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760
Li H, Peng Z, Yang X, Wang W, Fu J, Wang J, Han Y, Chai Y, Guo T et al (2013) Genome-wide association study dissects the genetic architecture of oil biosynthesis in maize kernels. Nat Genet 45:43–50
Li H, Luo N, Li YW, Cai QY, Li HY, Mo CH, Wong MH (2017) Cadmium in rice: transport mechanisms, influencing factors, and minimizing measures. Environ Pollut 224:622–630
Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury PJ, Gore MA, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2012) GAPIT: genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 28:2397–2399
Liu X, Huang M, Fan B, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2016) Iterative usage of fixed and random effect models for powerful and efficient genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet 12:e1005767
Liu C, Chen G, Li Y, Peng Y, Zhang A, Hong K, Jiang H, Ruan B, Zhang B et al (2017) Characterization of a major QTL for manganese accumulation in rice grain. Sci Rep 7:17704
Lu K, Li L, Zheng X, Zhang Z, Mou T, Hu Z (2008) Quantitative trait loci controlling Cu, Ca, Zn, Mn and Fe content in rice grains. J Genet 87:305–310
Mao D, Xin Y, Tan Y, Hu X, Bai J, Liu ZY, Yu Y, Li L, Peng C et al (2019) Natural variation in the HAN1 gene confers chilling tolerance in rice and allowed adaptation to a temperate climate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:3494–3501
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S et al (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303
Nawaz Z, Kakar KU, Li XB, Li S, Zhang B, Shou HX, Shu QY (2015) Genome-wide association mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for contents of eight elements in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem 63:8008–8016
Nielsen R, Williamson S, Kim Y, Hubisz MJ, Clark AG, Bustamante C (2005) Genomic scans for selective sweeps using SNP data. Genome Res 15:1566–1575
Norton GJ, Deacon CM, Xiong LZ, Huang SY, Meharg AA, Price AH (2010) Genetic mapping of the rice ionome in leaves and grain: identification of QTLs for 17 elements including arsenic, cadmium, iron and selenium. Plant Soil 329:139–153
Norton GJ, Douglas A, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Guerinot ML, Pinson SR, Tarpley L, Eizenga GC, McGrath SP et al (2014) Genome wide association mapping of grain arsenic, copper, molybdenum and zinc in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown at four international field sites. PLoS ONE 9:e89685
Nyquist WE (1991) Estimation of heritability and prediction of selection response in plant-populations. Crit Rev Plant Sci 10:235–322
Palanog AD, Calayugan MIC, Descalsota-Empleo GI, Amparado A, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Arocena EC, Sta Cruz PC, Borromeo TH, Lalusin A et al (2019) Zinc and iron nutrition status in the Philippines population and local soils. Frontiers Nutr 6:81
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38:904–909
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Rawat N, Neelam K, Tiwari VK, Dhaliwal HS (2013) Biofortification of cereals to overcome hidden hunger. Plant Breed 132:437–445
Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Ma JF (2012) Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice. Plant Cell 24:2155–2167
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Mori M, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Nagato Y, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Watanabe A, Akagi H (2012) Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium. Plant Cell Physiol 53:213–224
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Slamet-Loedin IH, Johnson-Beebout SE, Impa S, Tsakirpaloglou N (2015) Enriching rice with Zn and Fe while minimizing Cd risk. Frontiers Plant Sci 6:121
Stein JC, Yu Y, Copetti D, Zwickl DJ, Zhang L, Zhang C, Chougule K, Gao D, Iwata A et al (2018) Genomes of 13 domesticated and wild rice relatives highlight genetic conservation, turnover and innovation across the genus Oryza. Nat Genet 50:285–296
Swamy BPM, Descalsota GIL, Nha CT, Amparado A, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Manito C, Tesoro F, Reinke R (2018a) Identification of genomic regions associated with agronomic and biofortification traits in DH populations of rice. PLoS ONE 13:e0201756
Swamy BPM, Kaladhar K, Anuradha K, Batchu AK, Longvah T, Sarla N (2018b) QTL analysis for grain iron and zinc concentrations in two O. nivara derived backcross populations. Rice Sci 25:197–207
Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Senoura T, Shimo H, Ishikawa S, Arao T, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa NK (2011) The OsNRAMP1 iron transporter is involved in Cd accumulation in rice. J Exp Bot 62:4843–4850
Turner SD (2014) qqman: an R package for visualizing GWAS results using Q–Q and manhattan plots. Biorxiv. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.00731
Ueno D, Yamaji N, Kono I, Huang CF, Ando T, Yano M, Ma JF (2010) Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:16500–16505
Uraguchi S, Fujiwara T (2013) Rice breaks ground for cadmium-free cereals. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16:328–334
Wang Y, Song F, Zhu J, Zhang S, Yang Y, Chen T, Tang B, Dong L, Ding N et al (2017) GSA: genome sequence archive. Genom Proteom Bioinform 15:14–18
Wickham H (2016) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer, New York
Xu Q, Zheng TQ, Hu X, Cheng LR, Xu JL, Shi YM, Li ZK (2015) Examining two sets of introgression lines in rice (Oryza sativa L.) reveals favorable alleles that improve grain Zn and Fe concentrations. PLoS ONE 10:0131846
Xue W, Xing Y, Weng X, Zhao Y, Tang W, Wang L, Zhou H, Yu S, Xu C et al (2008) Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet 40:761–767
Yan H, Xu W, Xie J, Gao Y, Wu L, Sun L, Feng L, Chen X, Zhang T et al (2019) Variation of a major facilitator superfamily gene contributes to differential cadmium accumulation between rice subspecies. Nat Commun 10:2562
Yang M, Lu K, Zhao FJ, Xie W, Ramakrishna P, Wang G, Du Q, Liang L, Sun C et al (2018) Genome-wide association studies reveal the genetic basis of ionomic variation in rice. Plant Cell 30:2720–2740
Yano K, Yamamoto E, Aya K, Takeuchi H, Lo PC, Hu L, Yamasaki M, Yoshida S, Kitano H et al (2016) Genome-wide association study using whole-genome sequencing rapidly identifies new genes influencing agronomic traits in rice. Nat Genet 48:927–934
Yoneyama T, Ishikawa S, Fujimaki S (2015) Route and regulation of zinc, cadmium, and iron transport in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.) during vegetative growth and grain filling: metal transporters, metal speciation, grain Cd reduction and Zn and Fe biofortification. Int J Mol Sci 16:19111–19129
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Vroh Bi I, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM et al (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Yu YH, Shao YF, Liu J, Fan YY, Sun CX, Cao ZY, Zhuang JY (2015) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for contents of macro- and microelements in milled rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem 63:7813–7818
Zhang M, Pinson SR, Tarpley L, Huang XY, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Baxter I, Guerinot ML, Salt DE (2014) Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci associated with concentrations of 16 elements in unmilled rice grain. Theor Appl Genet 127:137–165
Zhang J, Zhou X, Yan W, Zhang Z, Lu L, Han Z, Zhao H, Liu H, Song P et al (2015) Combinations of the Ghd7, Ghd8 and Hd1 genes largely define the ecogeographical adaptation and yield potential of cultivated rice. New Phytol 208:1056–1066
Zhang GM, Zheng TQ, Chen Z, Wang YL, Wang Y, Shi YM, Wang CC, Zhang LY, Ma JT et al (2018) Joint exploration of favorable haplotypes for mineral concentrations in milled grains of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Frontiers Plant Sci 9:447
Zhao H, Yao W, Ouyang Y, Yang W, Wang G, Lian X, Xing Y, Chen L, Xie W (2015) RiceVarMap: a comprehensive database of rice genomic variations. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D1018–D1022
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by the National Key Research and Development Plan (2017YFD0800901), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470443 and 31501391) and the Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFZD-SW-111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CC and HX designed the research; YT and QS performed the genotyping; YT, LS, JZ, YJ, and JW performed the field experiments and elements concentration determination; YT, DM, LS, CC, QZ, and DH analyzed the data; YT, CC, DM, and TF wrote the paper. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The authors declare that the experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Additional information
Communicated by Albrecht E. Melchinger.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Y., Sun, L., Song, Q. et al. Genetic architecture of subspecies divergence in trace mineral accumulation and elemental correlations in the rice grain. Theor Appl Genet 133, 529–545 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03485-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03485-z