Abstract
Key message
Genetic relationships among Chinese maize germplasms reveal historical trends in heterotic patterns from Chinese breeding programs and identify line Dan340 as a potential genome donor for elite inbred line Zheng58.
Abstract
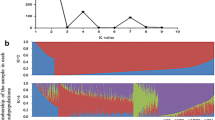
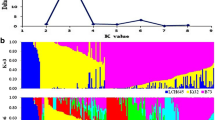
The characterization of the genetic relationships, heterotic patterns and breeding history of lines in maize breeding programs allows breeders to efficiently use maize germplasm for line improvement over time. In this study, 269 temperate inbred lines, most of which have been widely used in Chinese maize breeding programs since the 1970s, were genotyped using the Illumina MaizeSNP50 BeadChip, which contains 56,110 single-nucleotide polymorphisms. The STRUCTURE analysis, cluster analysis and principal coordinate analysis results consistently revealed seven groups, of which five were consistent with known heterotic groups within the Chinese maize germplasm—Domestic Reid, Lancaster, Zi330, Tang SPT and Tem-tropic I (also known as “P”). These genetic relationships also allowed us to determine the historical trends in heterotic patterns during the three decades from 1970 to 2000, represented by Mo17 from Lancaster, HuangZaoSi (HZS) from Tang SPT, Ye478 from Domestic Reid and P178 from Tem-tropic I heterotic groups. Mo17-related commercial hybrids were widely used in the 1970s and 1980s, followed by the release of HZS- and Ye478-related commercial hybrids in the 1980s and 1990s, and the introduction of Tem-tropic I group in the 1990s and 2000s. Additionally, we identified inbred line Dan340 as a potential genome donor for Zheng58, which is the female parent of the most widely grown commercial hybrid ZhengDan958 in China. We also reconstructed the recombination events of elite line HZS and its 14 derived lines. These findings provide useful information to direct future maize breeding efforts.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Chen L, Li YX, Li CH, Wu X, Qin WW, Li X, Jiao FC, Zhang XJ, Zhang DF, Shi YS, Song YC, Li Y, Wang TY (2016) Fine-mapping of qGW4.05, a major QTL for kernel weight and size in maize. BMC Plant Biol 16:81
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, Depristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT, Sherry ST (2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27:2156–2158
Du CX, Cao CJ, Cao Q, Bi MM, Dong ZK, Zhang FL (2006) The breeding and application of maize hybrid Zhengdan 958. J Maize Sci 14:43–45
Duvick DN (2005) Genetic progress in yield of United States maize (Zea mays L.). Maydica 50:193–202
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
FAO (2014) FAOSTAT, Production, http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data. Cited 23 Aug 2017
Ganal MW, Durstewitz G, Polley A, Berard A, Buckler ES, Charcosset A, Clarke JD, Graner EM, Hansen M, Joets J, Le Paslier MC, McMullen MD, Montalent P, Rose M, Schön CC, Sun Q, Walter H, Martin OC, Falque M (2011) A large maize (Zea mays L.) SNP genotyping array: development and germplasm genotyping, and genetic mapping to compare with the B73 reference genome. PLoS One 6:e28334
Heerwaarden JV, Hufford MB, Ross-Ibarra J (2012) Historical genomics of North American maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:12420–12425
Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA (2007) CLUMPP: a cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 23:1801–1806
Lai JS, Li RQ, Xun X, Jin WW, Xu ML, Zhao HN, Xiang ZK, Song WB, Ying K, Zhang M, Jiao Y, Ni PX, Zhang JG, Li D, Guo XS, Ye KX, Jian M, Wang B, Zheng HS, Liang HQ, Zhang XQ, Wang SC, Chen SJ, Li JS, Fu Y, Springer NM, Yang HM, Wang J, Dai JR, Schnable PS, Wang J (2010) Genome-wide patterns of genetic variation among elite maize inbred lines. Nat Genet 42:1027–1030
Lambert RJ, Alexander DE, Mejaya IJ (2004) Single kernel selection for increased grain oil in maize synthetics and high-oil hybrid development. Plant Breed Rev 24:153–175
Li Y (1998) Development and germplasm base of maize hybrids in China. Maydica 43:259–269
Li JS (2009) Production, breeding and process of maize in China. In: Jeff LB, Sarah CH (eds) Handbook of maize: its biology. Springer, New York, pp 563–576
Li Y, Wang TY (2010) Germplasm base of maize breeding in China and formation of foundation parents. J Maize Sci 18:1–8
Li CH, Li YX, Bradbury PJ, Wu X, Shi YS, Song YC, Zhang DF, Rodgersmelnick E, Buckler ES, Zhang ZW, Li Y, Wang TY (2015) Construction of high-quality recombination maps with low-coverage genomic sequencing for joint linkage analysis in maize. BMC Biol 13:1–12
Liu KJ, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129
Lu YL, Yan JB, Guimarães CT, Taba S, Hao ZF, Gao SB, Chen SJ, Li JS, Zhang SH, Vivek BS, Magorokosho C, Mugo S, Makumbi D, Parentoni SN, Shah T, Rong TZ, Crouch JH, Xu YB (2009) Molecular characterization of global maize breeding germplasm based on genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 120:93–115
Mikel MA (2011) Genetic composition of contemporary US commercial dent corn germplasm. Crop Sci 51:592–599
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Pollak LM, Salhuana W (2001) The Germplasm Enhancement of Maize (GEM) Project: Private and Public Sector Collaboration. CABI, Wallingford, pp 319–329
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Qin WW, Li YX, Li CH, Chen L, Wu X, Bai N, Shi YS, Song YC, Zhang DF, Wang TY, Li Y (2015) QTL mapping for kernel related traits based on a high-density genetic map. Acta Agron Sin 41:1510–1518
Qu G, Xu WW, Chen DY, Li FZ, Shi JG, Liu X, Ning JL (2002) The breeding and application of the elite maize inbred line Dan340. J Maize Sci 10:30–33
R Core Team (2015) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Computing 14:12–21
Reif JC, Xia XC, Melchinger AE, Warburton ML, Hoisington DA, Beck D, Bohn M, Frisch M (2004) Genetic diversity determined within and among CIMMYT maize populations of tropical, subtropical, and temperate germplasm by SSR markers. Crop Sci 44:326–334
Salhuana W, Pollak L (2006) Latin American Maize Project (LAMP) and Germplasm Enhancement of Maize (GEM) project: generating useful breeding germplasm. Maydica 51:339–355
Smith JSC, Chin ECL, Shu H, Smith OS, Wall SJ, Senior ML, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Ziegle J (1997) An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L): comparisons with data from RFLPS and pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 95:163–173
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tan WW, Wang Y, Li YX, Liu C, Liu ZZ, Peng B, Wang D, Zhang Y, Sun BC, Shi YS (2011) QTL analysis of ear traits in maize across multiple environments. Sci Agric Sin 44:233–244
Teng WT, Can JS, Chen YH, Liu XH, Jing XQ, Zhang FJ, Li JS (2004) Analysis of maize heterotic groups and patterns during past decade in China. Sci Agric Sin 37:1804–1811
The Service Center of China for Agricultural Science and Technology (2005) The brief introduction on crop approved varieties of china. China Agricultural Science Press, Beijing
Troyer AF (2009) Development of hybrid corn and the seed corn industry. In: Hake JL (ed) Maize handbook-volume II: genetics and genomics. Springer Science Business Media LLC, New York, pp 87–114
Wang RH, Yu YT, Zhao JR, Shi YS, Song YC, Wang TY, Li Y (2008) Population structure and linkage disequilibrium of a mini core set of maize inbred lines in China. Theor Appl Genet 117:1141–1153
Wang D, Li YX, Wang Y, Liu C, Liu ZZ, Peng B, Tan WW, Zhang Y, Sun BC, Shi YS (2010) QTL analysis of flowering-related traits in maize (Zea mays L.) using two connected populations. Sci Agric Sin 43:2633–2644
Wang TY, Ma XL, Li Y, Bai DP, Liu C, Liu ZZ, Tan XJ, Shi YS, Song YC, Carlone M, Bubeck D, Bhardwaj H, Jones E, Wright K, Smith S (2011) Changes in yield and yield components of single-cross maize hybrids released in China between 1964 and 2001. Crop Sci 51:512–525
Wu X, Li YX, Shi YS, Song YC, Wang TY, Huang YB, Li Y (2014) Fine genetic characterization of elite maize germplasm using high-throughput SNP genotyping. Theor Appl Genet 127:621–631
Wu X, Li YX, Shi YS, Song YC, Zhang DF, Li CH, Buckler ES, Li Y, Zhang ZW, Wang TY (2016) Joint-linkage mapping and GWAS reveal extensive genetic loci that regulate male inflorescence size in maize. Plant Biotechnol J 14:1551
Xie CX, Zhang SH, Li MS, Li XH, Hao ZF, Bai L, Zhang DG, Liang YH (2007) Inferring genome ancestry and estimating molecular relatedness among 187 chinese maize inbred lines. J Genet Genom 34:738–748
Yang XH, Yan JB, Shah T, Warburton ML, Li Q, Li L, Gao YF, Chai YC, Fu ZY, Zhou Y, Xu ST, Bai GH, Meng YJ, Zheng YP, Li JS (2010) Genetic analysis and characterization of a new maize association mapping panel for quantitative trait loci dissection. Theor Appl Genet 121:417–431
Yang XH, Gao SB, Xu ST, Zhang ZX, Prasanna BM, Li L, Li JS, Yan JB (2011) Characterization of a global germplasm collection and its potential utilization for analysis of complex quantitative traits in maize. Mol Breed 28:511–526
Zeng SX, Ren R, Liu XZ (1996) The important position of Huangzaosi in maize breeding and production in China. J Maize Sci 4:1–6
Zhang FL (2001) The breeding and application of maize elite inbred line Zheng58. Crops 4:21
Zhang X, Zhang H, Li LJ, Lan H, Ren ZY, Liu D, Wu L, Liu HL, Jaqueth J, Li BL, Pan GT, Gao SB (2016) Characterizing the population structure and genetic diversity of maize breeding germplasm in Southwest China using genome-wide SNP markers. BMC Genom 17:697
Zhao KM (2003) A list of maize hybrid crosses in China. J Maize Sci 10(s1):98–117
Zhao JR, Guo JL, Guo Q, Yu DM, Kong YF (1999) Heterotic grouping of 25 maize inbreds with RAPD markers. Acta Agric Boreali Sin 14:32–37
Zheng DH, Li YR, Jin FX, Jiang JJ (2002) Pedigree and germplasm base of inbreds of the Lancaster heterotic group of maize in China. Sci Agric Sin 1:595–604
Acknowledgements
We greatly appreciate Dr. Qing Li at Huazhong Agricultural University for manuscript language improvement. This research was supported by the National Science and Technology Support Program (Grant number 2014BAD01B02) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant number 2016YFD0101803 and 2016YFD0100303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Benjamin Stich.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Xu, G., Li, J. et al. Patterns of genomic variation in Chinese maize inbred lines and implications for genetic improvement. Theor Appl Genet 131, 1207–1221 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3072-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3072-z