Abstract
Key message
Genetic control of the resistance response against powdery mildew in common bean was studied combining genetic, genomic and transcriptomic analyses. A candidate resistance gene in cultivar Porrillo Sintetico was proposed.
Abstract
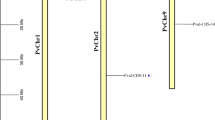
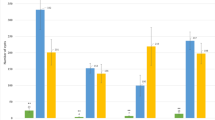
The species causing the fungal disease powdery mildew (PM) in the local common bean crop was identified as Erysiphe polygoni through the molecular analysis of the internal transcribed spacer region. A genetic analysis of the resistance in cultivar Porrillo Sintetico was conducted using different F2:3 populations, and a dominant gene conferring total resistance against a local PM isolate was physically located between 84,188 and 218,664 bp of chromosome Pv04. An in silico analysis of this region, based on the common bean reference sequence, revealed four genes candidate to be involved in the resistance reaction. Relative expression levels of these genes after PM infection showed a significant over-expression of the candidate gene Phvul.004G001500 in the resistant genotype Porrillo Sintetico. This gene was re-sequenced in the parental genotypes X2776 and Porrillo Sintetico to explain their different phenotypic responses against PM. Several substitutions where identified in exon regions, all of them synonymous, so differences in the produced amino acid sequence were not expected. However, a total of 37 mutations were identified in non-coding regions of the gene sequence, suggesting that intron variation could be responsible for the different gene expression levels after PM infection. No evidence of other regulatory mechanisms, such as alternative splicing or methylation, was identified. Candidate resistance gene Phvul.004G001500 codes for an elongation factor that is not a typical gene related to recognition of specific pathogens in plants, suggesting its involvement in the resistance through plant immune system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida AMR, Binneck E, Piuga FF, Marin SRR, Ribeiro do Valle PRZ, Silveira CA (2008) Characterization of powdery mildews strains from soybean, bean, sunflower, and weeds in Brazil using rDNA-ITS sequences. Trop Plant Pathol 33:20–26
Bilas R, Szafran K, Hnatuszko-Konka, Kononowicz (2016) Cis-regulatory elements used to control gene expression in plants. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 127:269–287
Borges A, Tsai SM, Caldas DGG (2012) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR normalization in common bean during biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 31:827–838
Broughton WJ, Hernández G, Blair M, Beebe S, Gepts P, Vanderleyden J (2003) Bean (Phaseolus spp.)—model food legumes. Plant Soil 252:55–128
Büschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, Simons G, Wolter M, Frijters A et al (1997) The barley Mlo gene: a novel control element of plant pathogen resistance. Cell 88:695–705
Campa A, Rodríguez-Suárez C, Giraldez R, Ferreira JJ (2014) Genetic analysis of the response to eleven Colletotrichum lindemuthianum races in a RIL population of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). BMC Plant Biol 14:115
Chinnusamy V, Zhu J-K (2009) Epigenetic regulation of stress responses in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:133–139
Chung E, Cho CW, So HA, Yun BH, Lee JH (2009) Differential expression of soybean SLTI100 gene encoding translation elongation factor 1 A by abiotic stresses. J Plant Biotechnol 36:255–260
Colot V, Rossignol J-L (1999) Eukaryotic DNA methylation as an evolutionary device. Bioessays 21:42–411
Condeelis J (1995) Elongation factor 1 alpha, translation and the cytoskeleton. Trends Biochem Sci 20:169–170
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defense responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
David P, Chen NWG, Pedrosa-Harand A, Thareau V, Sévignac M, Cannon SB et al (2009) A nomadic subtelomeric disease resistance gene cluster in common bean. Plant Physiol 151:1048–1065
Dinesh-Kumar SP, Baker BJ (2000) Alternatively spliced N resistance gene transcripts: their possible role in tobacco mosaic virus resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:1908–1913
Dodds PN, Rathjen JP (2010) Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant–pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet 11:539–548
Dowen RH, Pelizzola M, Schmitz RJ, Lister R, Dowen JM, Nery JR et al (2012) Widespread dynamic DNA methylation in response to biotic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:e2183–e2191
Dundas B (1936) Inheritance of resistance to powdery mildew in beans. Hilgardia 10:243–253
Dundas B (1941) Further studies on the inheritance of resistance to powdery mildews of beans. Hilgardia 13:551–565
Eichmann R, Hückelhoven R (2008) Accommodation of powdery mildew fungi in intact plant cells. J Plant Physiol 165:5–18
Ejiri S (2002) Moonlighting functions bundling to zinc finger of polypeptide elongation factor 1: from actin protein Rl-associated nuclear localization. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:1–21
FAO (1999). Database. http://www.fao.org/3/a-av015e.pdf
Ferreira JJ, Campa A, Kelly JD (2013) Organization of genes conferring resistance to anthracnose in common bean. In: Varshney RK, Tuberosa R (eds) Translational genomics for crop breeding: biotic stress, vol 1. Wiley, pp 151–182.
Ferrier-Cana E, Geffroy V, Macadré C, Creusot F, Imbert-Bollore P, Sévignac M et al (2003) Characterization of expressed NBS-LRR resistance gene candidates from common bean. Theor Appl Genet 106:251–261
Fiume E, Christou P, Giani S, Breviario D (2004) Introns are key regulatory elements of rice tubulin expression. Planta 218:693–703
Fritzemeier K-H, Cretin C, Kombrink E, Rohwer F, Taylor J, Scheel D et al (1987) Transient induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and 4-coumarate: CoA ligase mRNAs in potato leaves infected with virulent or avirulent races of Phytophthora infestans. Plant Physiol 85:34–41
Fu J, Momcilovic I, Prasad PVV (2012) Roles of protein synthesis elongation factor EF-Tu in heat tolerance in plants. J Bot. doi:10.1155/2012/835836
Furukawa T, Inagaki H, Takai R, Hirai H, Che F-S (2014) Two distinct EF-Tu epitopes induce immune responses in rice and Arabidopsis. MPMI 27:113–124
Glawe DA (2008) The powdery mildews. A review of the world’s most familiar (yet poorly known) plant pathogens. Ann Rev Phytopathol 46:27–51
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J et al (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucl Acids Res 40:1–9
Gross SR, Kinzy TG (2005) Translation elongation factor 1 A is essential for regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and cell morphology. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:772–778
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Heath MC (2000) Nonhost resistance and nonspecific plant defenses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:315–319
Hnatuszko-Konka K, Kowalczyk T, Gerszberg A, Wiktorek-Smagur A, Kononowicz AK (2014) Phaseolus vulgaris-recalcitrant potential. Biotechnol Adv 32:1205–1215
Hückelhoven R (2005) Powdery mildew susceptibility and biotrophic infection strategies. FEMS Microbiol Lett 245:9–17
Hückelhoven R, Panstruga R (2011) Cell biology of the plant-powdery mildew interaction. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:738–746
Janda M, Matousková J, Burketová L, Valentová O (2014) Interconnection between actin cytoskeleton and plant defense signaling. Plant Signal Behav 9:e976486
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329
Jordan T, Schornack S, Lahaye T (2002) Alternative splicing of transcripts encoding Toll-like plant resistance proteins—what’s the functional relevance to innate immunity? Trends Plant Sci 7:392–398
Kõljalg U, Nilsson RH, Abarenkov K, Tedersoo L, Taylor AF, Bahram M et al (2013) Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Mol Ecol 22:5271–5277
Kunze G, Zipfel C, Robarzek S, Niehaus K, Boller T, Felix G (2004) The N terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu elicits innate immunity in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 16:3496–3507
Lacombe S, Rougon-Cardoso A, Sherwood E, Peeters N, Dahlbeck D, van Esse HP et al (2010) Interfamily transfer of a plant pattern-recognition receptor confers broad-spectrum bacterial resistance. Nat Biotechnol 28:365–369
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Baarlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, et al (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Li LC, Dahiya R (2002) MethPrimer: designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 18:1427–1431
Li L, Hong H, Luan G, Mosel M, Malik M, Drlica K, et al (2014) Ribosomal elongation factor 4 promotes cell death associated with lethal stress. mBio 5:e01708–14
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆Ct method. Methods 25:402–408
Lu F, Wang H, Wang S, Jiang W, Shan C, Yang J et al (2015) Enhancement of innate immune system in monocot rice by transferring the dicotyledonous elongation factor Tu receptor EFR. JIPB 57:641–652
Marone D, Russo MA, Laido G, Leonardis AM, Mastrangelo AM (2013) Plant nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes: active guardians in host defense response. Int J Mol Sci 14:7302–7326
Mascarenhas D, Mettler IJ, Pierce DA, Lowe HW (1990) Intron-mediated enhancement of heterologous gene expression in maize. Plant Mol Biol 15:913–920
Meziadi C, Richard MMS, Derquennes A, Thareau V, Blanchet S, Gratias A et al (2016) Development of molecular markers linked to disease resistance genes in common bean based on whole genome sequence. Plant Sci 242:351–357
Moghaddam SM, Song Q, Mamidi S, Schmutz J, Lee R, Cregan P et al (2014) Developing market class specific InDel markers from next generation sequence data in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Front Plant Sci 5:185
Morales FJ, Singh SP (1991) Genetics of resistance to bean golden mosaic virus inPhaseolus vulgarisL. Euphytica 52:113–117
Muktar MS, Lübeck J, Strahwald J, Gebhardt C (2015) Selection and validation of potato candidate genes for maturity corrected resistance to Phytophthora infestans based on differential expression combined with SNP association and linkage mapping. Front Genet 6:294
Nilsson RH, Ryberg M, Kristiansson E, Abarenkov K, Larsson K-H, Kõljalg U (2006) Taxonomic reliability of DNA sequences in public sequence databases: a fungal perspective. Plos One 1:e59
Panduranga S, Diapari M, Yin F, Munholland S, Perry GE, Chapman BP et al (2016) Genomic analysis of storage protein deficiency in genetically related lines of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Front Plant Sci 7:389
Pérez-Vega E, Trabanco N, Campa A, Ferreira JJ (2013) Mapping of two genes conferring resistance to powdery mildew in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 126:1503–1512
Rezende VF, Patto RMA, Corte H (1999) Genetic control of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) resistance to powdery mildew (Erysiphe polygoni). Genet Mol Biol 22:233–236
Ristic Z, Bukovnik U, Momčilović I, Fu J, Vara Prasad PV (2008) Heat-induced accumulation of chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factor, EF-Tu, in winter wheat. J Plant Physiol 165:192–202
Sasikumar AN, Perez WB, Kinzy TG (2012) The many roles of the Eukaryotic elongation factor 1 complex. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. RNA 3(4):543–555
Schmutz J, McClean PE, Mamidi S, Wu GA, Cannon SB, Grimwood J et al (2014) A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat Genet 46:707–713
Schoch CL, Seifert KA, Huhndorf S, Robert V, Spouge JL, Levesque CA et al (2012) Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region as a universal DNA barcode marker for Fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:6241–6246
Schoonbeek HJ, Wang HH, Stefanato FL, Craze M, Bowden S, Wallington E et al (2015) Arabidopsis EF-Tu receptor enhances bacterial disease resistance in transgenic wheat. New Phytol 206:606–613
Schwartz HF, Katherman MJ, Thung MDT (1981) Yield response and resistance of dry beans to powdery mildew in Colombia. Plant Dis 65:737–738
Schwartz HF, Steadman JR, Hall R, Forster RL (2005) Compendium of bean diseases. 2nd edition. The American Phytopathology Society, pp 36–37
Simpson GG, Filipowicz W (1996) Splicing of precursors to mRNA in higher plants: mechanism, regulation and sub-nuclear organisation of the spliceosomal machinery. Plant Mol Biol 32:1–41
Singh BN, Mishra RN, Agarwal PK, Goswami M, Nair S, Sopory SK et al (2004) A pea chloroplast translation elongation factor that is regulated by abiotic factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 320:523–530
Somssich IE, Schmelzer E, Bollmann J, Hahlbrock K (1986) Rapid activation by fungal elicitor of genes encoding “pathogenesis-related” proteins in cultured parsley cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2427–2430
Takemoto D, Hardham AR (2004) The cytoskeleton as a regulator and target of biotic interactions in plants. Plant Physiol 136:3864–3876
Trabanco N, Pérez-Vega E, Campa A, Rubiales D, Ferreira JJ (2012) Genetic resistance to powdery mildew in common bean. Euphytica 186:875–882
Vlasova A, Capella-Gutiérrez S, Rendón-Anaya M, Hernández-Oñate M, Minoche AE, Erb I et al (2016) Genome and and transcriptome analysis of the Mesoamerican common bean and the role of gene duplications in establishing tissue and temporal specialization of genes. Genome Biol 17:32
Wang WM, Wen YQ, Berkey R, Xiao SY (2009) Specific targeting of the Arabidopsis resistance protein RPW8.2 to the interfacial membrane encasing the fungal haustorium renders broad-spectrum resistance to powdery mildew. Plant Cell 21:2898–2913
White TJ, Bruns TD, Lee SB, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis DH, Gelfand DH, Sinsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR - Protocols and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 315–322
Xiao SY, Ellwood S, Calis O, Patrick E, Li TX, Coleman M, Turner JG (2001) Broad-spectrum mildew resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana mediated by RPW8. Science 291:118–120
Yoder JA, Walsh CP, Bestor TH (1997) Cytosine methylation and the ecology of intragenomic parasites. Trends Genet 13:335–340
You FM, Huo N, Gu YQ, Luo M, Ma Y, Hane D et al (2008) BatchPrimer3: a high throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design. BMC Bioinform 9:253
Young ND (2000) The genetic architecture of resistance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:285–290
Zipfel C, Kunze G, Chinchilla D, Caniard A, Jones JDG, Boller T et al (2006) Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 125:749–760
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant RTA2012-0052 from INIA- Ministerio Economía y Competitividad (Spanish Government), cofinanced from FEDER funds. Ana Campa is recipient of a salary from the Instituto de Investigación y Tecnología Agraria y Alimentaria INIA-CCAA (DR13-0222), Spain. Authors thank Marcos Bueno for his technical assistance and the help of DREAMgenics S.L. (Asturias, Spain) in the genomic interpretation of the common bean sequences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Ethical standards
Authors declare that the experiments conducted in this work comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Additional information
Communicated by David A. Lightfoot.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campa, A., Ferreira, J.J. Gene coding for an elongation factor is involved in resistance against powdery mildew in common bean. Theor Appl Genet 130, 849–860 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2864-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2864-x