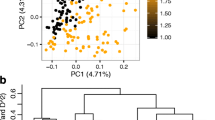
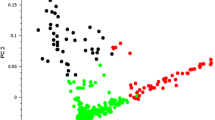
Abstract
Provitamin A (Pro-VA) is necessary for human vision and immune system health, especially in growing children. The first committed step in the maize carotenoid biosynthesis pathway is catalyzed by phytoene synthase 1 (encoded by PSY1) which controls the flux of substrates into the pathway. The flow of these substrates could be directed into production of the β-branch carotenoids (the step controlled largely by the lycopene epsilon cyclase gene), but terminated after the production of β-carotene, rather than allowing it to be converted into the next metabolite (the step controlled largely by the β-carotenoid hydroxylase gene). In this study, PSY1 was subjected to association mapping in two diverse maize populations, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping in one segregating population, and expression analysis of lines polymorphic for sites within PSY1. The results indicated that a 378-bp InDel upstream of the transcription start site and a SNP in the fifth exon resulting in a Thr to Asn substitution, explaining 7 and 8 % of the total carotenoid variation, respectively, may be functional sites associated with total carotenoid levels in maize grain. Analysis of the evolution of PSY1 strongly suggests that there was positive selection for these polymorphic sites after the divergence of yellow maize from white maize.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard RW (1960) Principles of plant breeding, 1st edn. Willey, New York, p 36
Bone RA, Landrum JT, Fernandez L, Tarsist SL (1988) Analysis of the macular pigment by HPLC: retinal distribution and age study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 29:843–849
Bradbury PJ, Zhang ZW, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Buckner B, Kelson TL, Robertson DS (1990) Cloning of the y1 locus of maize, a gene involved in the biosynthesis of carotenoids. Plant Cell 2:867–876
Buckner B, San Miguel P, Janick-Buckner D, Bennetzen JL (1996) The y1 gene of maize codes for phytoene synthase. Genetics 143:479–488
Chander S, Guo YQ, Yang XH, Zhang J, Lu XQ, Yan JB, Song TM, Rocheford TR, Li JS (2008a) Using molecular markers to identify two major loci controlling carotenoid contents in maize grain. Theor Appl Genet 16:223–233
Chander S, Meng YJ, Zhang YR, Yan JB, Li JS (2008b) Comparison of nutritional traits variability in selected eighty-seven inbreds from Chinese maize (Zea mays L.) germplasm. J Agr Food Chem 56:6506–6511
Chappell J (1995) Biochemistry and molecular biology of the isoprenoid biosynthetic pathway in plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Bio 46:521–547
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucl Acid Res 32:1792–1797
Fu ZY, Yan JB, Zheng YP, Warburton ML, Crouch JH, Li JS (2010) Nucleotide diversity and molecular evolution of the PSY1 gene in Zea mays compared to some other grass species. Theor Appl Genet 120:709–720
Gallagher CE, Matthews PD, Li FQ, Wurtzel ET (2004) Gene duplication in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway preceded evolution of the grassed. Plant Physiol 135:1776–1783
Hable WE, Oishi KK, Schumaker KS (1998) Viviparous-5 encodes phytoene desaturase, an enzyme essential for abscisic acid (aba) accumulation and seed development in maize. Mol Gen Genet 257:167–176
Handelman GJ, Dratz EA, Reay CC, Van Kujik FJGM (1988) Carotenoids in the human macula and whole retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 29:850–855
Hardy OJ, Vekemans X (2002) SPAGEDi: a versatile computer program to analyse spatial genetic structure at the individual or population levels. Mol Ecol Notes 2:618–620
Harjes CE, Rocheford T, Bai L, Brutnell T, Kandianis CB, Sowinski SG, Stapleton AE, Vallabhaneni R, Williams M, Wurtzel ET, Yan JB, Buckler ES (2008) Natural genetic variation in lycopene epsilon cyclase tapped for maize biofortification. Science 319:330–333
Hill WG, Robertson A (1968) Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theor Appl Genet 38:226–231
Kurilich AC, Juvik JA (1999) Simultaneous quantification of carotenoids and tocopherols in corn kernel extracts by HPLC. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol l22:2925–2934
Li ZH, Matthews PD, Burr B, Wurtzel ET (1996) Cloning and characterization of a maize cDNA encoding phytoene desaturase, an enzyme of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway. Plant Mol Biol 30:269–279
Li FQ, Vallabhaneni R, Yu J, Rocheford T, Wurtzel ET (2008) The maize phytoene synthase gene family: overlapping roles for carotenogenesis in endosperm, photomorphogenesis, and thermal stress-tolerance. Plant Physiol 147:1334–1346
Luo R, Wurtzel ET (1999) A maize cDNA encoding zeta carotene desaturase. Plant Physiol 120:1206
Mangelsdorf PC, Fraps GS (1931) A direct quantitative relationship between vitamin A in corn and the number of genes for yellow pigmentation. Science 73:241–242
Matthews PD, Luo R, Wurtzel ET (2003) Maize phytoene desaturase and zetacarotene desaturase catalyze a poly-Z desaturation pathway: implications for genetic engineering of carotenoid content among cereal crops. J Exp Botany 54:2215–2230
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high-molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acid Res 8:4321–4325
Paine JA, Shipton CA, Chaggar S, Howells RM, Kennedy MJ, ernon G, Wright SY, Hinchliffe E, Adams JL, Silverstone AL, Drake R (2005) Improving the nutritional value of golden rice through increased pro-vitamin A content. Nat Biotechnol 23:482–487
Palaisa K, Morgante M, Tingey S, Rafalski A (2004) Long-range patterns of diversity and linkage disequilibrium surrounding the maize Y1 gene are indicative of an asymmetric selective sweep. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9885–9890
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Singh M, Lewis PE, Hardeman K, Bai L, Rose JKC, Mazourek M, Chomet P, Brutnell TP (2003) Activator mutagenesis of the pink scutellum1/viviparous7 locus of maize. Plant Cell 15:874–884
StatSoft (1993) STATISTICA (data analysis software system)
Vallabhaneni R, Wurtzel ET (2009) Timing and biosynthetic potential for carotenoid accumulation in genetically diverse germplasm of maize. Plant Physiol Prev 150:562–572
Wong JC, Lambert RJ, Wurtzel ET (2004) QTL and candidate genes phytoene synthase and carotene desaturase associated with the accumulation of carotenoids in maize. Theor Appl Genet 108:349–359
Yan JB, Kandianis CB, Harjes CE, Bai L, Kim EH, Yang XH, Skinner DJ, Fu ZY, Mitchell S, Li Q, Salas Fernandez MG, Zaharieva M, Babu R, Fu Y, Palacios N, Li JS, DellaPenna D, Brutnell T, Buckler ES, Warburton ML, Rocheford T (2010) Rare genetic variation at Zea mays crtRB1 increases β-carotene in maize grain. Nat Genet 42:322–327
Yang XH, Yan JB, Shah T, Warburton M, Li Q, Li L, Gao YF, Chai YC, Fu ZY, Zhou Y, Xu ST, Bai GH, Meng YJ, Zheng YP, Li JS (2010) Genetic analysis and characterization of a new maize association mapping panel for quantitative trait loci dissection. Theo Appl Genet 121:417–431
Yang XH, Gao SB, Xu ST, Zhang ZX, Prasanna BM, Li L, Li JS, Yan JB (2011) Characterization of a global germplasm collection and its potential utilization for analysis of complex quantitative traits in maize. Mol Breeding 28:511–526
Yu JM, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Bi IV, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB, Kresovich S, Buckler ES (2006) A unified mixture-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Zhu CF, Naqvi S, Breitenbach J, Sandmann G, Christou P, Capell T (2008) Combinational genetic transformation generates a library of metabolic phenotypes for the carotenoid pathway in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:18232–18237
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Brent Buckner and Sherry Flint-Garcia for their useful comments and suggestions. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30821140352 and 31000715), the National Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (2012AA10A307), and the Harvest Plus Challenge Program. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Luebberstedt.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Z., Chai, Y., Zhou, Y. et al. Natural variation in the sequence of PSY1 and frequency of favorable polymorphisms among tropical and temperate maize germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 126, 923–935 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-2026-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-2026-0