Abstract
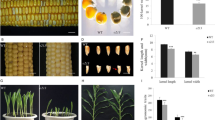
Most of the maize kernel oil is located in the embryo while the majority of starch is located in the endosperm. Maize kernel composition and value are affected significantly by the ratio of the embryo size to the endosperm size; however, the genetic regulation of embryo to endosperm ratio (EER) in maize is unknown. Here we identified ZmGE2 gene, which encodes a cytochrome p450 protein, as a gene associated with EER variation in maize. We first expressed rice Giant Embryo (GE) gene driven by oleosin promoter in maize and detected a 23.2 % reduction in EER in transgenic seeds, demonstrating the existence of evolutionarily conserved mechanisms for EER determination in rice and maize. We next identified maize GE2, a homolog of rice GE sharing 70 % identity in amino sequence, as a candidate based on the similar expression pattern and co-localization with a previously detected QTL for EER. Followed by linkage and association mapping, a 247-bp transposable element (TE) insertion in 3′-untranslated region of ZmGE2 gene was identified to be associated with increase in EER and kernel oil content. Expression level of the favorable ZmGE2 allele containing the 247-bp TE insertion was strongly reduced. In addition, the 247-bp TE insertion site was a selection target during the artificial long-term selection for the high EER trait in a high oil population. This is the first report that demonstrates an association of ZmGE2 with EER variation in maize and identifies ZmGE2 gene as a promising target for manipulation of EER and grain composition by either transgenic approach or molecular breeding in maize.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamski NM, Anastasiou E, Eriksson S, O’Neill CM, Lenhard M (2009) Local maternal control of seed size by KLUH/CYP78A5-dependent growth signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:20115–20120
Anastasiou E, Kenz S, Gerstung M, MacLean D, Timmer J et al (2007) Control of plant organ size by KLUH/CYP78A5-dependent intercellular signaling. Dev Cell 13:843–856
Bakb S, Beisson F, Bishop G, Hamberger B, Höfer R et al (2011) Cytochromes P450. The Arabidopsis Book 9:e0144. doi:10.1199/tab.0144
Bradbury PJ, Zhang ZW, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y et al (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635
Cahoon RE, Heppard EP, Nagasawa N and Sakai H (2003) Alteration of embryo/endosperm size during seed development. United States Patent Application Publication No. US2003/0126645 A1
Ching A, Caldwell KS, Jung M, Dolan M, Smith OS et al (2002) SNP frequency, haplotype structure and linkage disequilibrium in elite maize lines. BMC Genet 3:19
De Rijk P, Wuyts J, De Wachter R (2003) RnaViz 2: an improved representation of RNA secondary structure. Bioinformatics 19:299–300
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucl Acid Res 32(5):1792–1797
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—phylogeny inference package (version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Gao YF, Zhang P, Hao XM, Yan JB, Li JS (2011) A rapid DNA extraction method for large maize populations. Journal of China Agricultural University 16(6):32–36
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Imaishi H, Matsuo S, Swai E, Ohkawa H (2000) CYP78A1 preferentially expressed in developing inflorescences of Zea mays encoded a cytochrome P450-dependent lauric acid 12-monooxygenase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1696–1701
Ito T, Meyerowitz EM (2000) Overexpression of a gene encoding a cytochrome P450, CYP78A9, induces large and seedless fruit in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:1541–1550
Kai K, Hashidzume H, Yoshimura K, Suzuki H, Sakurai N et al (2009) Metabolomics for the characterization of cytochromes P450-dependent fatty acid hydroxylation reactions in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol 26:175–182
Koh HJ, Heu MH, McCouch SR (1996) Molecular mapping of the ge s gene controlling the super-giant embryo character in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 93:257–261
Kohany O, Gentles AJ, Hankus L, Jurka J (2006) Annotation, submission and screening of repetitive elements in Repbase: RepbaseSubmitter and Censor. BMC Bioinformatics 7:474
Kondou Y, Nakazawa M, Kawashima M, Ichikawa T, Yoshizumi T et al (2008) RETARDED GROWTH OF EMBRYO1, a new basic helix-loop-helix protein, expresses in endosperm to control embryo growth. Plant Physiol 147:1924–1935
Lambert RJ (2001) High-oil corn hybrids. In: Hallau AR (ed) Special corn. E. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, pp 131–153
Lambert RJ, Alexander DE, Mejaya IJ (2004) Single kernel selection for increased grain oil in maize synthetics and high-oil hybrid development. Plant Breed Rev 24:153–175
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Moose SP, Dudley JW, Rocheford TR (2004) Maize selection passes the century mark: a unique resource for 21st century genomics. Trends Plant Sci 9(7):358–364
Nelson D (2006) Plant cytochrome P450 s from moss to poplar. Phytochem Rev 5:193–204
Park DS, Park SK, Lee BC, Song SY, Jun NS et al (2009) Molecular characterization and physicochemical analysis of a new giant embryo mutant allele (ge t) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genes & Genomics 31:277–282
Reuter JS, Mathews DH (2010) RNA structure: software for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 11:129
Satoh H, Omura T (1981) New endosperm mutations induced by chemical mutagen in rice. Japanese J. Breeding 31:316–326
Schnable PS, Ware D, Fulton RS, Stein JC, Wei F et al (2009) The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity and dynamics. Science 326:1112–1115
Slotkin RK, Martienssen R (2007) Transposable elements and the epigenetic regulation of the genome. Nat Rev Genet 8:272–285
Slotkin RK, Freeling M, Lisch D (2005) Heritable transposon silencing initiated by a naturally occurring transposon inverted duplication. Nat Genet 37:641–644
Song TM, Chen SJ (2004) Long term selection for oil concentration in five maize populations. Maydica 49:9–14
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M et al (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Val DL, Schwartz SH, Kerns MR, Deikman J (2009) Development of a high oil trait for maize. In: Kriz AL, Larkins BA (eds) Molecular genetic approaches to maize improvement. Springer, Berlin, pp 303–323
Wang JW, Schwab R, Czech B, Mica E, Weigel D (2008) Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 20:1231–1243
Yang XH, Yan JB, Shah T, Warburton ML, Li Q et al (2010) Genetic analysis and characterization of a new maize association mapping panel for quantitative trait loci dissection. Theor Appl Genet 121(3):417–431
Yang XH, Ma HL, Zhang P, Yan JB, Guo YQ et al (2012) Characterization of QTL for oil content in maize kernel. Theor Appl Genet. doi:10.1007/s00122-012-1903-x
Yu JM, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Bi IV, Yamasaki M et al (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38(2):203–208
Zheng PZ, Allen WB, Roesler K, Williams ME, Zhang SR et al (2008) A phenylalanine in DGAT is a key determinant of oil content and composition in maize. Nat Genet 40:367–372
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31101156), the National Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (2012AA10A307), and a collaborative research project with Pioneer Hi-Bred International Inc. We thank Dr Lin Li, Dr Qing Li and Dr Jiming Li for their helpful suggestions on experiment design. We thank Dr Kent Wood and Dr J. Antoni Rafalski for their valuable comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by F. Hochholdinger.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Allen, W.B., Nagasawa, N. et al. A transposable element insertion within ZmGE2 gene is associated with increase in embryo to endosperm ratio in maize. Theor Appl Genet 125, 1463–1471 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1926-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1926-3