Abstract
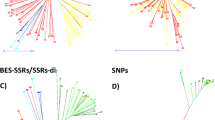
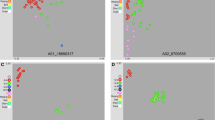
This report describes a set of 23 informative SNPs (BARCSoySNP23) distributed on 19 of the 20 soybean linkage groups that can be used for soybean cultivar identification. Selection of the SNPs to include in this set was made based upon the information provided by each SNP for distinguishing a diverse set of soybean genotypes as well as the linkage map position of each SNP. The genotypes included the ancestors of North American cultivars, modern North American cultivars and a group of Korean cultivars. The procedure used to identify this subset of highly informative SNP markers resulted in a significant increase in the power of identification versus any other randomly selected set of equal number. This conclusion was supported by a simulation which indicated that the 23-SNP panel can uniquely distinguish 2,200 soybean cultivars, whereas sets of randomly selected 23-SNP panels allowed the unique identification of only about 50 cultivars. The 23-SNP panel can efficiently distinguish each of the genotypes within four maturity group sets of additional cultivars/lines that have identical classical pigmentation and morphological traits. Comparatively, the 13 trinucleotide SSR set published earlier (BARCSoySSR13) has more power on a per locus basis because of the multi-allelic nature of SSRs. However, the assay of bi-allelic SNP loci can be multi-plexed using non-gel based techniques allowing for rapid determination of the SNP alleles present in soybean genotypes, thereby compensating for their relatively low information content. Both BARCSoySNP23 and BARCSoySSR13 were highly congruent relative to identifying genotypes and for estimating population genetic differences.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alifrangis M, Enosse S, Pearce R, Drakeley C, Roper C, Khalil IF, Nkya WM, Ronn AM, Theander TG, Bygbjerg IC (2005) A simple, high-throughput method to detect Plasmodium falciparum single nucleotide polymorphisms in the dihydrofolate reductase, dihydropteroate synthase, and P. falciparum chloroquine resistance transporter genes using polymerase chain reaction- and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-based technology. Am J Trop Med Hyg 72:155–162
Aranzana MJ, Carbo J, Arus P (2003) Microsatellite variability in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch]: cultivar identification, marker mutation, pedigree inferences and population structure. Theor Appl Genet 106:1341–1352
Awadalla P, Eyre-Walker A, Smith JM (1999) Linkage disequilibrium and recombination in hominid mitochondrial DNA. Science 286:2524–2525
Balamurugan K, Prabakaran N, Duncan G, Budowle B, Tahir M, Tracey M (2001) Allele frequencies of 13 STR loci and the D1S80 locus in a Tamil population from Madras, India. J Forensic Sci 46:1515–1517
Bashiardes E, Manoli P, Budowle B, Cariolou MA (2001) Data on nine STR loci used for forensic and paternity testing in the Greek Cypriot population of Cyprus. Forensic Sci Int 123:225–226
Brinkmann B, Klintschar M, Neuhuber F, Huhne J, Rolf B (1998) Mutation rate in human microsatellites: influence of the structure and length of the tandem repeat. Am J Hum Genet 62:1408–1415
Chakraborty R, Meagher TR, Smouse PE (1988) Parentage analysis with genetic markers in natural populations. I. The expected proportion of offspring with unambiguous paternity. Genet. 118:527–536
Chen J, Iannone MA, Li MS, Taylor JD, Rivers P, Nelson AJ, Slentz-Kesler KA, Roses A, Weiner MP (2000) A microsphere-based assay for multiplexed single nucleotide polymorphism analysis using single base chain extension. Genome Res 10:549–557
Diwan N, Cregan PB (1997) Automated sizing of fluorescent labelled simple sequence repeat markers to assay genetic variation in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 95:723–733
Esselink GD, Smulders MJ, Vosman B (2003) Identification of cut rose (Rosa hybrida) and rootstock varieties using robust sequence tagged microsatellite site markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:277–286
Faruqi AF, Hosono S, Driscoll MD, Dean FB, Alsmadi O, Bandaru R, Kumar G, Grimwade B, Zong Q, Sun Z, Du Y, Kingsmore S, Knott T, Lasken RS (2001) High-throughput genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms with rolling circle amplification. BMC Genomics 2:4
Gangitano DA, Garofalo MG, Juvenal GJ, Budowle B, Lorente JA, Padula RA (2002) STR data for the PowerPlex 16 loci in Buenos Aires population (Argentina). J Forensic Sci 47:418–420
Gizlice Z, Carter TE, Burton JW (1994) Genetic base for North American public soybean cultivars released between 1947 and 1988. Crop Sci 34:1143 1151
Glowatzki-Mullis ML, Gaillard C, Wigger G, Fries R (1995) Microsatellite-based parentage control in cattle. Anim Genet 26:7–12
Heaton MP, Harhay GP, Bennett GL, Stone RT, Grosse WM, Casas E, Keele JW, Smith TP, Chitko-McKown CG, Laegreid WW (2002) Selection and use of SNP markers for animal identification and paternity analysis in US beef cattle. Mamm Genome 13:272–281
Heyen DW, Beever JE, Da Y, Evert RE, Green C, Bates SR, Ziegle JS, Lewin HA (1997) Exclusion probabilities of 22 bovine microsatellite markers in fluorescent multiplexes for semiautomated parentage testing. Anim Genet 28:21–27
Hill WG, Robertson A (1968) Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theor Appl Genet 33:54–78
Hochberg EP, Miklos DB, Neuberg D, Eichner DA, McLaughlin SF, Mattes-Ritz A, Alyea EP, Antin JH, Soiffer RJ, Ritz J (2003) A novel rapid single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based method for assessment of hematopoietic chimerism after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 101:363–369
Hou P, Ji M, Li S, Lu Z (2004) Microarray-based approach for high-throughput genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms with layer-by-layer dual-color fluorescence hybridization. Clin Chem 50:1955–1957
Keim P, Olson T, Shoemaker R (1988) A rapid protocol for isolating soybean DNA. Soybean Genet Newslett 15:150–152
Kondrashov AS (2003) Direct estimates of human per nucleotide mutation rates at 20 loci causing Mendelian diseases. Hum Mutat 21:12–27
Krawczak M (1999) Informativity assessment for biallelic single nucleotide polymorphisms. Electrophoresis 20:1676–1681
Lee SH, Walker DR, Cregan PB, Boerma HR (2004) Comparison of four flow cytometric SNP detection assays and their use in plant improvement. Theor Appl Genet 110:167–174
Lee HY, Park MJ, Yoo JE, Chung U, Han GR, Shin KJ (2005) Selection of twenty-four highly informative SNP markers for human identification and paternity analysis in Koreans. Forensic Sci Int 148:107–112
Luikart G, Biju-Duval MP, Ertugrul O, Zagdsuren Y, Maudet C, Taberlet P (1999) Power of 22 microsatellite markers in fluorescent multiplexes for parentage testing in goats (Capra hircus). Anim Genet 30:431–438
Mantel N (1967) The detecting of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Melendez E, Martinez-Espin E, Karlson IS, Lorente JA, Budowle B (2004) Population data on 15 STR loci (PowerPlex 16 kit) in a Costa Rica (Central America) sample population. J Forensic Sci 49:170–172
Nachman MW, Crowell SL (2000) Estimate of the mutation rate per nucleotide in humans. Genetics 156:297–304
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Oganisian AS, Kochieva EZ, Ryskov AP (1996) [Fingerprinting of potato species and cultivar using RAPD-PCR]. Genetika 32:448–451
Olivier M, Chuang LM, Chang MS, Chen YT, Pei D, Ranade K, de Witte A, Allen J, Tran N, Curb D, Pratt R, Neefs H, de Arruda Indig M, Law S, Neri B, Wang L, Cox DR (2002) High-throughput genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms using new biplex invader technology. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e53
Petkovski E, Keyser-Tracqui C, Hienne R, Ludes B (2005) SNPs and MALDI-TOF MS: tools for DNA typing in forensic paternity testing and anthropology. J Forensic Sci 50:535–541
Ranade K, Chang MS, Ting CT, Pei D, Hsiao CF, Olivier M, Pesich R, Hebert J, Chen YD, Dzau VJ, Curb D, Olshen R, Risch N, Cox DR, Botstein D (2001) High-throughput genotyping with single nucleotide polymorphisms. Genome Res 11:1262–1268
SAS Institute (1999) SAS/STAT User’s Guide. Version 8. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC
Schueler S, Tusch A, Schuster M, Ziegenhagen B (2003) Characterization of microsatellites in wild and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) markers for individual identification and reproductive processes. Genome 46:95–102
Shirasawa K, Shiokai S, Yamaguchi M, Kishitani S, Nishio T (2006) Dot-blot-SNP analysis for practical plant breeding and cultivar identification in rice. Theor Appl Genet 113:147–155
Singh D, Ahuja PS (2006) 5S rDNA gene diversity in tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) and its use for variety identification. Genome 49:91–96
Sobotka R, Dolanska L, Curn V, Ovesna J (2004) Fluorescence-based AFLPs occur as the most suitable marker system for oilseed rape cultivar identification. J Appl Genet 45:161–173
Song QJ, Quigley CV, Carter TE, Nelson RL, Boerma HR, Strachan J, Cregan PB (1999) A selected set of trinucleotide simple sequence repeat markers for soybean cultivar identification. Plant Varieties and Seeds 12:207–220
Song QJ, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Concibido VC, Delannay X, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2004) A new integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109:122–128
Syn CK, Chuah SY, Ang HC, Lim SE, Tan-Siew WF, Chow ST, Budowle B (2005) Genetic data for the 13 CODIS STR loci in Singapore Chinese. Forensic Sci Int 152:285–288
Usha AP, Simpson SP, Williams JL (1995) Probability of random sire exclusion using microsatellite markers for parentage verification. Anim Genet 26:155–161
Weir BS (1990) Genetic data analysis methods for discrete genetic data. Sinauer Association, Sunderland
Werner FA, Durstewitz G, Habermann FA, Thaller G, Kramer W, Kollers S, Buitkamp J, Georges M, Brem G, Mosner J, Fries R (2004) Detection and characterization of SNPs useful for identity control and parentage testing in major European dairy breeds. Anim Genet 35:44–49
Williams JL, Usha AP, Urquhart BG, Kilroy M (1997) Verification of the identity of bovine semen using DNA microsatellite markers. Vet Rec 140:446–449
Zhu YL, Song QJ, Hyten DL, Van Tassell CP, Matukumalli LK, Grimm DR, Hyatt SM, Fickus EW, Young ND, Cregan PB (2003) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in soybean. Genetics 163:1123–1134
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their thanks for the excellent technical assistance of Charles Quigley and Mike Livingston. This work was supported in part by a grant from the United Soybean Board whose support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Bohn.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, M.S., Song, Q.J., Choi, I.Y. et al. BARCSoySNP23: a panel of 23 selected SNPs for soybean cultivar identification. Theor Appl Genet 114, 885–899 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0487-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0487-8