Abstract
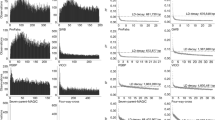
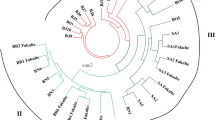
Polymorphism over ∼26 kb of DNA sequence spanning 22 loci and one region distributed on chromosomes 1, 2, 3 and 4 was studied in 30 accessions of cultivated rice, Oryza sativa, and its wild relatives. Phylogenetic analysis using all the DNA sequences suggested that O. sativa ssp. indica and ssp. japonica were independently domesticated from a wild species O. rufipogon. O. sativa ssp. indica contained substantial genetic diversity (π = 0.0024), whereas ssp. japonica exhibited extremely low nucleotide diversity (π = 0.0001) suggesting the origin of the latter from a small number of founders. O. sativa ssp. japonica contained a larger number of derived and fixed non-synonymous substitutions as compared to ssp. indica. Nucleotide diversity and genealogical history substantially varied across the 22 loci. A locus, RLD15 on chromosome 2, showed a distinct genealogy with ssp. japonica sequences distantly separated from those of O. rufipogon and O. sativa ssp. indica. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) was analyzed in two different regions. LD in O. rufipogon decays within 5 kb, whereas it extends to ∼50 kb in O. sativa ssp. indica.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akashi H (1995) Inferring weak selection from patterns of polymorphism and divergence at “silent” sites in Drosophila DNA. Genetics 139:1067–1076
Aquadro CF, Lado KM, Noon WA (1988) The rosy region of Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. I. Contrasting levels of naturally occurring DNA restriction map variation and divergence. Genetics 119:875–888
Bautista NS, Solis R, Kamijima O, Ishii T (2001) RAPD, RFLP and SSLP analyses of phylogenetic relationships between cultivated and wild species of rice. Genes Genet Syst 77:71–79
Begun DJ, Aquadro CF (1992) Levels of naturally occurring DNA polymorphism correlate with recombination rates in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 356:519–520
Bennetzen JL (2000) Comparative sequence analysis of plant genomes: microcolinearity and its many exceptions. Plant Cell 12:1021–1029
Chang TT (1995) Rice. In: Smartt J, Simmonds NW (eds) Evolution of crop plants. Longman, UK, pp 147–155
Cheng C, Motohashi R, Tsuchimoto S, Fukuta Y, Ohtsubo H, Ohtshubo E (2003) Polyphyletic origin of cultivated rice: based on the interspersion pattern of SINEs. Mol Biol Evol 20:67–75
Colbert T, Till BJ, Tompa R, Rynold S, Steine MN, Yeung AT, McCallum CM, Comai L, Henikoff S (2001) High-throughput screening for induced point mutations. Plant Physiol 126:480–484
Comai L, Young K, Till BJ, Reynolds SH, Greene EA, Codomo CA, Enns LC, Johnson JE, Burtner C, Odden AR, Henikoff S (2004) Efficient discovery of DNA polymorphisms in natural populations by EcoTILLING. Plant J 37:778–786
Eck RV, Dayhoff MO (1966) In: Dayhoff MO (ed) Atlas of protein sequence and structure. National Biomedical Research Foundation, Silver Springs
Felsenstein J (2005) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) version 3.6. Distributed by the author. Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle
Felsenstein J, Churchill GA (1996) A Hidden Markov Model approach to variation among sites in rate of evolution. Mol Biol Evol 13:93–104
Feltus FA, Wan J, Shulze SR, Estill JC, Jiang N, Paterson AH (2004) An SNP resource for rice genetics and breeding based on subspecies indica and japonica genome alignments. Genome Res 14:1812–1819
Ge S, Sang T, Lu BR, Hong DY (1999) Phylogeny of rice genomes with emphasis on origins of allotetraploid species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14400–14405
Gillespie JH (2004) Population genetics. A concise guide, 2nd edn. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, pp 214
Glinka S, Ometto L, Mousset S, Stephan W, De Lorenzo D (2003) Demography and natural selection have shaped genetic variation in Drosophila melanogaster: a multi-locus approach. Genetics 165:1269–1278
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong J, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang S, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen L, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa ssp. japonica). Science 286:91–100
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kulwal PL (2005) Linkage disequilibrium and association studies in higher plants: present status and future prospects. Plant Mol Biol 57:461–485
Harushima Y, Yano M, Shomura A, Sato M, Shimano T, Kuboki Y, Yamamoto T, Lin SY, Antonio BA, Parco A, Kajiya H, Huang N, Yamamoto K, Nagamura Y, Kurata N, Khush GS, Sasaki T (1998) A high-density rice genetic linkage map with 2275 markers using a single F2 population. Genetics 148:479–494
Hey J, Kliman RM (1993) Population genetics and phylogenetics of DNA sequence variation at multiple loci within the Drosophila melanogaster species complex. Mol Biol Evol 10:804–822
Hill WG, Robertson A (1968) Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theor Appl Genet 38:226–231
Hill WG, Weir BS (1988) Variances and covariances of squared linkage disequilibria in finite populations. Theor Popul Biol 33:54–78
Hudson RR, Kaplan NL (1988) The coalescent process in models with selection and recombination. Genetics 111:147–164
Hudson RR, Kreitman M, Aguade M (1987) A test of neutral molecular evolution based on nucleotide data. Genetics 136:1329–1340
Ingvarsson PK (2005) Nucleotide polymorphism and linkage disequilibrium within and among natural populations of European Aspen (Populus tremula L., Salicaceae). Genetics 169:945–953
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Ioerger TR, Clark AG, Kao TH (1991) Polymorphism at the self-incompatibility locus in Solanaceae predates speciation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9732–9735
Ishii T, Terauchi T, Tsunewaki K (1988) Restriction endonuclease analysis of chloroplast DNA from A-genome diploid species of rice. Jpn J Genet 63:523–536
Kawabe A, Miyashita NT (2003) Patterns of codon usage bias in three dicot and four monocot plant species. Genes Genet Syst 78:343–352
Khush GS (1997) Origin, dispersal, cultivation and variation of rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:25–34
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, London
Kishino H, Hasegawa M (1989) Evaluation of the maximum likelihood estimate of the evolutionary tree topologies from DNA sequence data, and the branching order in hominoidea. J Mol Evol 29:170–179
Kliman RM, Andolfatto P, Coyne JA, Depaulis F, Kreitman M, Berry AJ, McCarter J, Wakely J, Hey J (2000) The population genetics of the origin and divergence of the Drosophila simulans complex species. Genetics 156:1913–1931
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Lawlor DA, Ward FE, Ennis PD, Jackson AP, Parham P (1988) HLA-A and B polymorphisms predate the divergence of humans and chimpanzees. Nature 335:268–271
Ma J, Bennetzen JL (2004) Rapid recent growth and divergence of rice nuclear genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12404–12410
McDonald JH, Kreitman M (1991) Adaptive protein evolution at the Adh locus in Drosophila. Nature 351:652–654
Nasu S, Suzuki J, Ohta R, Hasegawa K, Yui R, Kitazawa N, Monna L, Minobe Y (2002) Search for and analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and establishment of SNP markers. DNA Res 9:163–171
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Nordborg M, Borevitz JO, Bergelson J, Berry CC, Chory J, Hagenblad J, Kreitman M, Maloof JN, Noyes T, Oefner PJ, Stahl EA, Weigel D (2002) The extent of linkage disequilibrium in Arabisopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 30:190–193
Nordborg M, Hu TT, Ishino Y, Jhaveri J, Toomajian C, Zheng H, Bakker E, Calabrese P, Gladstone J, Goyal R, Jakobsson M, Kim S, Morozov Y, Padhukasahasram B, Plagnol V, Rosenberg NA, Shah C, Wall JD, Wang J, Zhao K, Kalbfleisch T, Schulz V, Kreitman M, Bergelson J (2005) The pattern of polymorphism in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLOS Biol 3:1289–1299
Ohta T (1976) Role of very slightly deleterious mutations in molecular evolution and polymorphism. Theor Popul Biol 10:254–275
Oka HI (1988) Origin of cultivated rice. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo/Elsevier, Amsterdam
Oka HI, Chang WT (1959) The impact of cultivation on populations of wild rice, Oryza sativa f. spontanea. Phyton 13:105–117
Orengo DJ, Aguade M (2004) Detecting the footprint of positive selection in a European population of Drosophila melanogaster: multilocus pattern of variation and distance to coding regions. Genetics 167:1759–1766
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler ES 4th (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11479–11484
Rozas J, Rozas R (1999) DnaSP version 3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15:174–175
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Second G (1982) Origin of the genic diversity of cultivated rice (Oryza spp.): study of the polymorphism scored at 40 isozyme loci. Jpn J Genet 57:25–57
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Tajima F (1993) Simple methods for testing the molecular evolutionary clock hypothesis. Genetics 135:599–607
Vaughan DA, Morishima H, Kadowaki K (2003) Diversity in the Oryza genus. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:139–146
Watterson GA (1975) On the number of segregating sites in genetic models without recombination. Theor Popul Biol 7:256–276
Yoshida R, Miyashita NT, Ishii T (2004) Nucleotide polymorphism in the Adh1 locus region of the wild rice Oryza rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 109:1406–1416
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J, Wong GK, Li S, Liu B, Deng Y, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Cao M, Liu J, Sun J, Tang J, Chen Y, Huang X, Lin W, Ye C, Tong W, Cong L, Geng J, Han Y, Li L, Li W, Hu G, Huang X, Li W, Li J, Liu Z, Li L, Liu J, Qi Q, Liu J, Li L, Li T, Wang X, Lu H, Wu T, Zhu M, Ni P, Han H, Dong W, Ren X, Feng X, Cui P, Li X, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai W, Xu Z, Zhang J, He S, Zhang J, Xu J, Zhang K, Zheng X, Dong J, Zeng W, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren X, Chen X, He J, Liu D, Tian W, Tian C, Xia H, Bao Q, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao W, Li P, Chen W, Wang X, Zhang Y, Hu J, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang G, Xiong Y, Li Z, Mao L, Zhou C, Zhu Z, Chen R, Hao B, Zheng W, Chen S, Guo W, Li G, Liu S, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu L, Yuan L, Yang H (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L .ssp. indica). Science 296:79–92
Zhu Q, Ge S (2005) Phylogenetic relationships among A-genome species of the genus Oryza revealed by intron sequences of four nuclear genes. New Phytol 167:249–265
Acknowledgments
SR conducted this work under financial support from Japanese Society for Promotion of Sciences, Tokyo. RT thanks B. Till, L. Comai and S. Henikoff, Washington University, Seatle, USA for training him with TILLING technique. We thank N. Kurata, National Institute of Genetics, Mishima, Japan for providing rice seeds, and J. Rozas, University of Barcelona, Spain for guiding us with the DnaSP program, two anonymous reviewers and M. Morgante, University of Udine, Italy for valuable comments to the earlier version of the manuscript. This work was supported by the “Program for Promotion of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Biosciences” (Japan), “Iwate University 21st Century COE Program: Establishment of Thermo-Biosystem Research Program” and “JSPS grant no. 18310136” to RT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Morgante.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Fig7
Supplementary Fig. 1. Results of multilocus HKA test. Contributions to the overall χ2 test static by the polymorphism and divergence observations for each locus. Squares indicate divergence between African and Asian species, and circles correspond to polymorphism within Asian species. If the observed value was greater than the expected, then the point is placed above the line; otherwise it is placed below the line (JPG 74 kb)
122_2006_473_MOESM3_ESM.doc
Supplementary Table 3. DNA polymorphism of O. sativa and O. rufipogon for silent positions (non-coding and coding synonymous sites) at the 22 loci (DOC 34 kb)
122_2006_473_MOESM5_ESM.doc
Supplementary Table 5. Number of segregating sites within all positions (coding and non-coding positions) for Asian Oryza species (DOC 25 kb)
122_2006_473_MOESM6_ESM.doc
Supplementary Table 6. DNA variation in RLD15 locus (Only non-singleton mutations are shown. There were 67 singleton mutations specific to O. australiensis) (DOC 30 kb)
122_2006_473_MOESM7_ESM.doc
Supplementary Table 7. Shared polymorphism and fixed differences among O. sativa ssp. indica, ssp. japonica and O. rufipogon (DOC 33 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakshit, S., Rakshit, A., Matsumura, H. et al. Large-scale DNA polymorphism study of Oryza sativa and O. rufipogon reveals the origin and divergence of Asian rice. Theor Appl Genet 114, 731–743 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0473-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0473-1