Abstract
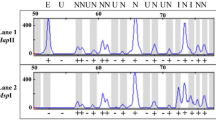
We have reported previously that introgression by Zizania latifolia resulted in extensive DNA methylation changes in the recipient rice genome, as detected by a set of pre-selected DNA segments. In this study, using the methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphism (MSAP) method, we globally assessed the extent and pattern of cytosine methylation alterations in three typical introgression lines relative to their rice parent at ∼2,700 unbiased genomic loci each representing a recognition site cleaved by one or both of the isoschizomers, HpaII/MspI. Based on differential digestion by the isoschizomers, it is estimated that 15.9% of CCGG sites are either fully methylated at the internal Cs and/or hemi-methylated at the external Cs in the rice parental cultivar Matsumae. In comparison, a statistically significant increase in the overall level of both methylation types was detected in all three studied introgression lines (19.2, 18.6, 19.6%, respectively). Based on comparisons of MSAP profiles between the isoschizomers within the rice parent and between parent and the introgression lines, four major groups of MSAP banding patterns are recognized, which can be further divided into various subgroups as a result of inheritance of, or variation in, parental methylation patterns. The altered methylation patterns include hyper- and hypomethylation changes, as well as inter-conversion of hemi- to full-methylation, or vice versa, at the relevant CCGG site(s). Most alterations revealed by MSAP in low-copy loci can be validated by DNA gel blot analysis. The changed methylation patterns are uniform among randomly selected individuals for a given introgression line within or among selfed generations. Sequencing on 31 isolated fragments that showed different changing patterns in the introgression line(s) allowed their mapping onto variable regions on one or more of the 12 rice chromosomes. These segments include protein-coding genes, transposon/retrotransposons and sequences with no homology. Possible causes for the introgression-induced methylation changes and their implications for genome evolution and crop breeding are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold ML (1997) Natural hybridization and evolution. Oxford University Press, New York
Arnold ML (2004) Transfer and origin of adaptations through natural hybridization: were Anderson and Stebbins right? Plant Cell 16:562–570
Ashikawa I (2001) Surveying CpG methylation at 5′-CCGG in the genomes of rice cultivars. Plant Mol Biol 45:31–39
Bender J (1998) Cytosine methylation of repeated sequences in eukaryotes: the role of DNA pairing. Trends Biochem Sci 23:252–256
Bourc’his D, Bestor TH (2004) Meiotic catastrophe and retrotransposon reactivation in male germ cells lacking Dnmt3L. Nature 431:96–99
Chan SW, Henderson IR, Jacobsen SE (2005) Gardening the genome: DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Rev Genet 6:351–360
Cervera MT, Ruiz-Garcia L, Martinez-Zapater JM (2002) Analysis of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana based on methylation-sensitive AFLP markers. Mol Genet Genomics 268:543–552
Comai L. (2005) The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid. Nat Rev Genet 6:836–846
Comai L, Madlung A, Josefsson C, Tyagi A (2003) Do the different parental ‘heteromes’ cause genomic shock in newly formed allopolyploids? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 358:1149–1155
Finnegan EJ (2001) Epialleles—a source of random variation in times of stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:101–106
Finnegan EJ, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES (1996) Reduced DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana results in abnormal plant development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:8449–8454
Geiman TM, Robertson KD (2002) Chromatin remodeling, histone modifications, and DNA methylation—how does it all fit together. J Cell Biochem 87:117–125
Grandbastien MA (1992) Retroelements in higher plants. Trends Genet 8:103–108
Grandbastien MA (1998) Activation of plant retrotransposons under stress conditions. Trends Plant Sci 3:181–187
Gruenbaum Y, Naveh-Many T, Cedar H, Razin A (1981) Sequence specificity of methylation in higher plant DNA. Nature 292:860–862
Heller H, Kammer C, Wilgenbus P, Doerfler W (1995) The chromosomal insertion of foreign (adenovirus type 12, plasmid of bacteriaphage) DNA is associated with enhanced methylation of cellular DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5515–5519
Hirochika H, Sugimoto K, Otsuki Y, Kanda M (1996) Retrotransposons of rice involved in mutations induced by tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7783–7787
Jiang N, Bao Z, Zhang X, Hirochika H, Eddy SR, McCouch SR, Wessler SR (2003) An active DNA transposon family in rice. Nature 421:163–167
Kakutani T (2002) Epi-alleles in plants: inheritance of epigenetic information over generations. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1106–1111
Kakutani T, Jeddeloh JA, Flowers SK, Munakata K, Richards EJ (1996) Developmental abnormalities and epimutations associated with DNA hypomethylation mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12406–12411
Kalisz S, Purugganan MD (2004) Epialleles via DNA methylation: consequences for plant evolution. Trend Ecol Evol 19:309–314
Kato M, Takashima K, Kakutani T (2004) Epigenetic control of CACTA transposon mobility in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 168:961–969
Kikuchi K, Terauchi K, Wada M, Hirano Y (2003) The plant MITE mPing is mobilized in anther culture. Nature 421:167–170
Kidwell KK, Osborn TC (1992) Simple plant DNA isolation procedures. In: Beckman JS, Osborn TC (eds) Plant genomes: methods for genetic and physical mapping. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 1–13
Levy AA, Feldman M (2004) Genetic and epigenetic reprogramming of the wheat genome upon allopolyploidization. Biol J Linn Soc 82:607–613
Liu B, Piao HM, Zhao FS, Zhao JH, Zhao R (1999) Production and molecular characterization of rice lines with introgressed traits from a wild species of Zizania latifolia Griseb. J Genet Breed 53:279–284
Liu B, Wendel JF (2000) Retrotransposon activation followed by rapid repression in introgressed rice plants. Genome 43:874–880
Liu Z, Wang Y, Shen Y, Guo W, Hao S, Liu B (2004) Extensive alterations in DNA methylation and transcription in rice caused by introgression from Zizania latifolia. Plant Mol Biol 54:571–582
Luff B, Pawlowski L, Bender J (1999) An inverted repeat triggers cytosine methylation of identical sequences in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 3:505–511
Madlung A, Masuelli RW, Watson B, Reynolds SH, Davison J, Comai L (2002) Remodeling of DNA methylation and phenotypic and transcriptional changes in synthetic Arabidopsis allotetraploids. Plant Physiol 129:733–746
Martienssen RA, Colot V (2001) DNA methylation and epigenetic inheritance in plants and lamentous fungi. Science 293:1070–1074
Matzke MA, Aufsatz W, Kanno T, Mette MF, Matzke AJ (2002) Homology-dependent gene silencing and host defense in plants. Adv Genet 46:235–275
Matzke MA, Scheid OM, Matzke AJ (1999) Rapid structural and epigenetic changes in polyploid and aneuploid genomes. BioEssays 21:761–767
McClelland M, Nelson M, Raschke E (1994) Effect of site-specific modification on restriction endonucleases and DNA modification methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3640–3659
Melquist S, Luff B, Bender J (1999) Arabidopsis PAI gene arrangements, cytosine methylation and expression. Genetics 153:401–413
Messeguer R, Ganal MW, Stevens JC, Tanksley SD (1991) Characterization of the level, target sites and inheritance of cytosine methylation in tomato nuclear DNA. Plant Mol Biol 16:753–770
Muller K, Heller H, Doerfler W (2001) Foreign DNA integration. Genome-wide perturbations of methylation and transcription in the recipient genomes. J Biol Chem 276:14271–14278
Nakazaki T, Okumoto Y, Horibata A, Yamahira S, Teraishi M, Nishida H, Inoue H, Tanisaka T (2003) Mobilization of a transposon in the rice genome. Nature 421:170–172
Pikaard CS (2001) Genomic change and gene silencing in polyploids. Trends Genet 17:675–677
Portis E, Acquadro A, Comino C, Lanteri S (2003) Analysis of DNA methylation during germination of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) seeds using methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism (MSAP). Plant Sci 166:169–178
Rangwala SH, Richards EJ (2004) The value-added genome: building and maintaining genomic cytosine methylation landscapes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 14:686–691
Rapp RA, Wendel JF (2005) Epigenetics and plant evolution. New Phytol 168:81–91
Remus R, Kammer C, Heller H, Schemitz B, Schell G, Doerfler W (1999) Insertion of foreign DNA into an established mammalian genome can alter the methylation of cellular DNA sequences. J Virol 73:1010–1022
Reyna-Lopez GE, Simpson J, Ruiz-Herrera J (1997) Differences in DNA methylation patterns are detectable during the dimorphic transition of fungi by amplification of restriction polymorphisms. Mol Gen Genet 253:703–710
Riddle NC, Richards EJ (2002) The control of natural variation in cytosine methylation in Arabidopsis. Genetics 162:355–363
Rieseberg LH (1995) The role of hybridization in evolution: old wine in new skins. Am J Bot 82:944–953
Rieseberg LH, Widmer A, Arntz AM, Burke JM (2003) The genetic architecture necessary for transgressive segregation is common in both natural and domesticated populations. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 358:1141–1147
Ronemus MJ, Galbiati M, Ticknor C, Chen J, Dellaporta SL (1996) Demethylation-induced developmental pleiotropy in Arabidopsis. Science 273:654–657
Ros F, Kunze R (2001) Regulation of activator/dissociation transposition by replication and DNA methylation. Genetics 157:1723–1733
Schumacher A, Koetsier PA, Hertz J, Doerfler W (2000) Epigenetic and genotype-specific effects on the stability of de novo imposed methylation patterns in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 275:37915–37921
Shaked H, Kashkush K, Ozkan H, Feldman M, Levy AA (2001) Sequence elimination and cytosine methylation are rapid and reproducible responses of the genome to wide hybridization and allopolyploidy in wheat. Plant Cell 13:1749–1759
Shan XH, Liu ZL, Dong ZY, Wang YM, Chen Y, Lin XY, Long LK, Han FP, Dong YS, Liu B (2005) Mobilization of the active mite transposons mPing and Pong in rice by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.). Mol Biol Evol 22:976–990
Scheid OM, Afsar K, Paszkowski J (2003) Formation of stable epialleles and their paramutation-like interaction in tetraploid Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 34:450–454
Tariq M, Paszkowski J (2004) DNA and histone methylation in plants. Trends Genet 20:244–251
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M et al (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang L, Heinlein M, Kunze R (1996) Methylation pattern of Activator transposase binding sites in maize endosperm. Plant Cell 8:747–758
Wang YM, Dong ZY, Zhang ZJ, Lin XY, Shen Y, Zhou D, Liu B (2005) Extensive de Novo genomic variation in rice induced by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.). Genetics 170:1945–1956
Ware DH, Jaiswal P, Ni J, Yap IV, Pan X, Clark KY, Teytelman L, Schmidt SC, Zhao W, Chang K, Cartinhour S, Stein LD, Mccouch SR (2002) Gramene, a tool for grass genomics. Plant Physiol 130:1606–1613
Wendel JF (2000) Genome evolution in polyploids. Plant Mol Biol 42:225–249
Wessler SR (1996) Plant retrotransposons: turned on by stress. Curr Biol 6:959–961
Wolffe AP, Matzke MA (1999) Epigenetics: regulation through repression. Science 286:481–486
Xiong LZ, Xu CG, Maroof MAS, Zhang Q (1999) Patterns of cytosine methyaltion in an elite rice hybrid and its parental lines, detected by a methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism technique. Mol Genet Genomics 261:439–446
Yoder JA, Walsh CP, Bestor TH (1997) Cytosine methylation and the ecology of intragenomic parasites. Trends Genet 13:335–340
Zilberman D, Henikoff S (2004) Silencing of transposons in plant genomes: kick them when they’re down. Genome Biol 5:249
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team (PCSIRT) in University, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30430060, 30370768), and the State Key Basic Research and Development Plan of China (2005CB120805). We are indebted to two anonymous reviewers for critical and constructive suggestions to improve this manuscript. We are also grateful to Dr. Jonathan Lamb of the University of Missouri-Columbia, USA, for editing the English. This work has been carried out in compliance with the current laws governing biological experimentation in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. Guiderdoni
Z. Y. Dong and Y. M. Wang have equally contributed to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Z.Y., Wang, Y.M., Zhang, Z.J. et al. Extent and pattern of DNA methylation alteration in rice lines derived from introgressive hybridization of rice and Zizania latifolia Griseb. Theor Appl Genet 113, 196–205 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0286-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0286-2