Abstract
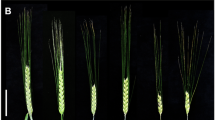
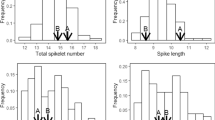
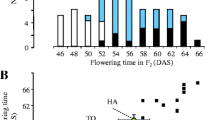
Only a few mutations affecting flowering time have been detected in maize. We analyzed a spontaneous early mutation, vgt-f7p, which appeared during production of the inbred line F7. This mutation shortens the time from planting to flowering by about 100 growing degree days (GDD), and reduces the number of nodes. It therefore seems to affect the timing of meristem differentiation from a vegetative to a reproductive state. It was mapped to a 6 cM confidence interval on chromosome 8, using a QTL mapping approach. QTL analysis of a mapping population generated by crossing the mutant F7 line (F7p) and the Gaspé flint population showed that vgt-f7p is probably allelic to vgt1, a QTL described in previous studies, and affects earliness more strongly than the Gaspé allele at vgt1. Global analysis of the QTL in the region suggested that there may be two consensus QTL, vgt1 and vgt2. These two QTL have contrasting allelic effects: rare alleles conferring extremely early flowering at vgt1 vs. greater diversity and milder effects at locus vgt2. Finally, detailed syntenic analysis showed that the vgt1 region displays a highly conserved duplicated region on chromosome 6, which also plays an important role in maize flowering time variation. The cloning of vgt1 should, therefore, also facilitate the analysis of the molecular basis of variation due to this second region.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaeffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, David JL (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research 25:3389–3402
Arcade A, Labourdette A, Falque M, Mangin B, Chardon F, Charcosset A, Joets J (2004) BioMercator: integrating genetic maps and QTL towards discovery of candidate genes. Bioinformatics 20:2324–2326
Armstead IP, Turner LB, Farrell M, Skot L, Gomez P, Montoya T, Donnison IS, King IP, Humphreys MO (2004) Synteny between a major heading-date QTL in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L) and the Hd3 heading-date locus in rice. Theor Appl Genet 108:822–828
Baldi P, Grossi M, Pecchioni N, Vale G, Cattivelli L (1999) High expression level of a gene coding for a chloroplastic amino acid selective channel protein is correlated to cold acclimation in cereals. Plant Mol Biol 41:233–243
Beadle GW (1939) Teosinte and the origin of maize. J. Hered. 30: 245–247
Bonhomme R, Derieux M, Edmeades GO (1994) Flowering of diverse maize cultivars in relation to temperature and photoperiod in multilocation field trials. Crop Sci 34:156–164
Bouchez A, Hospital F, Causse M, Gallais A, Charcosset A (2002) Marker-assisted introgression of favorable alleles at quantitative trait loci between maize elite lines. Genetics 162:1945–1959
Causse M, Santoni S, Damerval C, Maurice A, Charcosset A, Deatrick J, de Vienne D (1996) A composite map of expressed sequences in maize. Genome 39:418–432
Chardon F, Virlon B, Moreau L, Falque M, Joets J, Decousset L, Murigneux A, Charcosset A (2004) Genetic architecture of flowering time in maize as inferred from QTL meta-analysis and synteny conservation with the rice genome. Genetics 162:2169–2185
Colasanti J, Yuan Z, Sundaresan V (1998) The indeterminate gene encodes a zinc finger protein and regulates a leaf-generated signal required for the transition to flowering in maize. Cell 93:593–603
Dubreuil P, Dufour P, Krejci E, Causse M, de Vienne D, Gallais A, Charcosset A (1996) Organization of RFLP diversity among inbred lines of maize representing the most significant heterotic groups. Crop Sci 36:790–799
Falque M, Décousset L, Dervins D, Jacob A-M, Joets J, Martinant J-P, Raffoux X, Ribière N, Ridel C, Samson D, Charcosset A, Murigneux A (2005) Linkage mapping of 1454 new maize candidate gene loci. Genetics 170:1957–1966
Falque M, Décousset L, Murigneux A, Dautrevaux N, Dervins D, Jacob A-M, Ribiëre N, Ridel C, Albini G, Joets J, Charcosset A (2003) Large-scale maize cDNA mapping for candidate gene approach, in Maize Genetics Conference Abstracts. pp P116
Fengler K, Faller M, Dam T, Tingey S, Morgante M, Li B (2003) An integrated physical map in maize, in Maize Genetics Conference Abstracts. Lake Geneva, Wisconsin, pp. P122
Gaut BS, Doebley JF (1997) DNA sequence evidence for the segmental allotetraploid origin of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6809–6814
Goffinet B, Gerber S (2000) Quantitative Trait Loci: A Meta-analysis. Genetics 155:463–473
Gouesnard B, Rebourg C, Welcker C, Charcosset A (2002) Analysis of photoperiod sensitivity within a collection of tropical maize populations. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 49:471–481
Jansen RC (1993) Interval mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Genetics 135:205–211
Kearsey MJ, Farquhar AG (1998) QTL analysis in plants; where are we now? Heredity 80:137–142
Koester RP, Sisco PH, Stuber CW (1993) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling days to flowering and plant height in two near-isogenic lines of maize. Crop Sci 33:1209–1216
Kosarev P, Mayer KF, Hardtke CS (2002) Evaluation and classification of RING-finger domains encoded by the Arabidopsis genome. Genome Biology 3:1–16
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genome 1:174–181
Li Z, Pinson SRM, Stansel JW, Park WD (1995) Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for heading date and plant height in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 91:374–381
Lin SY, Sasaki T, Yano M (1998) Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling seed dormancy and heading date in rice, Oryza sativa L., using backcross inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 96:997–1003
Macdonald PM (1992) The Drosophila pumilio gene: an unusually long transcription unit and an unusual protein. Development 114:221–232
McSteen P, Laudencia-Chingcuanco D, Colasanti J (2000) A floret by any other name: control of meristem identity in maize. Trends in Plant Science 5:61–66
Méchin V, Argillier O, Hébert Y, Guingo E, Moreau L, Charcosset A, Barrière Y (2001) Genetic analysis and QTL mapping of cell wall digestibility and lignification in silage maize. Crop Sci. 41:690–697
Moreau L, Charcosset A, Gallais A (2004) Stability of QTL effects investigated in a large range of environmental conditions for grain yield and related traits in Maize. Theor Appl Genet 110:92–105
Neuffer MG, Coe EH, Wessler SR (1997) Mutants of Maize. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Pollacsek M, Caenen M (1980) Mutation for earliness. Maize Genetics Cooperation News Letter 54:21–22
Rebaï A, Blanchard P, Perret D, Vincourt P (1997). Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling silking date in a diallel cross among four lines in maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95:451–459
Rebourg C, Chastanet M, Gouesnard B, Welcker C, Dubreuil P, Charcosset A (2003) Maize introduction into Europe: the history reviewed in the light of molecular data. Theor Appl Genet 106:895–903
Salvi S, Tuberosa R, Chiapparino E, Maccaferri M, Veillet S, van Beuningen L, Isaac P, Edwards K, Phillips RL (2002) Toward positional cloning of Vgt1, a QTL controlling the transition from the vegetative to the reproductive phase in maize. Plant Mol Biol 48:601–613
Singleton WR (1946) Inheritance of indeterminate growth in maize. J Hered 37:61–64
Utz HF, Melchinger AE (1996) A program for composite interval mapping of QTL. J Agric Genomics 2:1–4
Salse J, Piegu B, Cooke R, Delseny M (2004) New in silico insight into the synteny between rice (Oryza sativa L) and maize (Zea mays L.) highlights reshuffling and identifies new duplications in the rice genome. Plant J 38:396–409
Stuber CW, Lincoln SE, Wolff DW, Helentjaris T, Lander ES (1992). Identification of genetic factor contributing to heterosis in a hybrid from two elite maize indred lines using molecular markers. Genetics 132:823–839
Vega SH, Sauer M, Orkwiszewski JA, Poethig RS (2002) The early phase change gene in maize. Plant Cell 14:133–147
Vladutu C, McLaughlin J, Phillips RL (1999) Fine mapping and characterization of linked quantitative trait loci involved in the transition of the maize apical meristem from vegetative to generative structures. Genetics 153:993–1007
Wharton RP, Sonoda J, Lee T, Patterson M, Murata Y (1998) The Pumilio RNA-binding domain is also a translational regulator. Molecular Cell 1:863–872
Yan L, Loukoianov A, Tranquilli G, Helguera M, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2003) Positional cloning of the wheat vernalization gene VRN1. PNAS 100:6263–6268
Yanagisawa S (2002) The Dof family pf plant transcription factors. Trends in Plant Science 7:555–560
Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Baba T, Yamamoto K, Umehara Y, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T (2000) Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity QTL in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS. Plant Cell 12:2473–2483
Yano M, Kojima S, Takahashi Y, Lin H, Sasaki T (2001) Genetic control of flowering time in rice, a short-day plant. Plant Physiol 127:1425–1429
Yano M, Sasaki T (1997) Genetic and molecular dissection of quantitative traits in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:145–153
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Maurice Pollacsek and Jacques Bordes, from INRA Clermont-Ferrand for providing the F7p mutant for this study. We also thank Laurence Moreau and Guylaine Blanc for providing data on QTL effects 7,8 and 9, and Alain Murigneux and Jean-Pierre Martinant (Biogemma) for helpful discussions and advice. We are grateful to Matthieu Falque and Laurent Décousset for the RFLP mapping results presented in Fig. 4. We would also like to thank Philippe Jamin, Daniel Jolivot, Denis Coubriche for expert assistance with field experimentation and Pascal Bertin for help in designing field experiments. Thanks are also due to Fabrice Dumas, Céline Ridel and Delphine Madur for expert assistance with marker analyses and to Marielle Merlino for helpful training in SSR analyses. This study was supported by the French genomics initiative “Genoplante”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. A. Hoisington
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chardon, F., Hourcade, D., Combes, V. et al. Mapping of a spontaneous mutation for early flowering time in maize highlights contrasting allelic series at two-linked QTL on chromosome 8. Theor Appl Genet 112, 1–11 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0050-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0050-z