Abstract
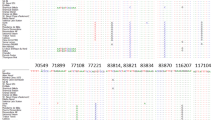
PCR amplification and restriction site analysis of chloroplast (cp) DNA regions was used to detect inter- and intraspecific differences in the genus Citrullus. More than 55 C. lanatus and 15 C. colocynthis accessions collected from diverse geographical areas, C. ecirrhosus and C. rehmii were used. Most of the cpDNA variation within Citrullus was the result of large indels and transitions and transversions. Indels at the ndhA, trnS-trnfM and trnC-trnD regions and several substitutions at restriction enzyme sites can be used to separate C. colocynthis from the other Citrullus species. A nucleotide substitution at a restriction enzyme site at the 3′ flanking region of ndhF provided a diagnostic haplotype for C. lanatus var. lanatus, the cultivated watermelon. Similarly, a nucleotide substitution at an intergenic spacer region of the trnC-trnD region resulted in a diagnostic haplotype for citron, C. lanatus var. citroides. Several C. lanatus var. citroides accessions showed the var. lanatus haplotype. C. rehmii showed almost the same haplotype as C. lanatus var. citroides with the exception of a unique insertion at a cpSSR site. Since C. ecirrhosus lacks the derived diagnostic nucleotide substitutions of C. lanatus, it is probably the progenitor of the cultivated watermelon. Intraspecific haplotypes detected within C. colocynthis were associated with geographic origin.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besnard G, Khadari B, Baradat P, Berville A(2002) Olea europaea (Oleraceae) phylogeography based on chloroplast DNA polymorphism. Theor Appl Genet 104:1353–1361
Buckler ES IV, Thornberry JM, Kresovich S (2001) Molecular diversity, structure and domestication of grasses. Genet Res 77:213–218
Chung S-M, Decker-Walters DS, Staub JE (2003) Genetic relationships within the Cucurbitaceae as assessed by ccSSR marker and sequence analysis. Can J Bot 81:814–832
Dane F (2002) Chloroplast DNA investigations in Citrullus using PCR-RFLP analysis. In: Maynard DN (ed) Cucurbitaceae 2002. ASHS Press, Naples, Fla., pp 100–108
Demesure B, Comps B (1996) Chloroplast DNA phylogeography of the common beech (Fagus sylvatica L ) in Europe. Evolution 50:2515–2520
Demesure B, Sozi N, Petit RJ (1995) A set of universal primers for amplification of polymorphic non-coding regions of mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA in plants. Mol Ecol 4:129–131
Desplanque B, Viard F, Bernard J, Forcioli D, Saumitou-Laprade P, Cuguen J, van Dijk H (2000) The linkage disequilibrium between chloroplast DNA and mitochondrial DNA haplotypes in Beta vulgaris spp. maritima (L.): The usefulness of both genomes for population genetic studies. Mol Ecol 9:141–154
De Winter B (1990) A new species of Citrullus (Benincaseae) from the Namib Desert, Namibia. Bothalia 20:209–211
Downie SR, Katz-Downie DS, Watson MF (2000) A phylogeny of the flowering plant family Apiaceae based on chloroplast DNA rpl16 and rpoC1 intron sequences: towards a suprageneric classification of subfamily Apioideae. Am J Bot 87:273–292
Dumolin-Lapegue S, Pemonge M-H, Petit RJ (1997a) An enlarged set of consensus primers for the study of organelle DNA in plants. Mol Ecol 6:393–397
Dumolin-Lapegue S, Demesure B, Fineschi S, Le Corre V, Petit RJ (1997b) Phylogeographic structure of white oaks throughout the European continent. Genetics 146:1475–1487
Fineschi S, Taurchini D, Villani F, Vendramin GG (2000) Chloroplast DNA polymorphism reveals little geographical structure in Castanea sativa mill. (Fagaceae) throughout southern European countries. Mol Ecol 9:1495–1503
Fofana B, Harvengt L, Baudoin JP, du Jardin P (1997) New primers for the polymerase chain amplification of cpDNA intergenic spacers in Phaseolus phylogeny. Belg J Bot 129:118–122
Forcioli D, Saumitou-Laprade P, Velero M, Vernet P, Cuguen J (1998) Distribution of chloroplast DNA diversity within and among populations in gynodioecious Beta vulgaris ssp maritima (Chenopodiaceae). Mol Ecol 7:1193–1204
Gepts P (2002) Ten thousand years of crop evolution. In: Chrispeels MJ, Sadava DE (ed) Plants, genes and crop biotechnology. Jones and Bartlett, Sudbury, Mass., pp 328–359
Gepts P, Clegg MT (1989) Genetic diversity in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L. R.Br.) at the DNA sequence level: consequences of genetic conservation. J Hered 81:183–188
Graham SW, Olmstead RG (2000) Utility of 17 chloroplast genes for inferring the phylogeny of the basal angiosperms. Am J Bot 87:1712–1730
Grivet D, Heinze B, Vendramin GG, Petit RJ (2001) Genome walking with consensus primers: application to the large single copy region of chloroplast DNA. Mol Ecol Notes 1:345–349
Harlan JR (1992) Crops and man. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, Wis.
Havey MJ, McCreight JD, Rhodes B, Taurick G (1998) Differential expression of the Cucumis organellar genomes. Theor Appl Genet 97:122–128
Heinze B (2002) http://fbva.forvie.ac.at/200/1892.html
Jarret RL, Merrick LC, Holms T, Evans J, Aradhya MK (1997) Simple sequence repeats in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. & Nakai). Genome 40:433–441
Katayama H, Uematsu C (2003) Comparative analysis of chloroplast DNA in Pyrus species: physical map and gene localization. Theor Appl Genet 106:303–310
Kelchner SA, Wendel JF (1996) Hairpins create minute inversions in non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Curr Genet 30:259–262
King RA, Ferris C (1998) Chloroplast DNA phylogeography of Alnus glutinosa L. Gaertn. Mol Ecol 7:1151–1161
Levi A, Thomas CE, Wehner TC, Zhang X (2001) Low genetic diversity indicated the need to broaden the genetic base of cultivated watermelon. Hortscience 36:1096–1101
Lim H, Gounaris I, Harrison RC, Boyer CD (1990) Restriction site and genetic map of Cucurbita pepo chloroplast DNA. Curr Genet 18:273–275
Mohanty A, Martin JP, Aguinagalde I (2001) Chloroplast DNA study in wild populations and some cultivars of Prunus avium L. Theor Appl Genet 103:112–117
Nesbitt TC, Tanksley SD (2002) Comparative sequencing in the genus Lycopersicon: Implications for the evolution of fruit size in the domestication of cultivated tomatoes. Genetics 162:365–379
Olmstead RG, Palmer JD (1994) Chloroplast DNA systematics: a review of methods and data analysis. Am J Bot 81:1205–1224
Olmstead RG, Sweere JA (1994) Combining data in phylogenetic systematics: An empirical approach using three molecular data sets in the Solanaceae. Syst Biol 43:467–481
Palmer JD (1982) Physical and gene mapping of chloroplast DNA from Atriplex triangularis and Cucumis sativus. Nucleic Acids Res 10:1593–1605
Parducci L, Szmidt A (1999) PCR-RFLP analysis of cpDNA in the genus Abies. Theor Appl Genet 98:802–808
Perl-Treves R, Galun E (1985) The Cucumis plastome: physical map, intrageneric variation and phylogenetic relationships. Theor Appl Genet 71:417–429
Petit RJ, Pineau E, Demesure B, Bacilieri R, Ducousso A, Kremer A (1997) Chloroplast DNA footprints of postglacial recolonization by oaks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9996–10001
Robinson RW, Decker-Walters DS (1997) Cucurbits. CAB Int, Wallingford, UK
Rubatzky VE (2001) Origin, distribution and uses. In: Maynard DN (ed) Watermelons. Characteristics, production and marketing. ASHS Press, Alexandria, Va., pp 21–26
Sang T, Crawford DJ, Stuessy TF (1997) Chloroplast DNA phylogeny, reticulate evolution, and biogeography of Paeonia (Paeoniaceae). Am J Bot 84:1120–1136
Schnabel A, Wendel JF (1998) Cladistic biogeography of Gleditsia (Leguminosae) based on ndhF and rpl16 chloroplast gene sequences. Am J Bot 85:1753–1765
Small RL, Ryburn JA, Cronn RC, Seelanan T, Wendel JF (1998) The tortoise and the hare: choosing between noncoding plastome and nuclear Adh sequences for phylogeny reconstruction in a recently diverged plant group. Am J Bot 85:1301–1315
Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Milligan BG (1992) Intraspecific chloroplast DNA variation: sytematic and phylogenetic implications. In: Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Doyle JJ (ed) Molecular systematics of plants. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 117–150
Soltis DE, Soltis,PS, Doyle JJ (1998) Molecular systematics of plants II. DNA sequencing. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17:1105–1109
Wehner TC, Shetty NV, Elmstrom GW (2001) Breeding and seed production. In: Maynard DN (ed) Watermelons. Characteristics, production and marketing. ASHS Press, Alexandria, Va., pp 27–73
Weising K, Gardner R (1999) A set of conserved PCR primers for the analysis of simple sequence repeat polymorphisms in chloroplast genomes of dicotyledonous angiosperms. Genome 42:9–19
Xu DH, Abe J, Kanazawa A, Gai JY, Shimamato Y (2001) Identification of sequence variation by PCR-RFLP and its application to the evaluation of cpDNA diversity in wild and cultivated soybeans. Theor Appl Genet 102:683–688
Xu DH, Abe J, Gai JY, Shimamato Y (2002) Diversity of chloroplast SSRs in wild and cultivated soybeans: evidence for multiple origins of cultivated soybean. Theor Appl Genet 105:645–653
Yanev Z, Shabelsky E, Schafferman D (1999) Colocynth: potential arid land oilseed from an ancient cucurbit. In: Janick J (ed) Perspectives on new crops and new uses. ASHS Press, Alexandria, Va., pp 257–261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Dvorak
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dane, F., Lang, P. & Bakhtiyarova, R. Comparative analysis of chloroplast DNA variability in wild and cultivated Citrullus species. Theor Appl Genet 108, 958–966 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1512-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1512-9