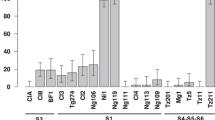
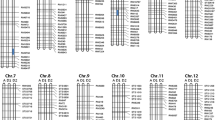
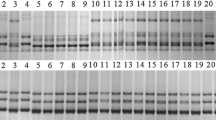
Abstract.
The very high resistance to Rice yellow mottle virus observed in the two rice varieties Gigante (Oryza sativa) and Tog 5681 (O. glaberrima) is monogenic and recessive. Bulked segregant analysis was carried out to identify AFLP markers linked to the resistance gene. Mapping of PCR-specific markers, CAPS and microsatellite markers on 429 individuals of an IR64 × Gigante F2 population pinpointed this resistance gene on the long arm of chromosome 4 in a 3.7-cM interval spanned by PCR markers. These markers also flanked the resistance gene of the O. glaberrima accession Tog 5681 and confirmed previous allelism tests. The rarity of this recessive natural resistance was in line with a resistance mechanism model based on point mutations of a host component required for cell-to-cell movement of the virus. Preliminary data on the genetic divergence between the two cultivated rice species in the vicinity of the resistance locus suggested that two different resistance alleles are present in Gigante and Tog 5681. A large set of recombinants is now available to envisage physical mapping and cloning of the gene.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo ME, Sy AA, Alegbejo MD (1998) Rice yellow mottle virus (RYMV) in Africa: evolution, distribution, economic significance on sustainable rice production and management strategies. J Sustain Agric 11:85–111
Albar L, Lorieux M, Ahmadi N, Rimbault I, Pinel A, Sy A, Fargette D, Ghesquière A (1998) Genetic basis and mapping of the resistance to Rice yellow mottle virus. I. QTLs identification and relationship between resistance and plant morphology. Theor Appl Genet 97:1145–1154
Allard RW (1956) Formulas and tables to facilitate the calculation of recombination values in heredity. Hilgardia 24:235–278
Antonio BA, Inoue T, Kajiya H, Nagamura Y, Kurata N, Minobe Y, Yano M, Nakagahra M, Sasaki T (1996) Comparison of genetic distance and order of DNA markers in five populations of rice. Genome 39:946–956
Barry G (2001) The use of the Monsanto draft rice genome sequence in research. Plant Physiol 125:1164–1165
Bendahmane A, Kanyuka K, Baulcombe DC (1999) The Rx gene from potato controls separate virus resistance and cell death responses. Plant Cell 11:781–791
Chen M, Presting G, Barbazuk W, Goicoechea J, Blackmon B, Fang G, Kim H, Frisch D, Yu Y, Sun S, Higingbottom S, Phimphilai J, Phimphilai D, Thurmond S, Gaudette B, Li P, Liu J, Hatfield J, Main D, Farrar K, Henderson C, Barnett L, Costa R, Williams B, Walser S, Atkins M, Hall C, Budiman M, Tomkins J, Luo M, Bancroft I, Salse J, Regad F, Mohapatra T, Singh N, Tyagi A, Soderlund C, Dean R, Wing R (2002) An integrated physical and genetic map of the rice genome. Plant Cell 14:537–545
Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, McCouch SR (1997) Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:553–567
Chisholm ST, Mahajan SK, Witham SA, Yamamoto ML, Carrington JC (2000) Cloning of the Arabidopsis RTM1 gene, which controls restriction of long-distance movement of Tobacco etch virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:489–494
Dally A, Second G (1989) Chloroplast DNA diversity in wild and cultivated species of rices (genus Oryza, section Oryza). Cladistic-mutation and genetic-distance analysis. Theor Appl Genet 80:209–222
Ellis J, Dodds P, Pryor T (2000) Structure, function and evolution of plant disease resistance genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:278–284
Fargette D, Pinel A, Traoré O, Ghesquière A, Konaté G (2002) Emergence of resistance-breaking isolates of Rice yellow mottle virus during serial inoculations. Eur J Plant Pathol 108:585–591
Ghesquière A, Lorieux M, Roumen E, Albar L, Fargette D, Huang N, Notteghem JL (1996) Indica/japonica doubled haploid population as a model for mapping rice yellow mottle virus and blast resistance genes. Int Rice Res Notes 21:47–49
Gibb K, Hellmann G, Pirone T (1989) Nature of resistance of a tobacco cultivar to Tobacco vein mottling virus. Mol Plant–Microbe Interact 2:332–339
Goff S, Ricke D, Lan T, Presting G, Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchinson D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange B, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong J, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang S, Colbert M, Sun W, Chen L, Cooper B, Park S, Wood T, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller R, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp japonica). Science 296:92–100
Grant MR, Mcdowell JM, Sharpe AG, Zabala MDT, Lydiate DJ, Dangl JL (1998) Independent deletions of a pathogen-resistance gene in Brassica and Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15,843–15,848
Guiderdoni E, Galinato E, Luistro J, Vergara G (1992) Anther culture of tropical japonica × indica hybrids of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 62:219–224
Hiei Y, Komari T, Kubo T (1997) Transformation of rice mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Mol Biol 35:205–218
Huang N, Parco A, Mew T, Magpantay G, Mccouch SR, Guiderdoni E, Xu J, Subudhi P, Angeles ER, Khush GS (1997) RFLP mapping of isozymes, RAPD and QTLs for grain shape, brown planthopper resistance in a doubled haploid rice population. Mol Breed 3:105–113
Ishii T, Terachi T, Mori N, Tsunewaki K (1993) Comparative study on the chloroplast, mitochondrial and nuclear genome differentiation in the two cultivated rice species, Oryza sativa and Oryza glaberrima, by RFLP analyses. Theor Appl Genet 86:88–96
Kilian A, Chen J, Han F, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (1997) Towards map-based cloning of the barley stem rust resistance genes Rpg1 and rpg4 using rice as an intergenomic cloning vehicle. Plant Mol Biol 35:187–195
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) mapmarker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lorieux M, Goffinet B, Perrier X, Gonzales De Leon D, Lanaud C (1995) Maximum-likelihood models for mapping genetic markers showing segregation distorsion: 1. Backcross populations. Theor Appl Genet 90:73–80
Lorieux M, Petrov M, Huang N, Guiderdoni E, Ghesquière A (1996) Aroma in rice: genetic analysis of a quantitative trait. Theor Appl Genet 93:1145–1151
Lorieux M, Ndjiondjop M-N, Ghesquière A (2000) A first interspecific Oryza sativa × Oryza glaberrima microsatellite-based genetic linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 100:593–601
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RY (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Ndjiondjop M-N, Albar L, Fargette D, Fauquet C, Ghesquière A (1999) The genetic basis of high resistance to Rice yellow mottle virus (RYMV) in cultivars of two cultivated rice species. Plant Dis 83:931–935
Ndjiondjop M-N, Brugidou C, Zang S, Fargette D, Ghesquière A, Fauquet C (2001) High resistance to Rice yellow mottle virus (RYMV) in two cultivated rice cultivars is correlated to the failure of cell-to-cell movement. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 59:309–316
Sano Y, Chu YE, Oka HI (1979) Genetic studies of speciation in cultivated rice. I. Genic analyses on the F1 sterility between O. sativa L. and O. glaberrima Steud. Jpn J Genet 54:121–132
Second G (1982) Origin of the genic diversity of cultivated rice (Oryza spp). Study of the polymorphism scored at 40 isozyme loci. Jpn J Genet 57:25–57
Stein N, Feuillet C, Wicker T, Schlagenhauf E, Keller B (2000) Subgenome chromosome walking in wheat: a 450-kb physical contig in Triticum monococcum L. spans the Lr10 resistance locus in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13,436–13,441
Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho Yg, Ishii T, Mccouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Thottappilly G, Rossel HW (1993) Evaluation of resistance to Rice yellow mottle virus in Oryza species. Indian J Virol 9:65–73
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Van De Lee T, Hornes M, Fritjers A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B (1994) The product of Tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: similarity to Toll and the Interleukine-1 receptor. Cell 78:1101–1115
Whitham SA, Anderberg RJ, Chisholm ST, Carrington JC (2000) Arabidopsis RTM2 gene is necessary for specific restriction of Tobacco etch virus and encodes an unusual small heat shock-like protein. Plant Cell 12:569–582
Xu Y, Zhu L, Xiao J, Huang N, Mccouch SR (1997) Chromosomal regions associated with segregation distorsion of molecular markers in F2, backcross, doubled haploid, and recombinant inbred populations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 253:535–545
Yadav R, Courtois B, Huang N, McLaren G (1997) Mapping genes controlling root morphology and root distribution in a doubled-haploid population of rice. Theor Appl Genet 94:619–632
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J, Wong G, Li S, Liu B, Deng Y, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Cao M, Liu J, Sun J, Tang J, Chen Y, Huang X, Lin W, Ye C, Tong W, Cong L, Geng J, Han Y, Li L, Li W, Hu G, Huang X, Li W, Li J, Liu Z, Li L, Liu J, Qi Q, Liu J, Li L, Li T, Wang X, Lu H, Wu T, Zhu M, Ni P, Han H, Dong W, Ren X, Feng X, Cui P, Li X, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai W, Xu Z, Zhang J, He S, Zhang J, Xu J, Zhang K, Zheng X, Dong J, Zeng W, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren X, Chen X, He J, Liu D, Tian W, Tian C, Xia H, Bao Q, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao W, Li P, Chen W, Wang X, Zhang Y, Hu J, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang G, Xiong Y, Li Z, Mao L, Zhou C, Zhu Z, Chen R, Hao B, Zheng W, Chen S, Guo W, Li G, Liu S, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu L, Yuan L, Yang H (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp indica). Science 296:79–92
Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Cheng Z, Chen M, Wang S, Feng Q, Huang Y, Li Y, Tang Y, Zhou B, Chen Z, Yu S, Zhu J, Hu X, Mu J, Ying K, Hao P, Zhang L, Lu Y, Zhang L, Liu Y, Yu Z, Fan D, Weng Q, Chen L, Lu T, Liu X, Jia P, Sun T, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Li C, Wang R, Lei H, Li T, Hu H, Wu M, Zhang R, Guan J, Zhu J, Fu G, Gu M, Hong G, Xue Y, Wing R, Jiang J, Han B (2002) A fine physical map of the rice chromosome 4. Genome Res 12:817–823
Acknowledgements.
This work is a part of the "Interspecific Hybridization Project Between African and Asian Cultivated Rice Species" funded by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan through UNDP/TCDC contribution and by the Rockefeller foundation. M.-N. Ndjiondjop is the recipient of a PhD grant from the Rockefeller Foundation training program on rice biotechnology. We thank M. Lorieux for useful discussions and C. Brugidou for critical reading of the manuscript. We are also grateful to J. Aribi and T. Mathieu for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Q. Zhang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albar, L., Ndjiondjop, MN., Esshak, Z. et al. Fine genetic mapping of a gene required for Rice yellow mottle virus cell-to-cell movement. Theor Appl Genet 107, 371–378 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1258-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1258-4