Abstract.
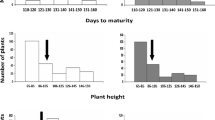
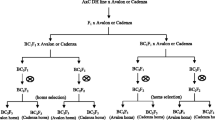
Advanced backcross QTL (AB-QTL) analysis was used to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for yield and yield components in a BC2F2 population derived from a cross between the German winter wheat variety 'Prinz' and the synthetic wheat line W-7984 developed by CIMMYT. Two hundred and ten microsatellite markers were employed to genotype 72 pre-selected BC2F2 plants and phenotypic data were collected for five agronomic traits from corresponding BC2F3 families that were grown at four locations in Germany. Using single-marker regression and interval mapping, a total of 40 putative QTLs derived from W-7984 were detected, of which 11 were for yield, 16 for yield components, eight for ear emergence time and five for plant height. For 24 (60.0%) of them, alleles from the synthetic wheat W-7984 were associated with a positive effect on agronomic traits, despite the fact that synthetic wheat was overall inferior with respect to agronomic appearance and performance. The present study indicated that favorable QTL alleles could be transferred from wild relatives of wheat into an elite wheat variety for improvement of quantitative trait loci like yield by the advanced backcross QTL strategy and molecular breeding. To our knowledge, the results presented here were the first report on AB-QTL analysis in wheat.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki E, Miura H, Sawada S (1999) Identification of genetic loci affecting amylose content and agronomic traits on chromosome 4A of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 98:977–984
Austin DF, Lee M (1996) Comparative mapping in F2:3 and F6:7 generations of quantitative trait loci for grain yield and yield components in maize. Theor Appl Genet 92:817–826
Bernacchi D, Beck-Bunn T, Eshed Y, Lopez J, Petiard V, Uhlig J, Zamir D, Tanksley S (1998) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in tomato. I. Identification of QTLs for traits of agronomic importance from Lycopersicon hirsutum. Theor Appl Genet 97:381–397
Bezant J, Laurie D, Pratchett N, Chojecki J, Kearsey M (1997) Mapping QTLs controlling yield and yield components in a spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cross using marker regression. Mol Breed 3:29–38
Börner A, Worland AJ, Plaschke J, Schumann E, Law CN (1993) Pleiotropic effects of genes for reduced height (Rht) and day length insensitivity (Ppd) on yield and its components for wheat grown in middle Europe. Plant Breed 111:204–216
Börner A, Röder M, Korzun V (1997) Comparative molecular mapping of GA insensitive Rht loci on chromosomes 4B and 4D of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:1133–1137
Börner A, Schumann E, Fürste A, Cöster H, Leithold B, Röder MS, Weber WE (2002) Mapping of quantitative trait loci for agronomic important characters in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:921–936
Cadalen T, Sourdille P, Charmet G, Tixier MH, Gay G, Boeuf C, Bernard S, Leroy P, Bernard M (1998) Molecular markers linked to genes affecting plant height in wheat using a doubled-haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 96:933–940
Chao S, Sharp PJ, Worland AJ, Warham EJ, Koebner RMD, Gale MD (1989) RFLP-based genetic maps of wheat homoeologous group-7 chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 78:495–504
Devos KM, Gale MD (1992) The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84:567–572
Faris JD, Li WL, Liu DJ, Chen PD, Gill BS (1999) Candidate gene analysis of quantitative disease resistance in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 98:219–225
Fulton TM, Beck-Bunn T, Emmatty D, Eshed Y, Lopez J, Petiard V, Uhlig J, Zamir D, Tanksley SD (1997a) QTL analysis of an advanced backcross of Lycopersicon peruvianum to the cultivated tomato and comparisons with QTLs found in other wild species. Theor Appl Genet 95:881–894
Fulton TM, Nelson JC, Tanksley SD (1997b) Introgression and DNA marker analysis of Lycopersicon peruvianum, a wild relative of the cultivated tomato, into Lycopersicon esculentum, followed through three successive backcross generations. Theor Appl Genet 95:895–902
Fulton TM, Grandillo S, Beck-Bunn T, Fridman E, Frampton A, Lopez J, Petiard V, Uhlig J, Zamir D, Tanksley SD (2000) Advanced backcross QTL analysis of a Lycopersicon esculentum × Lycopersicon parviflorum cross. Theor Appl Genet 100:1025–1042
Huang XQ, Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ, Wenzel G, Mohler V (2000a) Molecular mapping of the wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm24 and marker validation for molecular breeding. Theor Appl Genet 101:407–414
Huang XQ, Zeller FJ, Hsam SLK, Wenzel G, Mohler V (2000b) Chromosomal location of AFLP markers in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) utilizing nulli-tetrasomic stocks. Genome 43:298–305
Huang XQ, Röder MS, Pestsova E, Börner A, Ganal MW (2001) Development and use of wheat microsatellite markers for the characterization of germplasm of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). In: the Plant and Animal Genome IX Conference, January 13–17, 2001, San Diego, California, USA, p 260
Huang XQ, Börner A, Röder MS, Ganal MW (2002) Assessing genetic diversity of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) germplasm using microsatellite markers.Theor Appl Genet 105:699–707
Huang XQ, Wang LX, Xu MX, Röder MS (2003) Microsatellite mapping of the wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm5e in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet (in press)
Hyne V, Kearsey MJ, Martinez O, Gang W, Snape JW (1994) A partial genome assay for quantitative trait loci in wheat (Triticum aestivum) using different analytical techniques. Theor Appl Genet 89:735–741
Kato K, Miura H, Sawada S (1999) QTL mapping of genes controlling ear emergence time and plant height on chromosome 5A of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 98:472–477
Kato K, Miura H, Sawada S (2000) Mapping QTLs controlling grain yield and its components on chromosome 5A of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 101:1114–1121
Kihara H (1944) Die Entdeckung des DD Analysators beim Weizen. Agric Hort 19:889–890
Knot DR (1989) The wheat rusts: breeding for resistance. Monographs on Theoretical Applied Genetics 12, Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Law CN (1967) The locations of genetic factors controlling a number of quantitative characters in wheat. Genetics 56:445–461
Law CN, Wolfe MS (1966) Location of genetic factors for mildew resistance and ear emergence time on chromosome 7B of wheat. Can J Genet Cytol 8:462–470
Law CN, Worland AJ, Giorgi B (1976) The genetic control of ear-emergence time by chromosomes 5A and 5D of wheat. Heredity 36:49–58
Law CN, Snape JW, Worland AJ (1978) The genetic relationship between height and yield in wheat. Heredity 40:133–151
Lin HX, Qian HR, Zhuang JY, Lu J, Min SK, Xiong ZM, Huang N, Zheng KL (1996) RFLP mapping of QTLs for yield and related characters in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 92:920–927
Lin SY, Sasaki T, Yano M (1998) Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling seed dormancy and heading date in rice, Oryza sativa L., using backcross inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 96:997–1003
Lutz J, Hsam SLK, Limpert E, Zeller FJ (1995) Chromosomal location of powdery mildew resistance genes in Triticum aestivum L. (common wheat). 2. Genes Pm2 and Pm19 from Aegilops squarrosa L. Heredity 74:152–156
Marino C, Nelson J, Lu Y, Sorrels M, Leroy P, Tuleen N, Lopes C, Hart G (1996) Molecular genetic maps of the group-6 chromosomes of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum). Genome 39:359–366
Moncada P, Martínez CP, Borrero J, Chatel M, Gauch Jr H, Guimaraes E, Tohme J, McCouch SR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa × Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment. Theor Appl Genet 102:41–52
Nelson J (1997) QGene: software for marker-based genomic analysis and breeding. Mol Breed 3:239–245
Nelson J, Van Deynze AE, Autrique E, Sorrells ME, Lu YH, Negre S, Bernard M, Leroy P (1995a) Molecular mapping of wheat. Homoeologous group 3. Genome 38:525–533
Nelson JC, Van Deynze A, Autrique E, Sorrells ME, Lu YH, Merlino M, Atkinson M, Leroy P (1995b) Molecular mapping of wheat. Homoeologous group 2. Genome 38:516–524
Peng JH, Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC, Dahan A, Grama A, Ronin YI, Korol AB, Nevo E (1999) Microsatellite tagging of the stripe-rust resistance gene YrH52 derived from wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides, and suggestive negative crossover interference on chromosome 1B. Theor Appl Genet 98:862–872
Pestsova E, Ganal WM, Röder MS (2000) Isolation and mapping of microsatellite markers specific for the D genome of bread wheat. Genome 43:689–697
Plaschke J, Ganal MW, Röder MS (1995) Detection of genetic diversity in closely related bread wheat using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 91:1001–1007
Röder MS, Korzun V, Gill BS Ganal MW (1998a) The physical mapping of microsatellite markers in wheat. Genome 41:278–283
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998b) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Shah MM, Gill KS, Baenziger PS, Yen Y, Kaeppler SM, Ariyarathne HM (1999) Molecular mapping of loci for agronomic traits on chromosome 3A of bread wheat. Crop Sci 39:1728–1732
Tanksley SD, Nelson JC (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis: a method for the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTLs from unadapted germplasm into elite breeding lines.Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203
Tanksley SD, Grandillo S, Fulton TM, Zamir D, Eshed T, Petiard V, Lopez J, Beck-Bunn T (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in a cross between an elite processing line of tomato and its wild relative L. pimpinellifolium. Theor Appl Genet 92:213–224
Veldboom LR, Lee M (1994) Molecular-marker facilitated studies of morphological traits in maize. II. Determination of QTLs for grain yield and yield components. Theor Appl Genet 89:451–458
Worland AJ, Korzun V, Röder MS, Ganal MW, Law CN (1998) Genetic analysis of the dwarfing gene Rht8 in wheat. Part II. The distribution and adaptive significance of allelic variants at the Rht8 locus of wheat as revealed by microsatellite screening. Theor Appl Genet 96:1110–1120
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan L, Tanksley SD (1996) Identification of QTLs affecting traits of agronomic importance in a recombinant inbred population derived from a subspecific rice cross. Theor Appl Genet 92:230–244
Xiao JH, Li JM, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan LP, TanksleySD, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from a wild rice relative, Oryza rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Acknowledgements.
We thank E. Ebmeyer at Lochow-Petkus GmbH, H. Kempf at Saatzucht H. Schweiger, J. Breun at Saatzucht J. Breun and R. Schachschneider at Nordsaat Saatzucht GmbH for the field experiments and evaluations in this study, J. Schondelmaier in Saaten-Union Resistenzlabor GmbH for the coordination of this project, A. Heber for excellent technical assistance and Dr. G. H. Buck-Sorlin for assistance with the program Minitab to perform ANOVA. This research was supported by a grant from Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen (AiF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X.Q., Cöster, H., Ganal, M.W. et al. Advanced backcross QTL analysis for the identification of quantitative trait loci alleles from wild relatives of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 106, 1379–1389 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1179-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1179-7