Abstract
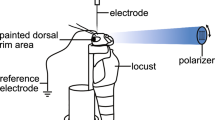
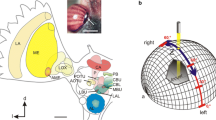
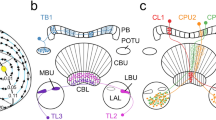
Desert ants, Cataglyphis bicolor (Hymenoptera), navigate by using compass information provided by skylight polarization. In this study, electrophysiological recordings were made from polarization-sensitive interneurons (POL-neurons) in the optic lobe of Cataglyphis. The POL-neurons exhibit a characteristic polarization opponency. They receive monochromatic input from the UV receptors of the specialized dorsal rim area of the compound eye. Both polarization opponency and monochromacy are features also found in the POL-neurons of crickets (Orthoptera).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 September 1999 / Accepted in revised form: 13 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labhart, T. Polarization-Sensitive Interneurons in the Optic Lobe of the Desert Ant Cataglyphis bicolor . Naturwissenschaften 87, 133–136 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001140050691
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001140050691