Abstract
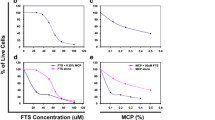
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a neuroendocrine malignancy showing poor response to a variety of therapeutic strategies. We evaluated the antitumor activity of S-trans, trans-farnesylthiosalicylic acid (FTS), a new inhibitor of Ras signal transduction, in a newly established SCID mouse xenotransplantation model for human MCC (seven animals per group). FTS injected intraperitoneally at 5 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks up-regulated the tumor suppressor p53 and induced tumor cell apoptosis in established MCCs growing subcutaneously in SCID mice. These effects led to a statistically significant inhibition of MCC growth (P<0.002). The mean tumor weights following FTS or control treatment were 0.32±0.15 g and 1.08±0.29 g, respectively. There was no evidence of FTS related toxicity at the effective dose used. Our findings stress the notion that FTS may qualify as a novel and rational treatment approach for MCC and possibly for other tumors that rely on tyrosine kinase signaling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jansen, B., Heere-Ress, E., Schlagbauer-Wadl, H. et al. Farnesylthiosalicylic acid inhibits the growth of human Merkel cell carcinoma in SCID mice. J Mol Med 77, 792–797 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001099900052
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001099900052