Abstract
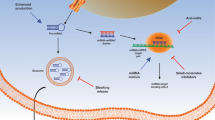
Studies suggested that long noncoding HAR1A RNA may be a tumor suppressor, but its association with oral cancer remains unclear. Here, we show the functional role and mechanisms of HAR1A in oral cancer progression. Microarray analysis was performed to screen the related candidates of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) in human monocytes. Following lncRNA HAR1A, the regulation of HAR1A, ALPK1, myosin IIA, and BRD7 was tested using reverse-transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) in oral cancer cells. The inflammatory and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition marker expressions were analyzed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and western blot. Phenotypic experiments were verified by colony formation assay, transwell migration assay, and Annexin V-apoptotic assay. In the nuclei of cancer cells, HAR1A functions upstream of signaling pathways and knockdown of HAR1A promoted ALPK1 expression and downregulated BRD7 resulting in inflammation and oral cancer progression. In monocytes, the expressions of TNF-α and CCL2 were increased following HAR1A knockdown and reduced following ALPK1 knockdown. HAR1A knockdown upregulated the expression of ALPK1, slug, vimentin, fibronectin, and N-cadherin but reduced the expression of E-cadherin in oral cancer cells. Myosin IIA was primarily located in the cytoplasm and that its decrease in the nuclei of oral cancer cells was likely to demonstrate suppressive ability in late-stage cancer. Our findings suggest that the HAR1A, BRD7, and myosin IIA are tumor suppressors while ALPK1 has oncogene-like property in the nucleus and is involved in inflammation and oral cancer progression. More research for HAR1A activators or ALPK1 inhibitors is required to develop potential therapeutic agents for advanced oral cancer.
Key messages
-
lncRNA HAR1A, BRD7, and myosin IIA are tumor suppressors whereas ALPK1 has an oncogenic-like property in the nucleus.
-
lncRNA HAR1A/ALPK1/BRD7/myosin IIA axis plays a critical role in the progression of oral cancer.
-
lncRNA HAR1A localizes upstream of signaling pathways to inhibit ALPK1 expression and then upregulated BRD7.
-
lncRNA HAR1A and ALPK1 are involved in cancer progression via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition regulations.
-
ALPK1 inhibitors are potential kinase-targeted therapeutic agents for patients with advanced oral cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its Supplementary Materials).
References
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M (2019) SEER cancer statistics review 1975-2016. National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health-USA
Zhang L, Meng X, Zhu XW, Yang DC, Chen R, Jiang Y, Xu T (2019) Long non-coding RNAs in oral squamous cell carcinoma: biologic function, mechanisms and clinical implications. Mol Cancer 18:102
Shi Z, Luo Y, Zhu M, Zhou Y, Zheng B, Wu D, Wang S, Xie X, Lin H, Yu X (2019) Expression analysis of long non-coding RNA HAR1A and HAR1B in HBV-induced hepatocullular carcinoma in Chinese patients. Lab Med 50:150–157
Zou H, Wu LX, Yang Y, Li S, Mei Y, Liu YB, Zhang L, Cheng Y, Zhou HH (2017) LncRNAs PVT1 and HAR1A are prognosis biomarkers and indicate therapy outcome for diffuse glioma patients. Oncotarget 8:78767–78780
Lee CP, Huang YN, Nithiyanantham S, Huang CM, Ko YC (2019) LncRNA-Jak3: Jak3 coexpressed pattern regulates monosodium urate crystal-induced osteoclast differentiation through Nfatc1/Ctsk expression. Environ Toxicol 34:179–187
Bauer M, Nascakova Z, Mihai AI, Cheng PF, Levesque MP, Lampart S, Hurwitz R, Pfannkuch L, Dobrovolna J, Jacobs M et al (2020) The ALPK1/TIFA/NF-kappaB axis links a bacterial carcinogen to R-loop-induced replication stress. Nat Commun 11:5117
Lee CP, Chiang SL, Ko AM, Liu YF, Ma C, Lu CY, Huang CM, Chang JG, Kuo TM, Chen CL et al (2016) ALPK1 phosphorylates myosin IIA modulating TNF-alpha trafficking in gout flares. Sci Rep 6:25740
Kuo TM, Yeh KT, Hsu HT, Chiang SL, Chang JG, Huang CM, Tu HP, Liu CS, Ko YC (2015) ALPK1 affects testosterone mediated regulation of proinflammatory cytokines production. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 154:150–158
Wang SJ, Tu HP, Ko AM, Chiang SL, Chiou SJ, Lee SS, Tsai YS, Lee CP, Ko YC (2011) Lymphocyte alpha-kinase is a gout-susceptible gene involved in monosodium urate monohydrate-induced inflammatory responses. J Mol Med (Berl) 89:1241–1251
Rashid M, van der Horst M, Mentzel T, Butera F, Ferreira I, Pance A, Rutten A, Luzar B, Marusic Z, de Saint AN et al (2019) ALPK1 hotspot mutation as a driver of human spiradenoma and spiradenocarcinoma. Nat Commun 10:2213
Liao HF, Lee HH, Chang YS, Lin CL, Liu TY, Chen YC, Yen JC, Lee YT, Lin CY, Wu SH et al (2016) Down-regulated and commonly mutated ALPK1 in lung and colorectal cancers. Sci Rep 6:27350
Chen PK, Hua CH, Hsu HT, Kuo TM, Chung CM, Lee CP, Tsai MH, Yeh KT, Ko YC (2019) ALPK1 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis and tumor growth in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Am J Pathol 189:190–199
Ryazanov AG, Pavur KS, Dorovkov MV (1999) Alpha-kinases: a new class of protein kinases with a novel catalytic domain. Curr Biol 9:R43–R45
Heine M, Cramm-Behrens CI, Ansari A, Chu HP, Ryazanov AG, Naim HY, Jacob R (2005) Alpha-kinase 1, a new component in apical protein transport. J Biol Chem 280:25637–25643
Lee CP, Nithiyanantham S, Hsu HT, Yeh KT, Kuo TM, Ko YC (2019) ALPK1 regulates streptozotocin-induced nephropathy through CCL2 and CCL5 expressions. J Cell Mol Med 23:7699–7708
Zhou P, She Y, Dong N, Li P, He H, Borio A, Wu Q, Lu S, Ding X, Cao Y et al (2018) Alpha-kinase 1 is a cytosolic innate immune receptor for bacterial ADP-heptose. Nature 561:122–126
Ko AM, Tu HP, Liu TT, Chang JG, Yuo CY, Chiang SL, Chang SJ, Liu YF, Ko AM, Lee CH et al (2013) ALPK1 genetic regulation and risk in relation to gout. Int J Epidemiol 42:466–474
Strietz J, Stepputtis SS, Preca BT, Vannier C, Kim MM, Castro DJ, Au Q, Boerries M, Busch H, Aza-Blanc P et al (2016) ERN1 and ALPK1 inhibit differentiation of bi-potential tumor-initiating cells in human breast cancer. Oncotarget 7:83278–83293
Ryzhakov G, West NR, Franchini F, Clare S, Ilott NE, Sansom SN, Bullers SJ, Pearson C, Costain A, Vaughan-Jackson A et al (2018) Alpha kinase 1 controls intestinal inflammation by suppressing the IL-12/Th1 axis. Nat Commun 9:3797
Vicente-Manzanares M, Ma X, Adelstein RS, Horwitz AR (2009) Non-muscle myosin II takes centre stage in cell adhesion and migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:778–790
Betapudi V, Licate LS, Egelhoff TT (2006) Distinct roles of nonmuscle myosin II isoforms in the regulation of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell spreading and migration. Cancer Res 66:4725–4733
Xia ZK, Yuan YC, Yin N, Yin BL, Tan ZP, Hu YR (2012) Nonmuscle myosin IIA is associated with poor prognosis of esophageal squamous cancer. Dis Esophagus 25:427–436
Xiong D, Ye YL, Chen MK, Qin ZK, Li MZ, Zhang H, Xu LH, Xu ZZ, Zeng MS (2012) Non-muscle myosin II is an independent predictor of overall survival for cystectomy candidates with early-stage bladder cancer. Oncol Rep 28:1625–1632
Liu D, Zhang L, Shen Z, Tan F, Hu Y, Yu J, Li G (2012) Clinicopathological significance of NMIIA overexpression in human gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci 13:15291–15304
Schramek D, Sendoel A, Segal JP, Beronja S, Heller E, Oristian D, Reva B, Fuchs E (2014) Direct in vivo RNAi screen unveils myosin IIA as a tumor suppressor of squamous cell carcinomas. Science 343:309–313
Conti MA, Saleh AD, Brinster LR, Cheng H, Chen Z, Cornelius S, Liu C, Ma X, Van Waes C, Adelstein RS (2015) Conditional deletion of nonmuscle myosin II-A in mouse tongue epithelium results in squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep 5:14068
Kas SM, de Ruiter JR, Schipper K, Annunziato S, Schut E, Klarenbeek S, Drenth AP, van der Burg E, Klijn C, Ten Hoeve JJ et al (2017) Insertional mutagenesis identifies drivers of a novel oncogenic pathway in invasive lobular breast carcinoma. Nat Genet 49:1219–1230
Wang B, Qi X, Liu J, Zhou R, Lin C, Shangguan J, Zhang Z, Zhao L, Li G (2019) MYH9 promotes growth and metastasis via activation of MAPK/AKT signaling in colorectal cancer. J Cancer 10:874–884
Yu X, Li Z, Shen J (2016) BRD7: a novel tumor suppressor gene in different cancers. Am J Transl Res 8:742–748
Lee CP, Ko AM, Chiang SL, Lu CY, Tsai EM, Ko YC (2018) Regulatory elements in vectors containing the ctEF-1α first intron and double enhancers for an efficient recombinant protein expression system. Sci Rep 8:15396
Chen Y, Guo Y, Chen H, Ma F (2020) Long non-coding RNA expression profiling identifies a four-long non-coding RNA Prognostic signature for isocitrate dehydrogenase mutant glioma. Front Neurol 11:573264
Tu HP, Min-Shan Ko A, Lee SS, Lee CP, Kuo TM, Huang CM, Ko YC (2018) Variants of ALPK1 with ABCG2, SLC2A9, and SLC22A12 increased the positive predictive value for gout. J Hum Genet 63:63–70
Yamada Y, Nishida T, Ichihara S, Kato K, Fujimaki T, Oguri M, Horibe H, Yoshida T, Watanabe S, Satoh K et al (2013) Identification of chromosome 3q28 and ALPK1 as susceptibility loci for chronic kidney disease in Japanese individuals by a genome-wide association study. J Med Genet 50:410–418
Yamada Y, Matsui K, Takeuchi I, Oguri M, Fujimaki T (2015) Association of genetic variants of the alpha-kinase 1 gene with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a longitudinal population-based genetic epidemiological study. Biomed Rep 3:347–354
Kuo TM, Huang CM, Tu HP, Min-Shan Ko A, Wang SJ, Lee CP, Ko YC (2017) URAT1 inhibition by ALPK1 is associated with uric acid homeostasis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56:654–659
Kuo TM, Hsu HT, Chung CM, Yeh KT, Wu CT, Lee CP, Chiang SL, Huang CM, Ko YC (2016) Enhanced alpha-kinase 1 accelerates multiple early nephropathies in streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:2034–2042
Tang D, Tao D, Fang Y, Deng C, Xu Q, Zhou J (2017) TNF-alpha promotes invasion and metastasis via NF-kappa B pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Med Sci Monit Basic Res 23:141–149
Chuang JY, Huang YL, Yen WL, Chiang IP, Tsai MH, Tang CH (2014) Syk/JNK/AP-1 signaling pathway mediates interleukin-6-promoted cell migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 15:545–559
Chuang JY, Yang WH, Chen HT, Huang CY, Tan TW, Lin YT, Hsu CJ, Fong YC, Tang CH (2009) CCL5/CCR5 axis promotes the motility of human oral cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 220:418–426
Ko AM, Lee CH, Ko YC (2020) Betel quid-associated cancer: prevention strategies and targeted treatment. Cancer Lett 477:60–69
Wang Y, Liu S, Zhang Y, Yang J (2019) Myosin heavy chain 9: oncogene or tumor suppressor gene? Med Sci Monit 25:888–892
Chan JYK, Zhen G, Agrawal N (2019) The role of tumor DNA as a diagnostic tool for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 55:1–7
Zhao R, Liu Y, Wang H, Yang J, Niu W, Fan S, Xiong W, Ma J, Li X, Phillips JB et al (2017) BRD7 plays an anti-inflammatory role during early acute inflammation by inhibiting activation of the NF-small ka, CyrillicB signaling pathway. Cell Mol Immunol 14:830–841
Zhou J, Tao D, Xu Q, Gao Z, Tang D (2015) Expression of E-cadherin and vimentin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:3150–3154
Nguyen PT, Kudo Y, Yoshida M, Kamata N, Ogawa I, Takata T (2011) N-cadherin expression is involved in malignant behavior of head and neck cancer in relation to epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Histol Histopathol 26:147–156
Chiang SL, Velmurugan BK, Chung CM, Lin SH, Wang ZH, Hua CH, Tsai MH, Kuo TM, Yeh KT, Chang PY et al (2017) Preventive effect of celecoxib use against cancer progression and occurrence of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep 7:6235
Gopal S, Veracini L, Grall D, Butori C, Schaub S, Audebert S, Camoin L, Baudelet E, Radwanska A, Beghelli-de la Forest Divonne S, et al. (2017) Fibronectin-guided migration of carcinoma collectives. Nat Commun 8:14105
Bhullar KS, Lagaron NO, McGowan EM, Parmar I, Jha A, Hubbard BP, Rupasinghe HPV (2018) Kinase-targeted cancer therapies: progress, challenges and future directions. Mol Cancer 17:48
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (grant number MOST 106-2314-B-039-017-MY3) and the China Medical University & Hospital (grant number DMR-108-042, DMR-109-156).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: YC Ko. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: CP Lee, AMS Ko, S Nithiyanantham, CH Lai, and YC Ko. Drafting the manuscript: CP Lee, AMS Ko, and YC Ko. All authors approved the final manuscript for submission and final approval of the version to be published. We thank Dr. Po-Ku Chen for his technical assistance.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 44 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CP., Ko, A.MS., Nithiyanantham, S. et al. Long noncoding RNA HAR1A regulates oral cancer progression through the alpha-kinase 1, bromodomain 7, and myosin IIA axis. J Mol Med 99, 1323–1334 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-021-02095-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-021-02095-x