Abstract
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been reported to be involved in many important biological processes including proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, and survival. Recently, nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1), a novel lncRNA, serves as a crucial regulator in tumors. However, the biological role of NEAT1 in liver fibrosis is largely unknown. In this study, the role of NEAT1 was explored in primary mouse hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced mouse liver fibrosis models. We found that NEAT1 expression was significantly increased in CCl4-induced mice and activated HSCs. Loss of NEAT1 suppressed liver fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Conversely, NEAT1 overexpression accelerated HSC activation, including increased cell proliferation and collagen expression. Further studies indicated that the microRNA-122 (miR-122)-Kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) axis was involved in the effects of NEAT1 on HSC activation. The effects of NEAT1 on HSC activation were almost blocked down by miR-122 mimics or KLF6 knockdown. Interestingly, both NEAT1 and KLF6 are targets of miR-122. In addition, miR-122 led to a significant reduction in NEAT1 level while NEAT1 overexpression resulted in the suppression of miR-122 expression. Pull-down assay confirmed a direct interaction between miR-122 and NEAT1. NEAT1 contributes to HSC activation via the miR-122-KLF6 axis. In human fibrotic liver samples, increased NEAT1 levels positively correlated with liver fibrosis markers. In conclusion, we disclose a novel NEAT1-miR-122-KLF6 signaling cascade and its implication in liver fibrosis.
Key messages
-
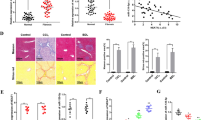
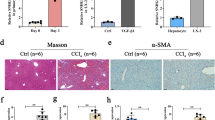
NEAT1 was significantly increased in CCl4-induced mice and activated HSCs.
-
Loss of NEAT1 suppressed liver fibrosis in vivo and in vitro.
-
KLF6 and miR-122 were required for the effects of NEAT1 on HSC activation.
-
NEAT1 contributes to HSC activation via competitively binding miR-122.
-
We disclose a novel NEAT1-miR-122-KLF6 signaling cascade.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schickel R, Boyerinas B, Park SM, Peter ME (2008) MicroRNAs: key players in the immune system, differentiation, tumorigenesis and cell death. Oncogene 27:5959–5974
Wang J, Chu ES, Chen HY, Man K, Go MY, Huang XR, Lan HY, Sung JJ, Yu J (2015) microRNA-29b prevents liver fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget 6:7325–7338
Tu X, Zhang H, Zhang J, Zhao S, Zheng X, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Chen J, Dong L, Zang Y (2014) MicroRNA-101 suppresses liver fibrosis by targeting the TGFbeta signalling pathway. J Pathol 234:46–59
Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ (2009) Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136:642–655
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, Vucur M, Zimmermann H, Schmidt S, Janssen J, Koppe C, Knolle P, Castoldi M et al (2011) Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 53:209–218
Zheng J, Wu C, Lin Z, Guo Y, Shi L, Dong P, Lu Z, Gao S, Liao Y, Chen B et al (2014) Curcumin up-regulates phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 through microRNA-mediated control of DNA methylation—a novel mechanism suppressing liver fibrosis. FEBS J 281:88–103
Fatica A, Bozzoni I (2014) Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet 15:7–21
Cao C, Sun J, Zhang D, Guo X, Xie L, Li X, Wu D, Liu L (2015) The long intergenic noncoding RNA UFC1, a target of MicroRNA 34a, interacts with the mRNA stabilizing protein HuR to increase levels of beta-catenin in HCC cells. Gastroenterology 148(415–426):e418
Wang F, Yuan JH, Wang SB, Yang F, Yuan SX, Ye C, Yang N, Zhou WP, Li WL, Li W et al (2014) Oncofetal long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and stem cell-like property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilizing NOP2. Hepatology 60:1278–1290
He Y, Wu YT, Huang C, Meng XM, Ma TT, Wu BM, Xu FY, Zhang L, Lv XW, Li J (2014) Inhibitory effects of long noncoding RNA MEG3 on hepatic stellate cells activation and liver fibrogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:2204–2215
Yu F, Zheng J, Mao Y, Dong P, Lu Z, Li G, Guo C, Liu Z, Fan X (2015) Long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5) inhibits liver fibrogenesis through a mechanism of competing endogenous RNA. J Biol Chem 290:28286–28298
Zheng J, Dong P, Mao Y, Chen S, Wu X, Li G, Lu Z, Yu F (2015) lincRNA-p21 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis via p21. FEBS J 282:4810–4821
Naganuma T, Hirose T (2013) Paraspeckle formation during the biogenesis of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol 10:456–461
Ma Y, Liu L, Yan F, Wei W, Deng J, Sun J (2016) Enhanced expression of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 is associated with the progression of gastric adenocarcinomas. World J Surg Oncol 14:41
Wang P, Wu T, Zhou H, Jin Q, He G, Yu H, Xuan L, Wang X, Tian L, Sun Y et al (2016) Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes laryngeal squamous cell cancer through regulating miR-107/CDK6 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:22
Choudhry H, Albukhari A, Morotti M, Haider S, Moralli D, Smythies J, Schodel J, Green CM, Camps C, Buffa F et al (2015) Tumor hypoxia induces nuclear paraspeckle formation through HIF-2alpha dependent transcriptional activation of NEAT1 leading to cancer cell survival. Oncogene 34:4482–4490
Guo S, Chen W, Luo Y, Ren F, Zhong T, Rong M, Dang Y, Feng Z, Chen G (2015) Clinical implication of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:5395–5402
Chang W, Yang M, Song L, Shen K, Wang H, Gao X, Li M, Niu W, Qin X (2014) Isolation and culture of hepatic stellate cells from mouse liver. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai 46:291–298
Bertolino P, Trescol-Biemont MC, Rabourdin-Combe C (1998) Hepatocytes induce functional activation of naive CD8+ T lymphocytes but fail to promote survival. Eur J Immunol 28:221–236
Gao Y, Wu F, Zhou J, Yan L, Jurczak MJ, Lee HY, Yang L, Mueller M, Zhou XB, Dandolo L et al (2014) The H19/let-7 double-negative feedback loop contributes to glucose metabolism in muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res 42:13799–13811
Yu F, Lu Z, Cai J, Huang K, Chen B, Li G, Dong P, Zheng J (2015) MALAT1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to mediate Rac1 expression by sequestering miR-101b in liver fibrosis. Cell Cycle 14:3885–3896
Lakner AM, Steuerwald NM, Walling TL, Ghosh S, Li T, McKillop IH, Russo MW, Bonkovsky HL, Schrum LW (2012) Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate cell-mediated fibrogenesis. Hepatology 56:300–310
Tu X, Zheng X, Li H, Cao Z, Chang H, Luan S, Zhu J, Chen J, Zang Y, Zhang J (2015) MicroRNA-30 protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by attenuating transforming growth factor Beta signaling in hepatic stellate cells. Toxicol Sci 146:157–169
Zeng C, Wang YL, Xie C, Sang Y, Li TJ, Zhang M, Wang R, Zhang Q, Zheng L, Zhuang SM (2015) Identification of a novel TGF-beta-miR-122-fibronectin 1/serum response factor signaling cascade and its implication in hepatic fibrogenesis. Oncotarget 6:12224–12233
He Y, Huang C, Sun X, Long XR, Lv XW, Li J (2012) MicroRNA-146a modulates TGF-beta1-induced hepatic stellate cell proliferation by targeting SMAD4. Cell Signal 24:1923–1930
Zheng J, Lin Z, Dong P, Lu Z, Gao S, Chen X, Wu C, Yu F (2013) Activation of hepatic stellate cells is suppressed by microRNA-150. Int J Mol Med 32:17–24
Lu CH, Hou QR, Deng LF, Fei C, Xu WP, Zhang Q, Wu KM, Ning BF, Xie WF, Zhang X (2015) MicroRNA-370 attenuates hepatic fibrogenesis by targeting smoothened. Dig Dis Sci 60:2038–2048
Hyun J, Wang S, Kim J, Rao KM, Park SY, Chung I, Ha CS, Kim SW, Yun YH, Jung Y (2016) MicroRNA-378 limits activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by suppressing Gli3 expression. Nat Commun 7:10993
Tsai WC, Hsu SD, Hsu CS, Lai TC, Chen SJ, Shen R, Huang Y, Chen HC, Lee CH, Tsai TF et al (2012) MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest 122:2884–2897
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2002) Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol 12:735–739
Xu H, He JH, Xiao ZD, Zhang QQ, Chen YQ, Zhou H, Qu LH (2010) Liver-enriched transcription factors regulate microRNA-122 that targets CUTL1 during liver development. Hepatology 52:1431–1442
Kim N, Kim H, Jung I, Kim Y, Kim D, Han YM (2011) Expression profiles of miRNAs in human embryonic stem cells during hepatocyte differentiation. Hepatol Res 41:170–183
Esau C, Davis S, Murray SF, Yu XX, Pandey SK, Pear M, Watts L, Booten SL, Graham M, McKay R et al (2006) miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab 3:87–98
Kim Y, Ratziu V, Choi SG, Lalazar A, Theiss G, Dang Q, Kim SJ, Friedman SL (1998) Transcriptional activation of transforming growth factor beta1 and its receptors by the Kruppel-like factor Zf9/core promoter-binding protein and Sp1. Potential mechanisms for autocrine fibrogenesis in response to injury. J Biol Chem 273:33750–33758
Ratziu V, Lalazar A, Wong L, Dang Q, Collins C, Shaulian E, Jensen S, Friedman SL (1998) Zf9, a Kruppel-like transcription factor up-regulated in vivo during early hepatic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:9500–9505
Friedman SL, Yamasaki G, Wong L (1994) Modulation of transforming growth factor beta receptors of rat lipocytes during the hepatic wound healing response. Enhanced binding and reduced gene expression accompany cellular activation in culture and in vivo. J Biol Chem 269:10551–10558
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115:209–218
George J, Roulot D, Koteliansky VE, Bissell DM (1999) In vivo inhibition of rat stellate cell activation by soluble transforming growth factor beta type II receptor: a potential new therapy for hepatic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:12719–12724
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y, Song Y (2013) Long non-coding RNAs: a new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett 339:159–166
Huang Y, Nayak S, Jankowitz R, Davidson NE, Oesterreich S (2011) Epigenetics in breast cancer: what’s new? Breast Cancer Res 13:225
Cooper C, Guo J, Yan Y, Chooniedass-Kothari S, Hube F, Hamedani MK, Murphy LC, Myal Y, Leygue E (2009) Increasing the relative expression of endogenous non-coding steroid receptor RNA activator (SRA) in human breast cancer cells using modified oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 37:4518–4531
Tripathi V, Ellis JD, Shen Z, Song DY, Pan Q, Watt AT, Freier SM, Bennett CF, Sharma A, Bubulya PA et al (2010) The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol Cell 39:925–938
Xing CY, Hu XQ, Xie FY, Yu ZJ, Li HY, Bin Z, Wu JB, Tang LY, Gao SM (2015) Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates c-KIT expression through sponging miR-193a in acute myeloid leukemia. FEBS Lett 589:1981–1987
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A, Bozzoni I (2011) A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 147:358–369
Sun C, Li S, Zhang F, Xi Y, Wang L, Bi Y, Li D (2016) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through regulation of miR-377-3p-E2F3 pathway. Oncotarget. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10108
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LY16H030012 and No. LY13H030006), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81500458/H0317), and Wenzhou Municipal Science and technology Bureau (No. Y20150091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All animals were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Wenzhou Medical University. The animal experimental protocol was approved by the University Animal Care and Use Committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 890 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, F., Jiang, Z., Chen, B. et al. NEAT1 accelerates the progression of liver fibrosis via regulation of microRNA-122 and Kruppel-like factor 6. J Mol Med 95, 1191–1202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1586-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1586-5