Abstract
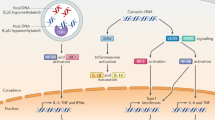
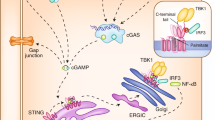
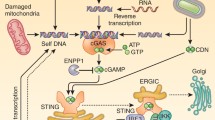
The sensing of foreign DNA is crucial for host defense against several pathogens. In the cytosol the enzyme cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) is critical for the recognition of pathogen-derived DNA and provides key signals that initiate immune responses. Beyond infection, accumulating evidence indicates that cGAS is also active during autoimmune diseases and controls immune responses that underlie cancer immunosurveillance. In this review, we highlight our current understanding of DNA sensing by cGAS and its involvement in human disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science 339:826–830
Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 339:786–791
Ishikawa H, Ma Z, Barber GN (2009) STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature 461:788–792
Burdette DL, Monroe KM, Sotelo-Troha K, Iwig JS, Eckert B, Hyodo M, Hayakawa Y, Vance RE (2011) STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic di-GMP. Nature 478:515–518
Ablasser A, Goldeck M, Cavlar T, Deimling T, Witte G, Rohl I, Hopfner KP, Ludwig J, Hornung V (2013) cGAS produces a 2′-5′-linked cyclic dinucleotide second messenger that activates STING. Nature 498:380–384
Diner EJ, Burdette DL, Wilson SC, Monroe KM, Kellenberger CA, Hyodo M, Hayakawa Y, Hammond MC, Vance RE (2013) The innate immune DNA sensor cGAS produces a noncanonical cyclic dinucleotide that activates human STING. Cell Rep 3:1355–1361
Gao P, Ascano M, Wu Y, Barchet W, Gaffney BL, Zillinger T, Serganov AA, Liu Y, Jones RA, Hartmann G et al (2013) Cyclic [G(2′,5′)pA(3′,5′)p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase. Cell 153:1094–1107
Zhang X, Shi H, Wu J, Zhang X, Sun L, Chen C, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING. Mol Cell 51:226–235
Civril F, Deimling T, de Oliveira Mann CC, Ablasser A, Moldt M, Witte G, Hornung V, Hopfner KP (2013) Structural mechanism of cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS. Nature 498:332–337
Kranzusch PJ, Lee AS, Berger JM, Doudna JA (2013) Structure of human cGAS reveals a conserved family of second-messenger enzymes in innate immunity. Cell Rep 3:1362–1368
Li X, Shu C, Yi G, Chaton CT, Shelton CL, Diao J, Zuo X, Kao CC, Herr AB, Li P (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is activated by double-stranded DNA-induced oligomerization. Immunity 39:1019–1031
Zhang X, Wu J, Du F, Xu H, Sun L, Chen Z, Brautigam CA, Zhang X, Chen ZJ (2014) The cytosolic DNA sensor cGAS forms an oligomeric complex with DNA and undergoes switch-like conformational changes in the activation loop. Cell Rep 6:421–430
Li XD, Wu J, Gao D, Wang H, Sun L, Chen ZJ (2013) Pivotal roles of cGAS-cGAMP signaling in antiviral defense and immune adjuvant effects. Science 341:1390–1394
Schoggins JW, MacDuff DA, Imanaka N, Gainey MD, Shrestha B, Eitson JL, Mar KB, Richardson RB, Ratushny AV, Litvak V et al (2014) Pan-viral specificity of IFN-induced genes reveals new roles for cGAS in innate immunity. Nature 505:691–695
Kranzusch PJ, Wilson SC, Lee AS, Berger JM, Doudna JA, Vance RE (2015) Ancient origin of cGAS-STING reveals mechanism of universal 2′,3′ cGAMP signaling. Mol Cell 59:891–903
Liang Q, Seo GJ, Choi YJ, Kwak MJ, Ge J, Rodgers MA, Shi M, Leslie BJ, Hopfner KP, Ha T et al (2014) Crosstalk between the cGAS DNA sensor and beclin-1 autophagy protein shapes innate antimicrobial immune responses. Cell Host Microbe 15:228–238
Barber GN (2015) STING: infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol 15:760–770
Liu S, Cai X, Wu J, Cong Q, Chen X, Li T, Du F, Ren J, Wu YT, Grishin NV et al (2015) Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science 347:aaa2630
Abe T, Barber GN (2014) Cytosolic-DNA-mediated, STING-dependent proinflammatory gene induction necessitates canonical NF-kappaB activation through TBK1. J Virol 88:5328–5341
Dobbs N, Burnaevskiy N, Chen D, Gonugunta VK, Alto NM, Yan N (2015) STING activation by translocation from the ER is associated with infection and autoinflammatory disease. Cell Host Microbe 18:157–168
Ablasser A, Schmid-Burgk JL, Hemmerling I, Horvath GL, Schmidt T, Latz E, Hornung V (2013) Cell intrinsic immunity spreads to bystander cells via the intercellular transfer of cGAMP. Nature 503:530–534
Bridgeman A, Maelfait J, Davenne T, Partridge T, Peng Y, Mayer A, Dong T, Kaever V, Borrow P, Rehwinkel J (2015) Viruses transfer the antiviral second messenger cGAMP between cells. Science 349:1228–1232
Gentili M, Kowal J, Tkach M, Satoh T, Lahaye X, Conrad C, Boyron M, Lombard B, Durand S, Kroemer G et al (2015) Transmission of innate immune signaling by packaging of cGAMP in viral particles. Science 349:1232–1236
Schoggins JW, Wilson SJ, Panis M, Murphy MY, Jones CT, Bieniasz P, Rice CM (2011) A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 472:481–485
Xia T, Konno H, Ahn J, Barber GN (2016) Deregulation of STING signaling in colorectal carcinoma constrains DNA damage responses and correlates with tumorigenesis. Cell Rep 14:282–297
Seo GJ, Yang A, Tan B, Kim S, Liang Q, Choi Y, Yuan W, Feng P, Park HS, Jung JU (2015) Akt kinase-mediated checkpoint of cGAS DNA sensing pathway. Cell Rep 13:440–449
Xia P, Ye B, Wang S, Zhu X, Du Y, Xiong Z, Tian Y, Fan Z (2016) Glutamylation of the DNA sensor cGAS regulates its binding and synthase activity in antiviral immunity. Nat Immunol. doi:10.1038/ni.3356
Collins AC, Cai H, Li T, Franco LH, Li XD, Nair VR, Scharn CR, Stamm CE, Levine B, Chen ZJ et al (2015) Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is an innate immune DNA sensor for mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell Host Microbe 17:820–828
Watson RO, Bell SL, MacDuff DA, Kimmey JM, Diner EJ, Olivas J, Vance RE, Stallings CL, Virgin HW, Cox JS (2015) The cytosolic sensor cGAS detects mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA to induce type I interferons and activate autophagy. Cell Host Microbe 17:811–819
Konno H, Konno K, Barber GN (2013) Cyclic dinucleotides trigger ULK1 (ATG1) phosphorylation of STING to prevent sustained innate immune signaling. Cell 155:688–698
Wu JJ, Li W, Shao Y, Avey D, Fu B, Gillen J, Hand T, Ma S, Liu X, Miley W et al (2015) Inhibition of cGAS DNA sensing by a herpesvirus virion protein. Cell Host Microbe 18:333–344
Ma Z, Jacobs SR, West JA, Stopford C, Zhang Z, Davis Z, Barber GN, Glaunsinger BA, Dittmer DP, Damania B (2015) Modulation of the cGAS-STING DNA sensing pathway by gammaherpesviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:E4306–4315
Lau L, Gray EE, Brunette RL, Stetson DB (2015) DNA tumor virus oncogenes antagonize the cGAS-STING DNA-sensing pathway. Science 350:568–571
Dansako H, Ueda Y, Okumura N, Satoh S, Sugiyama M, Mizokami M, Ikeda M, Kato N (2016) The cyclic GMP-AMP synthetase-STING signaling pathway is required for both the innate immune response against HBV and the suppression of HBV assembly. FEBS J 283:144–156
Dai P, Wang W, Cao H, Avogadri F, Dai L, Drexler I, Joyce JA, Li XD, Chen Z, Merghoub T et al (2014) Modified vaccinia virus Ankara triggers type I IFN production in murine conventional dendritic cells via a cGAS/STING-mediated cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway. PLoS Pathog 10:e1003989
Lam E, Stein S, Falck-Pedersen E (2014) Adenovirus detection by the cGAS/STING/TBK1 DNA sensing cascade. J Virol 88:974–981
Wang IH, Suomalainen M, Andriasyan V, Kilcher S, Mercer J, Neef A, Luedtke NW, Greber UF (2013) Tracking viral genomes in host cells at single-molecule resolution. Cell Host Microbe 14:468–480
Horan KA, Hansen K, Jakobsen MR, Holm CK, Soby S, Unterholzner L, Thompson M, West JA, Iversen MB, Rasmussen SB et al (2013) Proteasomal degradation of herpes simplex virus capsids in macrophages releases DNA to the cytosol for recognition by DNA sensors. J Immunol 190:2311–2319
Gao D, Wu J, Wu YT, Du F, Aroh C, Yan N, Sun L, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is an innate immune sensor of HIV and other retroviruses. Science 341:903–906
Rasaiyaah J, Tan CP, Fletcher AJ, Price AJ, Blondeau C, Hilditch L, Jacques DA, Selwood DL, James LC, Noursadeghi M et al (2013) HIV-1 evades innate immune recognition through specific cofactor recruitment. Nature 503:402–405
Lahaye X, Satoh T, Gentili M, Cerboni S, Conrad C, Hurbain I, El Marjou A, Lacabaratz C, Lelievre JD, Manel N (2013) The capsids of HIV-1 and HIV-2 determine immune detection of the viral cDNA by the innate sensor cGAS in dendritic cells. Immunity 39:1132–1142
Herzner AM, Hagmann CA, Goldeck M, Wolter S, Kubler K, Wittmann S, Gramberg T, Andreeva L, Hopfner KP, Mertens C et al (2015) Sequence-specific activation of the DNA sensor cGAS by Y-form DNA structures as found in primary HIV-1 cDNA. Nat Immunol 16:1025–1033
Wassermann R, Gulen MF, Sala C, Perin SG, Lou Y, Rybniker J, Schmid-Burgk JL, Schmidt T, Hornung V, Cole ST et al (2015) Mycobacterium tuberculosis differentially activates cGAS- and inflammasome-dependent intracellular immune responses through ESX-1. Cell Host Microbe 17:799–810
Man SM, Karki R, Malireddi RK, Neale G, Vogel P, Yamamoto M, Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD (2015) The transcription factor IRF1 and guanylate-binding proteins target activation of the AIM2 inflammasome by Francisella infection. Nat Immunol 16:467–475
Storek KM, Gertsvolf NA, Ohlson MB, Monack DM (2015) cGAS and Ifi204 cooperate to produce type I IFNs in response to Francisella infection. J Immunol 194:3236–3245
Zhang Y, Yeruva L, Marinov A, Prantner D, Wyrick PB, Lupashin V, Nagarajan UM (2014) The DNA sensor, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, is essential for induction of IFN-beta during Chlamydia trachomatis infection. J Immunol 193:2394–2404
West AP, Khoury-Hanold W, Staron M, Tal MC, Pineda CM, Lang SM, Bestwick M, Duguay BA, Raimundo N, MacDuff DA et al (2015) Mitochondrial DNA stress primes the antiviral innate immune response. Nature 520:553–557
White MJ, McArthur K, Metcalf D, Lane RM, Cambier JC, Herold MJ, van Delft MF, Bedoui S, Lessene G, Ritchie ME et al (2014) Apoptotic caspases suppress mtDNA-induced STING-mediated type I IFN production. Cell 159:1549–1562
Rongvaux A, Jackson R, Harman CC, Li T, West AP, de Zoete MR, Wu Y, Yordy B, Lakhani SA, Kuan CY et al (2014) Apoptotic caspases prevent the induction of type I interferons by mitochondrial DNA. Cell 159:1563–1577
Hartlova A, Erttmann SF, Raffi FA, Schmalz AM, Resch U, Anugula S, Lienenklaus S, Nilsson LM, Kroger A, Nilsson JA et al (2015) DNA damage primes the type I interferon system via the cytosolic DNA sensor STING to promote anti-microbial innate immunity. Immunity 42:332–343
Zeng M, Hu Z, Shi X, Li X, Zhan X, Li XD, Wang J, Choi JH, Wang KW, Purrington T et al (2014) MAVS, cGAS, and endogenous retroviruses in T-independent B cell responses. Science 346:1486–1492
Ablasser A, Hemmerling I, Schmid-Burgk JL, Behrendt R, Roers A, Hornung V (2014) TREX1 deficiency triggers cell-autonomous immunity in a cGAS-dependent manner. J Immunol 192:5993–5997
Gao D, Li T, Li XD, Chen X, Li QZ, Wight-Carter M, Chen ZJ (2015) Activation of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase by self-DNA causes autoimmune diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:E5699–5705
Gray EE, Treuting PM, Woodward JJ, Stetson DB (2015) Cutting edge: cGAS is required for lethal autoimmune disease in the Trex1-deficient mouse model of aicardi-goutieres syndrome. J Immunol 195:1939–1943
Crow YJ, Manel N (2015) Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome and the type I interferonopathies. Nat Rev Immunol 15:429–440
Pokatayev V, Hasin N, Chon H, Cerritelli SM, Sakhuja K, Ward JM, Morris HD, Yan N, Crouch RJ (2016) RNase H2 catalytic core Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome-related mutant invokes cGAS-STING innate immune-sensing pathway in mice. J Exp Med. doi:10.1084/jem.20151464
Mackenzie KJ, Carroll P, Lettice L, Tarnauskaite Z, Reddy K, Dix F, Revuelta A, Abbondati E, Rigby RE, Rabe B et al (2016) Ribonuclease H2 mutations induce a cGAS/STING-dependent innate immune response. EMBO J. doi:10.15252/embj.201593339
Yoshida H, Okabe Y, Kawane K, Fukuyama H, Nagata S (2005) Lethal anemia caused by interferon-beta produced in mouse embryos carrying undigested DNA. Nat Immunol 6:49–56
Lan YY, Londono D, Bouley R, Rooney MS, Hacohen N (2014) Dnase2a deficiency uncovers lysosomal clearance of damaged nuclear DNA via autophagy. Cell Rep 9:180–192
Kawane K, Ohtani M, Miwa K, Kizawa T, Kanbara Y, Yoshioka Y, Yoshikawa H, Nagata S (2006) Chronic polyarthritis caused by mammalian DNA that escapes from degradation in macrophages. Nature 443:998–1002
Lood C, Blanco LP, Purmalek MM, Carmona-Rivera C, De Ravin SS, Smith CK, Malech HL, Ledbetter JA, Elkon KB, Kaplan MJ (2016) Neutrophil extracellular traps enriched in oxidized mitochondrial DNA are interferogenic and contribute to lupus-like disease. Nat Med 22:146–153
Sharma S, Campbell AM, Chan J, Schattgen SA, Orlowski GM, Nayar R, Huyler AH, Nundel K, Mohan C, Berg LJ et al (2015) Suppression of systemic autoimmunity by the innate immune adaptor STING. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:E710–717
Lemos H, Huang L, Chandler PR, Mohamed E, Souza GR, Li L, Pacholczyk G, Barber GN, Hayakawa Y, Munn DH et al (2014) Activation of the STING adaptor attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalitis. J Immunol 192:5571–5578
Liu Y, Jesus AA, Marrero B, Yang D, Ramsey SE, Montealegre Sanchez GA, Tenbrock K, Wittkowski H, Jones OY, Kuehn HS et al (2014) Activated STING in a vascular and pulmonary syndrome. N Engl J Med 371:507–518
Jeremiah N, Neven B, Gentili M, Callebaut I, Maschalidi S, Stolzenberg MC, Goudin N, Fremond ML, Nitschke P, Molina TJ et al (2014) Inherited STING-activating mutation underlies a familial inflammatory syndrome with lupus-like manifestations. J Clin Invest 124:5516–5520
Deng L, Liang H, Xu M, Yang X, Burnette B, Arina A, Li XD, Mauceri H, Beckett M, Darga T et al (2014) STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensing promotes radiation-induced type I interferon-dependent antitumor immunity in immunogenic tumors. Immunity 41:843–852
Ahn J, Xia T, Konno H, Konno K, Ruiz P, Barber GN (2014) Inflammation-driven carcinogenesis is mediated through STING. Nat Commun 5:5166
Shen YJ, Le Bert N, Chitre AA, Koo CX, Nga XH, Ho SS, Khatoo M, Tan NY, Ishii KJ, Gasser S (2015) Genome-derived cytosolic DNA mediates type I interferon-dependent rejection of B cell lymphoma cells. Cell Rep 11:460–473
Ahn J, Konno H, Barber GN (2015) Diverse roles of STING-dependent signaling on the development of cancer. Oncogene 34:5302–5308
Zhu Q, Man SM, Gurung P, Liu Z, Vogel P, Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD (2014) Cutting edge: STING mediates protection against colorectal tumorigenesis by governing the magnitude of intestinal inflammation. J Immunol 193:4779–4782
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
A.A. receives funds from the Swiss National Science Foundation (BSSGI0-155984 and 31003A_159836) and the Gebert Rüf Stiftung (GRS-059_14).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ablasser, A., Gulen, M.F. The role of cGAS in innate immunity and beyond. J Mol Med 94, 1085–1093 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1423-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1423-2