Abstract
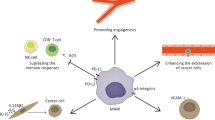
Cancer cells that succeed in forming lung metastases need to survive in a foreign microenvironment and to protect themselves against immune surveillance. Lung metastatic niches facilitate this process. They can develop as pre-metastatic niches by inflammatory events that are provoked by primary tumors before tumor cell arrival, and/or they can be post-formed by reciprocal signaling between metastasizing tumor cells and local non-tumor cells. Primary tumor-derived factors induce expression of chemokines in the lungs to which bone marrow-derived myeloid cells are recruited. These cells work in concert with lung-specific resident cells to establish pre-metastatic niches. The role of the endogenous TLR4-dependent innate immune system in pre-metastatic niche formation illustrates this point. During lung infection, endotoxin induces inflammation by increasing vascular permeability and leukocyte mobilization to the lungs through the endotoxin receptor TLR4 that is expressed in endothelial cells and leukocytes, respectively. This innate immune system can be hijacked by primary tumors to generate a pre-metastatic niche. Specifically, primary tumor-produced chemokine CCL2 works in an endocrine manner to induce pulmonary overexpression of endogenous TLR4 ligands such as S100A8 and SAA3 resulting in lung inflammation similar to that caused by endotoxin. An endotoxin analog Eritoran inhibits pre-metastatic niche formation in this system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schofield R (1978) The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells 4:7–25
Shiozawa Y, Pedersen EA, Havens AM, Jung Y, Mishra A, Joseph J, Kim JK, Patel LR, Ying C, Ziegler AM et al (2011) Human prostate cancer metastases target the hematopoietic stem cell niche to establish footholds in mouse bone marrow. J Clin Invest 121:1298–1312
Irwin RS, Augustyn N, French CT, Rice J, Tedeschi V, Welch SJ (2013) Spread the word about the journal in 2013: from citation manipulation to invalidation of patient-reported outcomes measures to renaming the Clara cell to new journal features. Chest 143:1–4
Kim CF, Jackson EL, Woolfenden AE, Lawrence S, Babar I, Vogel S, Crowley D, Bronson RT, Jacks T (2005) Identification of bronchioalveolar stem cells in normal lung and lung cancer. Cell 121:823–835
Nicolson G, Nakajima M, Irimura T (1986) Invasion of vascular endothelium and organ tissue in vitro by B16 melanoma variants. In: Honn K, Powers W, Sloane B (eds) Mechanisms of cancer metastasis. Springer, USA, pp 275–297
Bocklage T, Leslie K, Yousem S, Colby T (2001) Extracutaneous angiosarcomas metastatic to the lungs: clinical and pathologic features of twenty-one cases. Mod Pathol 14:1216–1225
Kaplan RN, Rafii S, Lyden D (2006) Preparing the "soil": the premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 66:11089–11093
Tomita T, Sakurai Y, Ishibashi S, Maru Y (2011) Imbalance of Clara cell-mediated homeostatic inflammation is involved in lung metastasis. Oncogene 30:3429–3439
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Aburatani H, Maru Y (2006) Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 8:1369–1375
Tomita T, Ieguchi K, Deguchi A, Takita M, Tsukaha F, Hiratsuka S, Maru Y (2015) Tumor cell lung recruitment assay. J Vis Exp (in press)
Vadrevu SK, Chintala NK, Sharma SK, Sharma P, Cleveland C, Riediger L, Manne S, Fairlie DP, Gorczyca W, Almanza O et al (2014) Complement c5a receptor facilitates cancer metastasis by altering T-cell responses in the metastatic niche. Cancer Res 74:3454–3465
Sharma SK, Chintala NK, Vadrevu SK, Patel J, Karbowniczek M, Markiewski MM (2015) Pulmonary alveolar macrophages contribute to the premetastatic niche by suppressing antitumor T cell responses in the lungs. J Immunol 194:5529–5538
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Deguchi A, Tomita T, Omori T, Komatsu A, Ohto U, Takahashi S, Tanimura N, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K, Maru Y (2013) Serum amyloid A3 binds MD-2 to activate p38 and NF-κB pathways in a MyD88-dependent manner. J Immunol 191:1856–1864
Maus UA, Wellmann S, Hampl C, Kuziel WA, Srivastava M, Mack M, Everhart MB, Blackwell TS, Christman JW, Schlondorff D et al (2005) CCR2-positive monocytes recruited to inflamed lungs downregulate local CCL2 chemokine levels. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L350–L358
Bessede A, Gargaro M, Pallotta MT, Matino D, Servillo G, Brunacci C, Bicciato S, Mazza EM, Macchiarulo A, Vacca C et al (2014) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor control of a disease tolerance defence pathway. Nature 511:184–190
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Sakurai Y, Akashi-Takamura S, Ishibashi S, Miyake K, Shibuya M, Akira S, Aburatani H, Maru Y (2008) The S100A8-serum amyloid A3-TLR4 paracrine cascade establishes a pre-metastatic phase. Nat Cell Biol 10:1349–1355
He Q, Zhang C, Wang L, Zhang P, Ma D, Lv J, Liu F (2015) Inflammatory signaling regulates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell emergence in vertebrates. Blood 125:1098–1106
Shi C, Jia T, Mendez-Ferrer S, Hohl Tobias M, Serbina Natalya V, Lipuma L, Leiner I, Li Ming O, Frenette Paul S, Pamer Eric G (2011) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem and progenitor cells induce monocyte emigration in response to circulating toll-like receptor ligands. Immunity 34:590–601
Bugl S, Wirths S, Radsak MP, Schild H, Stein P, Andre MC, Muller MR, Malenke E, Wiesner T, Marklin M et al (2013) Steady-state neutrophil homeostasis is dependent on TLR4/TRIF signaling. Blood 121:723–733
Deguchi A, Tomita T, Ohto U, Takemura K, Kitao A, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K, Maru Y (2015) Eritoran inhibits S100A8-mediated TLR4/MD-2 activation and tumor growth by changing the immune microenvironment. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.211
Kim HM, Park BS, Kim JI, Kim SE, Lee J, Oh SC, Enkhbayar P, Matsushima N, Lee H, Yoo OJ et al (2007) Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist Eritoran. Cell 130:906–917
Hiratsuka S, Ishibashi S, Tomita T, Watanabe A, Akashi-Takamura S, Murakami M, Kijima H, Miyake K, Aburatani H, Maru Y (2013) Primary tumours modulate innate immune signalling to create pre-metastatic vascular hyperpermeability foci. Nat Commun 4:1853
Kaplan RN, Riba RD, Zacharoulis S, Bramley AH, Vincent L, Costa C, MacDonald DD, Jin DK, Shido K, Kerns SA et al (2005) VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature 438:820–827
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Cox TR, Lang G, Bird D, Koong A, Le QT, Giaccia AJ (2009) Hypoxia-induced lysyl oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell 15:35–44
Chen Q, Zhang XH, Massague J (2011) Macrophage binding to receptor VCAM-1 transmits survival signals in breast cancer cells that invade the lungs. Cancer Cell 20:538–549
Gao D, Joshi N, Choi H, Ryu S, Hahn M, Catena R, Sadik H, Argani P, Wagner P, Vahdat LT et al (2012) Myeloid progenitor cells in the premetastatic lung promote metastases by inducing mesenchymal to epithelial transition. Cancer Res 72:1384–1394
Hiratsuka S, Nakamura K, Iwai S, Murakami M, Itoh T, Kijima H, Shipley JM, Senior RM, Shibuya M (2002) MMP9 induction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 is involved in lung-specific metastasis. Cancer Cell 2:289–300
Yan HH, Pickup M, Pang Y, Gorska AE, Li Z, Chytil A, Geng Y, Gray JW, Moses HL, Yang L (2010) Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells tip the balance of immune protection to tumor promotion in the premetastatic lung. Cancer Res 70:6139–6149
Hsu MY, Rovinsky SA, Lai CY, Qasem S, Liu X, How J, Engelhardt JF, Murphy GF (2008) Aggressive melanoma cells escape from BMP7-mediated autocrine growth inhibition through coordinated Noggin upregulation. Lab Investig 88:842–855
Gao H, Chakraborty G, Lee-Lim AP, Mo Q, Decker M, Vonica A, Shen R, Brogi E, Brivanlou AH, Giancotti FG (2012) The BMP inhibitor Coco reactivates breast cancer cells at lung metastatic sites. Cell 150:764–779
Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, Zhang XH, Vanharanta S, Tavazoie SF, Morris PG, Downey RJ, Manova-Todorova K, Brogi E, Massague J (2011) Breast cancer cells produce tenascin C as a metastatic niche component to colonize the lungs. Nat Med 17:867–874
Saupe F, Schwenzer A, Jia Y, Gasser I, Spenle C, Langlois B, Kammerer M, Lefebvre O, Hlushchuk R, Rupp T et al (2013) Tenascin-C downregulates wnt inhibitor dickkopf-1, promoting tumorigenesis in a neuroendocrine tumor model. Cell Rep 5:482–492
Warren RS, Yuan H, Matli MR, Gillett NA, Ferrara N (1995) Regulation by vascular endothelial growth factor of human colon cancer tumorigenesis in a mouse model of experimental liver metastasis. J Clin Invest 95:1789–1797
Bais C, Wu X, Yao J, Yang S, Crawford Y, McCutcheon K, Tan C, Kolumam G, Vernes JM, Eastham-Anderson J et al (2010) PlGF blockade does not inhibit angiogenesis during primary tumor growth. Cell 141:166–177
Garmy-Susini B, Avraamides CJ, Desgrosellier JS, Schmid MC, Foubert P, Ellies LG, Lowy AM, Blair SL, Vandenberg SR, Datnow B et al (2013) PI3Kα activates integrin α4β1 to establish a metastatic niche in lymph nodes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:9042–9047
Magnon C, Hall SJ, Lin J, Xue X, Gerber L, Freedland SJ, Frenette PS (2013) Autonomic nerve development contributes to prostate cancer progression. Science 341:1236361
Ferjancic S, Gil-Bernabe AM, Hill SA, Allen PD, Richardson P, Sparey T, Savory E, McGuffog J, Muschel RJ (2013) VCAM-1 and VAP-1 recruit myeloid cells that promote pulmonary metastasis in mice. Blood 121:3289–3297
Palumbo JS, Kombrinck KW, Drew AF, Grimes TS, Kiser JH, Degen JL, Bugge TH (2000) Fibrinogen is an important determinant of the metastatic potential of circulating tumor cells. Blood 96:3302–3309
Palumbo JS, Potter JM, Kaplan LS, Talmage K, Jackson DG, Degen JL (2002) Spontaneous hematogenous and lymphatic metastasis, but not primary tumor growth or angiogenesis, is diminished in fibrinogen-deficient mice. Cancer Res 62:6966–6972
Kim S, Takahashi H, Lin WW, Descargues P, Grivennikov S, Kim Y, Luo JL, Karin M (2009) Carcinoma-produced factors activate myeloid cells through TLR2 to stimulate metastasis. Nature 457:102–106
Liu J, Liao S, Diop-Frimpong B, Chen W, Goel S, Naxerova K, Ancukiewicz M, Boucher Y, Jain RK, Xu L (2012) TGF-β blockade improves the distribution and efficacy of therapeutics in breast carcinoma by normalizing the tumor stroma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:16618–16623
Bandyopadhyay A, Agyin JK, Wang L, Tang Y, Lei X, Story BM, Cornell JE, Pollock BH, Mundy GR, Sun LZ (2006) Inhibition of pulmonary and skeletal metastasis by a transforming growth factor-β type I receptor kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res 66:6714–6721
Kowanetz M, Wu X, Lee J, Tan M, Hagenbeek T, Qu X, Yu L, Ross J, Korsisaari N, Cao T et al (2010) Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor promotes lung metastasis through mobilization of Ly6G+Ly6C+ granulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:21248–21255
Contador-Troca M, Alvarez-Barrientos A, Barrasa E, Rico-Leo EM, Catalina-Fernandez I, Menacho-Marquez M, Bustelo XR, Garcia-Borron JC, Gomez-Duran A, Saenz-Santamaria J et al (2013) The dioxin receptor has tumor suppressor activity in melanoma growth and metastasis. Carcinogenesis 34:2683–2693
Malanchi I, Santamaria-Martinez A, Susanto E, Peng H, Lehr HA, Delaloye JF, Huelsken J (2012) Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization. Nature 481:85–89
Laubli H, Spanaus KS, Borsig L (2009) Selectin-mediated activation of endothelial cells induces expression of CCL5 and promotes metastasis through recruitment of monocytes. Blood 114:4583–4591
D'Alterio C, Barbieri A, Portella L, Palma G, Polimeno M, Riccio A, Ierano C, Franco R, Scognamiglio G, Bryce J et al (2012) Inhibition of stromal CXCR4 impairs development of lung metastases. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61:1713–1720
Paolino M, Choidas A, Wallner S, Pranjic B, Uribesalgo I, Loeser S, Jamieson AM, Langdon WY, Ikeda F, Fededa JP et al (2014) The E3 ligase Cbl-b and TAM receptors regulate cancer metastasis via natural killer cells. Nature 507:508–512
Bandapalli OR, Ehrmann F, Ehemann V, Gaida M, Macher-Goeppinger S, Wente M, Schirmacher P, Brand K (2012) Down-regulation of CXCL1 inhibits tumor growth in colorectal liver metastasis. Cytokine 57:46–53
Acharyya S, Oskarsson T, Vanharanta S, Malladi S, Kim J, Morris PG, Manova-Todorova K, Leversha M, Hogg N, Seshan VE et al (2012) A CXCL1 paracrine network links cancer chemoresistance and metastasis. Cell 150:165–178
Podsypanina K, Du YC, Jechlinger M, Beverly LJ, Hambardzumyan D, Varmus H (2008) Seeding and propagation of untransformed mouse mammary cells in the lung. Science 321:1841–1844
Maru Y (2007) Which came first, tumor cells or macrophages? Cell Adhes Migr 1:107–109
Ellwood-Yen K, Graeber TG, Wongvipat J, Iruela-Arispe ML, Zhang J, Matusik R, Thomas GV, Sawyers CL (2003) Myc-driven murine prostate cancer shares molecular features with human prostate tumors. Cancer Cell 4:223–238
Simon RH, Lovett EJ 3rd, Tomaszek D, Lundy J (1980) Electrical stimulation of the midbrain mediates metastatic tumor growth. Science 209:1132–1133
Volpert OV, Lawler J, Bouck NP (1998) A human fibrosarcoma inhibits systemic angiogenesis and the growth of experimental metastases via thrombospondin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:6343–6348
Paez-Ribes M, Allen E, Hudock J, Takeda T, Okuyama H, Vinals F, Inoue M, Bergers G, Hanahan D, Casanovas O (2009) Antiangiogenic therapy elicits malignant progression of tumors to increased local invasion and distant metastasis. Cancer Cell 15:220–231
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Cruz-Munoz W, Bjarnason GA, Christensen JG, Kerbel RS (2009) Accelerated metastasis after short-term treatment with a potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 15:232–239
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), Japan (21117008) to YM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no competing interests.