Abstract
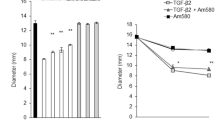
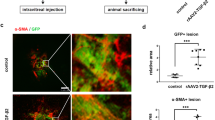
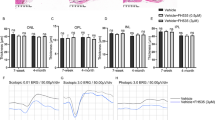
Subretinal fibrosis contributes to the loss of vision associated with age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells play a key role in the pathogenesis of AMD including the fibrotic reaction. We examined the role of retinoic acid receptor-γ (RAR-γ) in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and other fibrosis-related processes in mouse RPE cells cultured in a type I collagen gel. Transforming growth factor-β2 (TGF-β2)–induced collagen gel contraction mediated by the RPE cells was inhibited by the RAR-γ agonist R667 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Expression of the mesenchymal markers α-smooth muscle actin and fibronectin, the release of interleukin-6, and the phosphorylation of paxillin, mitogen-activated protein kinases (ERK, p38, and JNK), Smad2, and AKT induced by TGF-β2 were also suppressed by the RAR-γ agonist. Furthermore, gelatin zymography and immunoblot analysis revealed that the TGF-β2-induced release of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-3, MMP-8, and MMP-9 from RPE cells was inhibited by R667, and the MMP inhibitor GM6001 attenuated TGF-β2-induced RPE cell contraction. Finally, immunohistofluorescence analysis with antibodies to glial fibrillary acidic protein showed that R667 inhibited the development of subretinal fibrosis in a mouse model in vivo. Our results thus suggest that RAR-γ agonists may prove effective for the treatment of subretinal fibrosis associated with AMD.
Key message
-
RAR-γ agonist R667 suppressed collagen gel contraction mediated by RPE cells.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in RPE cells was inhibited by RAR-γ agonist R667.
-
RAR-γ agonist R667 inhibited fibrosis-related processes in RPE cells.
-
RAR-γ agonists may attenuate AMD-associated fibrosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Lookeren Campagne M, LeCouter J, Yaspan BL, Ye W (2014) Mechanisms of age-related macular degeneration and therapeutic opportunities. J Pathol 232:151–164
Hong YJ, Miura M, Ju MJ, Makita S, Iwasaki T, Yasuno Y (2014) Simultaneous investigation of vascular and retinal pigment epithelial pathologies of exudative macular diseases by multi-functional optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. doi:10.1167/iovs.14-14005
Miller JW (2010) Treatment of age-related macular degeneration: beyond VEGF. Jpn J Ophthalmol 54:523–528
Lim WK, Chee SP, Sng I, Nussenblatt RB, Chan CC (2004) Immunopathology of progressive subretinal fibrosis: a variant of sympathetic ophthalmia. Am J Ophthalmol 138:475–477
Saika S, Kono-Saika S, Tanaka T, Yamanaka O, Ohnishi Y, Sato M, Muragaki Y, Ooshima A, Yoo J, Flanders KC et al (2004) Smad3 is required for dedifferentiation of retinal pigment epithelium following retinal detachment in mice. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol 84:1245–1258
Kalluri R, Neilson EG (2003) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Invest 112:1776–1784
Lee H, O’Meara SJ, O’Brien C, Kane R (2007) The role of gremlin, a BMP antagonist, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:4291–4299
Simoni D, Tolomeo M (2001) Retinoids, apoptosis and cancer. Curr Pharm Des 7:1823–1837
Conde I, Paniagua R, Fraile B, Ruiz A, Arenas MI (2004) Expression of vitamin D3 receptor and retinoid receptors in human breast cancer: identification of potential heterodimeric receptors. Int J Oncol 25:1183–1191
Soderpalm AK, Fox DA, Karlsson JO, van Veen T (2000) Retinoic acid produces rod photoreceptor selective apoptosis in developing mammalian retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:937–947
Clagett-Dame M, McNeill EM, Muley PD (2006) Role of all-trans retinoic acid in neurite outgrowth and axonal elongation. J Neurobiol 66:739–756
Liu Y, Kimura K, Orita T, Teranishi S, Suzuki K, Sonoda KH (2014) Inhibition by all-trans-retinoic acid of transforming growth factor-beta-induced collagen gel contraction mediated by human tenon fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55:4199–4205
Jo YJ, Sonoda KH, Oshima Y, Takeda A, Kohno R, Yamada J, Hamuro J, Yang Y, Notomi S, Hisatomi T et al (2011) Establishment of a new animal model of focal subretinal fibrosis that resembles disciform lesion in advanced age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:6089–6095
Kimura K, Orita T, Fujitsu Y, Liu Y, Wakuta M, Morishige N, Suzuki K, Sonoda KH (2014) Inhibition by female sex hormones of collagen gel contraction mediated by retinal pigment epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55:2621–2630
Ngo P, Ramalingam P, Phillips JA, Furuta GT (2006) Collagen gel contraction assay. Methods Mol Biol 341:103–109
Ramachandran C, Patil RV, Combrink K, Sharif NA, Srinivas SP (2011) Rho-Rho kinase pathway in the actomyosin contraction and cell-matrix adhesion in immortalized human trabecular meshwork cells. Mol Vis 17:1877–1890
Lan HY, Chung AC (2011) Transforming growth factor-beta and Smads. Contrib Nephrol 170:75–82
Zhang H, Liu ZL (2012) Transforming growth factor-beta neutralizing antibodies inhibit subretinal fibrosis in a mouse model. Int J Ophthalmol 5:307–311
Hinz B, Celetta G, Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Chaponnier C (2001) Alpha-smooth muscle actin expression upregulates fibroblast contractile activity. Mol Biol Cell 12:2730–2741
Liu Y, Yanai R, Lu Y, Kimura K, Nishida T (2006) Promotion by fibronectin of collagen gel contraction mediated by human corneal fibroblasts. Exp Eye Res 83:1196–1204
Kischer CW, Shetlar MR, Chvapil M (1982) Hypertrophic scars and keloids: a review and new concept concerning their origin. Scan Electron Microsc :1699–1713
Hammer M, Konigsdorffer E, Liebermann C, Framme C, Schuch G, Schweitzer D, Strobel J (2008) Ocular fundus auto-fluorescence observations at different wavelengths in patients with age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246:105–114
Stodtler M, Mietz H, Wiedemann P, Heimann K (1994) Immunohistochemistry of anterior proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Report of 11 cases. Int Ophthalmol 18:323–328
Eckes B, Nischt R, Krieg T (2010) Cell-matrix interactions in dermal repair and scarring. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 3:4
Suzuki R, Miyazaki Y, Takagi K, Torii K, Taniguchi H (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of asthma and COPD: implications for therapy. Treat Respir Med 3:17–27
Giambernardi TA, Sakaguchi AY, Gluhak J, Pavlin D, Troyer DA, Das G, Rodeck U, Klebe RJ (2001) Neutrophil collagenase (MMP-8) is expressed during early development in neural crest cells as well as in adult melanoma cells. Matrix Biol J Int Soc Matrix Biol 20:577–587
Kijlstra A, La Heij E, Hendrikse F (2005) Immunological factors in the pathogenesis and treatment of age-related macular degeneration. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 13:3–11
Kaiser PK, Gragoudas ES (1996) The subretinal fibrosis and uveitis syndrome. Int Ophthalmol Clin 36:145–152
Baudouin C, Fredj-Reygrobellet D, Brignole F, Negre F, Lapalus P, Gastaud P (1993) Growth factors in vitreous and subretinal fluid cells from patients with proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Ophthalmic Res 25:52–59
Benson MT, Shepherd L, Rees RC, Rennie IG (1992) Production of interleukin-6 by human retinal pigment epithelium in vitro and its regulation by other cytokines. Curr Eye Res 11(Suppl):173–179
King RE, Kent KD, Bomser JA (2005) Resveratrol reduces oxidation and proliferation of human retinal pigment epithelial cells via extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibition. Chem Biol Interact 151:143–149
Yao HW, Xie QM, Chen JQ, Deng YM, Tang HF (2004) TGF-beta1 induces alveolar epithelial to mesenchymal transition in vitro. Life Sci 76:29–37
Liu Y, Ko JA, Yanai R, Kimura K, Chikama T, Sagara T, Nishida T (2008) Induction by latanoprost of collagen gel contraction mediated by human tenon fibroblasts: role of intracellular signaling molecules. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:1429–1436
Lotan R (1997) Roles of retinoids and their nuclear receptors in the development and prevention of upper aerodigestive tract cancers. Environ Health Perspect 105(Suppl 4):985–988
Schambach F, Schupp M, Lazar MA, Reiner SL (2007) Activation of retinoic acid receptor-alpha favours regulatory T cell induction at the expense of IL-17-secreting T helper cell differentiation. Eur J Immunol 37:2396–2399
Chen F, Desai TJ, Qian J, Niederreither K, Lu J, Cardoso WV (2007) Inhibition of Tgf beta signaling by endogenous retinoic acid is essential for primary lung bud induction. Development 134:2969–2979
Morales SA, Mareninov S, Prasad P, Wadehra M, Braun J, Gordon LK (2007) Collagen gel contraction by ARPE-19 cells is mediated by a FAK-Src dependent pathway. Exp Eye Res 85:790–798
Huang Z, Yan DP, Ge BX (2008) JNK regulates cell migration through promotion of tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin. Cell Signal 20:2002–2012
Kamato D, Burch ML, Piva TJ, Rezaei HB, Rostam MA, Xu S, Zheng W, Little PJ, Osman N (2013) Transforming growth factor-beta signalling: role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation. Cell Signal 25:2017–2024
Thomas PE, Peters-Golden M, White ES, Thannickal VJ, Moore BB (2007) PGE(2) inhibition of TGF-beta1-induced myofibroblast differentiation is Smad-independent but involves cell shape and adhesion-dependent signaling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 293:L417–L428
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Takeda Science Foundation. We thank Yukari Mizuno and Shizuka Murata for technical assistance.
Disclosure statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, K., Orita, T., Liu, Y. et al. Attenuation of EMT in RPE cells and subretinal fibrosis by an RAR-γ agonist. J Mol Med 93, 749–758 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1289-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-015-1289-8