Abstract
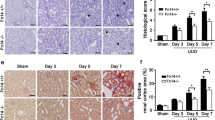
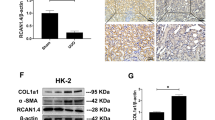
The pathophysiology of chronic renal disease is characterized by a progressive loss of renal function and deposition of the extracellular matrix, leading to widespread tissue fibrosis. Much of the matrix in chronic renal disease is synthesized by interstitial myofibroblasts, recruited from resident fibroblasts and circulating precursors. These changes are believed to be derived from epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) of tubuloepithelial cells. To develop a novel therapeutic approach for treating renal fibrosis, we examined the simultaneous inhibition of the transcription factors NF-κB and Sp1 in a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). To simultaneously inhibit both NF-κB and Sp1, we developed chimeric (Chi) decoy oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) which contained binding sequences for both NF-κB and Sp1 in a single decoy molecule to enhance the effective use of decoy ODN strategy. Chi decoy ODN significantly attenuated tubulointerstitial fibrosis in a mouse model of UUO compared to scrambled decoy ODN, as demonstrated by the reduced interstitial volume, macrophage infiltration, and fibrosis-related gene expression. Interestingly, Chi decoy ODN also regulated EMT-related gene expression, leading to the inhibition of renal fibrotic changes in vivo and in vitro. The present study demonstrates the feasibility of Chi decoy ODN treatment for preventing renal fibrosis and EMT processes. This strategy might be useful to improve the clinical outcome after chronic renal disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li MX, Liu BC (2007) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in the progression of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Chin Med J (Engl) 120:1925–1930
Roberts IS, Burrows C, Shanks JH, Venning M, McWilliam LJ (1997) Interstitial myofibroblasts: predictors of progression in membranous nephropathy. J Clin Pathol 50:123–127
Essawy M, Soylemezoglu O, Muchaneta-Kubara EC, Shortland J, Brown CB, el Nahas AM (1997) Myofibroblasts and the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:43–50
Tang WW, Ulich TR, Lacey DL, Hill DC, Qi M, Kaufman SA, Van GY, Tarpley JE, Yee JS (1996) Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces renal tubulointerstitial myofibroblast formation and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Am J Pathol 148:1169–1180
Iwano M, Plieth D, Danoff TM, Xue C, Okada H, Neilson EG (2002) Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium during tissue fibrosis. J Clin Invest 110:341–350
Yang J, Liu Y (2001) Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition and its implications in renal interstitial fibrosis. Am J Pathol 159:1465–1475
Kalluri R, Neilson EG (2003) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Invest 112:1776–1784
Fan JM, Ng YY, Hill PA, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Mu W, Atkins RC, Lan HY (1999) Transforming growth factor-beta regulates tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in vitro. Kidney Int 56:1455–1467
Bascands JL, Schanstra JP (2005) Obstructive nephropathy: insights from genetically engineered animals. Kidney Int 68:925–937
Docherty NG, O’Sullivan OE, Healy DA, Fitzpatrick JM, Watson RW (2006) Evidence that inhibition of tubular cell apoptosis protects against renal damage and development of fibrosis following ureteric obstruction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F4–F13
Wang X, Zhou Y, Tan R, Xiong M, He W, Fang L, Wen P, Jiang L, Yang J (2010) Mice lacking the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene reduce renal interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299:F973–F982
Li Y, Yang J, Dai C, Wu C, Liu Y (2003) Role for integrin-linked kinase in mediating tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrogenesis. J Clin Invest 112:503–516
Zeisberg M, Strutz F, Muller GA (2001) Renal fibrosis: an update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 10:315–320
Guijarro C, Egido J (2001) Transcription factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) and renal disease. Kidney Int 59:415–424
Kassimatis TI, Nomikos A, Giannopoulou I, Lymperopoulos A, Moutzouris DA, Varakis I, Nakopoulou L (2010) Transcription factor Sp1 expression is upregulated in human glomerulonephritis: correlation with pSmad2/3 and p300 expression and renal injury. Ren Fail 32:243–253
Klahr S, Morrissey J (2002) Obstructive nephropathy and renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F861–F875
Chevalier RL (2006) Obstructive nephropathy: towards biomarker discovery and gene therapy. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2:157–168
Noronha IL, Kruger C, Andrassy K, Ritz E, Waldherr R (1993) In situ production of TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta and IL-2R in ANCA-positive glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 43:682–692
Gerondakis S, Grossmann M, Nakamura Y, Pohl T, Grumont R (1999) Genetic approaches in mice to understand Rel/NF-kappaB and IkappaB function: transgenics and knockouts. Oncogene 18:6888–6895
Tomita N, Kashihara N, Morishita R (2007) Transcription factor decoy oligonucleotide-based therapeutic strategy for renal disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 11:7–17
Kim KH, Lee ES, Cha SH, Park JH, Park JS, Chang YC, Park KK (2009) Transcriptional regulation of NF-kappaB by ring type decoy oligodeoxynucleotide in an animal model of nephropathy. Exp Mol Pathol 86:114–120
Park JH, Jo JH, Kim KH, Kim SJ, Lee WR, Park KK, Park JB (2009) Antifibrotic effect through the regulation of transcription factor using ring type-Sp1 decoy oligodeoxynucleotide in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. J Gene Med 11:824–833
Ahn JD, Kim CH, Magae J, Kim YH, Kim HJ, Park KK, Hong S, Park KG, Lee IK, Chang YC (2003) E2F decoy oligodeoxynucleotides effectively inhibit growth of human tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310:1048–1053
Cao CC, Ding XQ, Ou ZL, Liu CF, Li P, Wang L, Zhu CF (2004) In vivo transfection of NF-kappaB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides attenuate renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Kidney Int 65:834–845
Miwa K, Nakashima H, Aoki M, Miyake T, Kawasaki T, Iwai M, Oishi M, Kataoka K, Ohgi S, Ogihara T et al (2005) Inhibition of ets, an essential transcription factor for angiogenesis, to prevent the development of abdominal aortic aneurysm in a rat model. Gene Ther 12:1109–1118
Miyake T, Aoki M, Masaki H, Kawasaki T, Oishi M, Kataoka K, Ogihara T, Kaneda Y, Morishita R (2007) Regression of abdominal aortic aneurysms by simultaneous inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB and ets in a rabbit model. Circ Res 101:1175–1184
Goodarzi H, Najafabadi HS, Oikonomou P, Greco TM, Fish L, Salavati R, Cristea IM, Tavazoie S (2012) Systematic discovery of structural elements governing stability of mammalian messenger RNAs. Nature 485:264–268
Baeuerle PA, Henkel T (1994) Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 12:141–179
Jimenez SA, Varga J, Olsen A, Li L, Diaz A, Herhal J, Koch J (1994) Functional analysis of human alpha 1(I) procollagen gene promoter. Differential activity in collagen-producing and -nonproducing cells and response to transforming growth factor beta 1. J Biol Chem 269:12684–12691
Greenwel P, Inagaki Y, Hu W, Walsh M, Ramirez F (1997) Sp1 is required for the early response of alpha2(I) collagen to transforming growth factor-beta1. J Biol Chem 272:19738–19745
Inagaki Y, Truter S, Ramirez F (1994) Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates alpha 2(I) collagen gene expression through a cis-acting element that contains an Sp1-binding site. J Biol Chem 269:14828–14834
Infantino V, Convertini P, Iacobazzi F, Pisano I, Scarcia P, Iacobazzi V (2011) Identification of a novel Sp1 splice variant as a strong transcriptional activator. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 412:86–91
Chae YM, Park KK, Lee IK, Kim JK, Kim CH, Chang YC (2006) Ring-Sp1 decoy oligonucleotide effectively suppresses extracellular matrix gene expression and fibrosis of rat kidney induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. Gene Ther 13:430–439
Nathan CF (1987) Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest 79:319–326
Gu L, Ni Z, Qian J, Tomino Y (2007) Pravastatin inhibits carboxymethyllysine-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 expression in podocytes via prevention of signalling events. Nephron Exp Nephrol 106:e1–e10
Goumenos DS, Brown CB, Shortland J, el Nahas AM (1994) Myofibroblasts, predictors of progression of mesangial IgA nephropathy? Nephrol Dial Transplant 9:1418–1425
Hewitson TD, Wu HL, Becker GJ (1995) Interstitial myofibroblasts in experimental renal infection and scarring. Am J Nephrol 15:411–417
Liu Y (2004) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal fibrogenesis: pathologic significance, molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1–12
Kassimatis TI, Nomikos A, Giannopoulou I, Lymperopoulos A, Moutzouris DA, Varakis I, Nakopoulou L (2010) Transcription factor Sp1 expression is upregulated in human glomerulonephritis: correlation with pSmad2/3 and p300 expression and renal injury. Ren Fail 32:243–253
Choi J, Park SY, Joo CK (2007) Transforming growth factor-beta1 represses E-cadherin production via slug expression in lens epithelial cells. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:2708–2718
Mirza A, Liu SL, Frizell E, Zhu J, Maddukuri S, Martinez J, Davies P, Schwarting R, Norton P, Zern MA (1997) A role for tissue transglutaminase in hepatic injury and fibrogenesis, and its regulation by NF-kappaB. Am J Physiol 272:G281–G288
Chua HL, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Clare SE, Morimiya A, Badve S, Nakshatri H (2007) NF-kappaB represses E-cadherin expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of mammary epithelial cells: potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2. Oncogene 26:711–724
Strutz F, Okada H, Lo CW, Danoff T, Carone RL, Tomaszewski JE, Neilson EG (1995) Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J Cell Biol 130:393–405
Barnes PJ, Karin M (1997) Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 336:1066–1071
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2009-353-E00022). This work was also supported by the grant of Research Institute of Medical Science, Catholic University of Daegu (2010).
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to disclose for any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, KH., Park, JH., Lee, WR. et al. The inhibitory effect of chimeric decoy oligodeoxynucleotide against NF-κB and Sp1 in renal interstitial fibrosis. J Mol Med 91, 573–586 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-012-0972-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-012-0972-2