Abstract
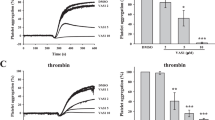
Andrographolide is a novel NF-κB inhibitor from the leaves of Andrographis paniculata. Platelet activation is relevant to a variety of thrombotic diseases. However, no data are available concerning the effects of andrographolide in platelet activation. The aim of this study was to examine the mechanisms of andrographolide in preventing platelet activation. Andrographolide (25–75 μΜ) exhibited a more potent activity of inhibiting platelet aggregation stimulated by collagen. Andrographolide inhibited collagen-stimulated platelet activation accompanied by relative Ca2+ mobilization; thromboxane A2 formation; and phospholipase C (PLC)γ2, protein kinase C (PKC), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and Akt phosphorylation. Andrographolide markedly increased cyclic GMP, but not cyclic AMP levels. Andrographolide also stimulated endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression, NO release, and vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) phosphorylation. ODQ, an inhibitor of guanylate cyclase, markedly reversed the andrographolide-mediated inhibitory effects on platelet aggregation, p38 MAPK and Akt phosphorylation, and the andrographolide-mediated stimulatory effect on VASP phosphorylation. Furthermore, a PI3 kinase inhibitor (LY294002) but not a PKC inhibitor (Ro318220) significantly diminished p38 MAPK phosphorylation; nevertheless, a p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) and LY294002 diminished PKC activity stimulated by collagen. Andrographolide also reduced collagen-triggered hydroxyl radical (OH⋅) formation. In vivo studies revealed that andrographolide (22 and 55 μg/kg) is effective in reducing the mortality of ADP-induced acute pulmonary thromboembolism and significantly prolonged platelet plug formation in mice. This study demonstrates for the first time that andrographolide possesses a novel role of antiplatelet activity, which may involve the activation of the eNOS-NO/cyclic GMP pathway, resulting in the inhibition of the PI3 kinase/Akt-p38 MAPK and PLCγ2–PKC cascades, thereby leading to inhibition of platelet aggregation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coon JT, Ernst E (2004) Andrographis paniculata in the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections: a systematic review of safety and efficacy. Planta Med 70:293–298
Poolsup N, Suthisisang C, Prathanturarug S, Asawamekin A, Chanchareon U (2004) Andrographis paniculata in the symptomatic treatment of uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infection: systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Pharm Ther 29:37–45
Bao Z, Guan S, Cheng C, Wu S, Wong SH, Kemeny DM, Leung BP, Wong WS (2009) A novel antiinflammatory role for andrographolide in asthma via inhibition of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179:657–665
Negi AS, Kumar JK, Luqman S, Shanker K, Gupta MM, Khanuja SP (2008) Recent advances in plant hepatoprotectives: a chemical and biological profile of some important leads. Med Res Rev 28:746–772
Zhou J, Lu GD, Ong CS, Ong CN, Shen HM (2008) Andrographolide sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via p53-mediated death receptor 4 up-regulation. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2170–2180
Iruretagoyena MI, Tobar JA, Gonzalez PA, Sepulveda SE, Figueroa CA, Burgos RA, Hancke JL, Kalergis AM (2005) Andrographolide interferes with T cell activation and reduces experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:366–372
Chiou WF, Chen CF, Lin JJ (2000) Mechanisms of suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in RAW 264.7 cells by andrographolide. Br J Pharmacol 129:1553–1560
Xia YF, Ye BQ, Li YD, Wang JG, He XJ, Lin X, Yao X, Ma D, Slungaard A, Hebbel RP, Key NS, Geng JG (2004) Andrographolide attenuates inflammation by inhibition of NF-kappa B activation through covalent modification of reduced cysteine 62 of p50. J Immunol 173:4207–4217
Hidalgo MA, Romero A, Figueroa J, Cortes P, Concha II, Hancke JL, Burgos RA (2005) Andrographolide interferes with binding of nuclear factor-kappaB to DNA in HL-60-derived neutrophilic cells. Br J Pharmacol 144:680–686
Wang YJ, Wang JT, Fan QX, Geng JG (2007) Andrographolide inhibits NF-kappaBeta activation and attenuates neointimal hyperplasia in arterial restenosis. Cell Res 17:933–941
Hsieh CY, Hsu MJ, Hsiao G, Wang YH, Huang CW, Chen SW, Jayakumar T, Chiu PT, Chiu YH, Sheu JR (2011) Andrographolide enhances NF-{kappa}B subunit p65 Ser536 dephosphorylation through activation of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 286:5942–5955
Hsiao G, Lin KH, Chang Y, Chen TL, Tzu NH, Chou DS, Sheu JR (2005) Protective mechanisms of inosine in platelet activation and cerebral ischemic damage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:1998–2004
von Hundelshausen P, Weber C (2007) Platelets as immune cells: bridging inflammation and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 100:27–40
Amroyan E, Gabrielian E, Panossian A, Wikman G, Wagner H (1999) Inhibitory effect of andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata on PAF-induced platelet aggregation. Phytomedicine 6:27–31
Thisoda P, Rangkadilok N, Pholphana N, Worasuttayangkurn L, Ruchirawat S, Satayavivad J (2006) Inhibitory effect of Andrographis paniculata extract and its active diterpenoids on platelet aggregation. Eur J Pharmacol 553:39–45
Sheu JR, Hung WC, Wu CH, Ma MC, Kan YC, Lin CH, Lin MS, Luk HN, Yen MH (1999) Reduction in lipopolysaccharide-induced thrombocytopenia by triflavin in a rat model of septicemia. Circulation 99:3056–3062
Sheu JR, Chao SH, Yen MH, Huang TF (1994) In vivo antithrombotic effect of triflavin, an Arg-Gly-Asp containing peptide on platelet plug formation in mesenteric microvessels of mice. Thromb Haemost 72:617–621
Tyers M, Rachubinski RA, Stewart MI, Varrichio AM, Shorr RG, Haslam RJ, Harley CB (1988) Molecular cloning and expression of the major protein kinase C substrate of platelets. Nature 333:470–473
Aszodi A, Pfeifer A, Ahmad M, Glauner M, Zhou XH, Ny L, Andersson KE, Kehrel B, Offermanns S, Fassler R (1999) The vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is involved in cGMP- and cAMP-mediated inhibition of agonist-induced platelet aggregation, but is dispensable for smooth muscle function. EMBO J 18:37–48
Suo XB, Zhang H, Wang YQ (2007) HPLC determination of andrographolide in rat whole blood: study on the pharmacokinetics of andrographolide incorporated in liposomes and tablets. Biomed Chromatogr 21:730–734
Singer WD, Brown HA, Sternweis PC (1997) Regulation of eukaryotic phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and phospholipase D. Annu Rev Biochem 66:475–509
Ragab A, Severin S, Gratacap MP, Aguado E, Malissen M, Jandrot-Perrus M, Malissen B, Ragab-Thomas J, Payrastre B (2007) Roles of the C-terminal tyrosine residues of LAT in GPVI-induced platelet activation: insights into the mechanism of PLC gamma 2 activation. Blood 110:2466–2474
Adam F, Kauskot A, Rosa JP, Bryckaert M (2008) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in hemostasis and thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost 6:2007–2016
Oury C, Toth-Zsamboki E, Vermylen J, Hoylaerts MF (2002) P2X(1)-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 contributes to platelet secretion and aggregation induced by collagen. Blood 100:2499–2505
Garcia A, Shankar H, Murugappan S, Kim S, Kunapuli SP (2007) Regulation and functional consequences of ADP receptor-mediated ERK2 activation in platelets. Biochem J 404:299–308
Hughes PE, Renshaw MW, Pfaff M, Forsyth J, Keivens VM, Schwartz MA, Ginsberg MH (1997) Suppression of integrin activation: a novel function of a Ras/Raf-initiated MAP kinase pathway. Cell 88:521–530
Coulon L, Calzada C, Moulin P, Vericel E, Lagarde M (2003) Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/cytosolic phospholipase A2 cascade in hydroperoxide-stressed platelets. Free Radic Biol Med 35:616–625
Franke TF, Yang SI, Chan TO, Datta K, Kazlauskas A, Morrison DK, Kaplan DR, Tsichlis PN (1995) The protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell 81:727–736
Walter U, Eigenthaler M, Geiger J, Reinhard M (1993) Role of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases and their common substrate VASP in the regulation of human platelets. Adv Exp Med Biol 344:237–249
Gkaliagkousi E, Ritter J, Ferro A (2007) Platelet-derived nitric oxide signaling and regulation. Circ Res 101:654–662
Chen JH, Hsiao G, Lee AR, Wu CC, Yen MH (2004) Andrographolide suppresses endothelial cell apoptosis via activation of phosphatidyl inositol-3-kinase/Akt pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 67:1337–1345
Chao WW, Kuo YH, Lin BF (2010) Anti-inflammatory activity of new compounds from Andrographis paniculata by NF-kappaB transactivation inhibition. J Agric Food Chem 58:2505–2512
Schwertz H, Tolley ND, Foulks JM, Denis MM, Risenmay BW, Buerke M, Tilley RE, Rondina MT, Harris EM, Kraiss LW, Mackman N, Zimmerman GA, Weyrich AS (2006) Signal-dependent splicing of tissue factor pre-mRNA modulates the thrombogenicity of human platelets. J Exp Med 203:2433–2440
Eisenreich A, Boltzen U, Poller W, Schultheiss HP, Rauch U (2008) Effects of the Cdc2-like kinase-family and DNA topoisomerase I on the alternative splicing of eNOS in TNF-alpha-stimulated human endothelial cells. Biol Chem 389:1333–1338
Eisenreich A, Bogdanov VY, Zakrzewicz A, Pries A, Antoniak S, Poller W, Schultheiss HP, Rauch U (2009) Cdc2-like kinases and DNA topoisomerase I regulate alternative splicing of tissue factor in human endothelial cells. Circ Res 104:589–599
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC94-2321-B-038-001 and NSC97-2320-B-038-016-MY3) and the Committee on Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy (CCMP97-RD-008).
Disclosure of potential conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests related to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Supplementary Figure for Reviewer (DOCX 216 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, WJ., Lee, JJ., Chou, DS. et al. A novel role of andrographolide, an NF-kappa B inhibitor, on inhibition of platelet activation: the pivotal mechanisms of endothelial nitric oxide synthase/cyclic GMP. J Mol Med 89, 1261–1273 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0800-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0800-0