Abstract
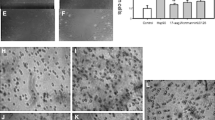
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can contribute to tissue repair by actively migrating to sites of tissue injury. However, the cellular and molecular mechanisms of MSC recruitment are largely unknown. The nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway plays a pivotal role in regulating genes that influence cell migration, cell differentiation, inflammation, and proliferation. One of the major cytokines released at sites of injury is tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), which is known to be a key regulator of the NF-κB pathway. Therefore, we hypothesized that TNF-α may lead to MSC invasion and proliferation by activation of the NF-κB pathway. TNF-receptor 1 and 2, NF-κB (p65), and IκB kinase 2 (IKK-2) are expressed in human MSCs (hMSCs). Stimulation of hMSCs with TNF-α caused a p65 translocation from the cytoplasm to nucleoplasm but did not change the expression profile of MSC markers. TNF-α strongly augmented the migration of hMSCs through the human extracellular matrix. Using lentiviral gene transfer, overexpressing a dominant-negative mutant of IKK-2 (dn-IKK-2) significantly blocked this effect. NF-κB target genes associated with migration (vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, CD44, and matrix metalloproteinase 9) were upregulated by TNF-α stimulation and blocked by dn-IKK-2. Moreover, using the bromodeoxyuridine assay, we showed that the inhibition of the NF-κB pathway caused a significant reduction in the basal proliferation rate. TNF-α stimulated the proliferation of hMSCs, whereas overexpression of dn-IKK-2 significantly blocked this effect. TNF-α led to the upregulated expression of the proliferation-associated gene cyclin D1. In conclusion, we demonstrated that the NF-κB pathway components, p65 and IKK-2, are expressed in hMSCs. Our data provide evidence that this signal transduction pathway is implicated in TNF-α-mediated invasion and proliferation of hMSCs. Therefore, hMSC recruitment to sites of tissue injury may, at least in part, be regulated by the NF-κB signal transduction pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prockop MF (1997) Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for non-haematopoietic tissues. Science 276:71–74
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC et al (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147
Docheva D, Popov C, Mutschler W et al (2007) Human mesenchymal stem cells in contact with their environment: surface characteristics and the integrin system. J Cell Mol Med 11:1–17
Ji JF, He BP, Dheen ST et al (2004) Interactions of chemokines and chemokine receptors mediate the migration of mesenchymal stem cells to the impaired site in the brain after hypoglossal nerve injury. Stem Cells 22:415–427
Wang L, Li Y, Chen X et al (2002) MCP-1, MIP-1, IL-8 and ischemic cerebral tissue enhance human bone marrow stromal cell migration in interface culture. Hematology 7:113–117
Roufosse CA, Direkze NC, Otto WR et al (2004) Circulating mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:585–597
Devine MJ, Mierisch CM, Jang E et al (2002) Transplanted bone marrow cells localize to fracture callus in a mouse model. J Orthop Res 20:1232–1239
Kawada H, Fujita J, Kinjo K et al (2004) Nonhematopoietic mesenchymal stem cells can be mobilized and differentiate into cardiomyocytes after myocardial infarction. Blood 104:3581–3587
Mackenzie TC, Flake AW (2001) Human mesenchymal stem cells persist, demonstrate site-specific multipotential differentiation, and are present in sites of wound healing and tissue regeneration after transplantation into fetal sheep. Blood Cells Mol Dis 27:601–604
Liechty K, MacKenzie T, Shaaban A et al (2000) Human mesenchymal stem cells engraft and demonstrate site-specific differentiation after in utero transplantation in sheep. Nat Med 6:1282–1286
Kan I, Melamed E, Offen D (2005) Integral therapeutic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Drug Targets 6:31–41
Fiedler J, Etzel N, Brenner RE (2004) To go or not to go: migration of human mesenchymal progenitor cells stimulated by isoforms of PDGF. J Cell Biochem 93:990–998
Schmidt A, Ladage DST, Klausman U et al (2006) Basic fibroblast growth factor controls migration in human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 24:1750–1758
Fiedler J, Leucht F, Waltenberger J et al (2005) VEGF-A and PlGF-1 stimulate chemotactic migration of human mesenchymal progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:561–568
Sordi V, Malosio ML, Marchesi F et al (2005) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells express a restricted set of functionally active chemokine receptors capable of promoting migration to pancreatic islets. Blood 106:419–427
Ozaki Y, Nishimura M, Sekiya K et al (2007) Comprehensive analysis of chemotactic factors for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 16:119–129
Ries C, Egea V, Karow M et al (2007) MMP-2, MT1-MMP, and TIMP-2 are essential for the invasive capacity of human mesenchymal stem cells: differential regulation by inflammatory cytokines. Blood 109:4055–4063
Efron PA, Moldawer LL (2004) Cytokines and wound healing: the role of cytokine and anticytokine therapy in the repair response. J Burn Care Rehabil 25:149–160
Dimitriou R, Tsiridis E, Giannoudis PV (2005) Current concepts of molecular aspects of bone healing. Injury 36:1392–1404
Widera D, Mikenberg I, Elvers M et al (2006) Tumor necrosis factor alpha triggers proliferation of adult neural stem cells via IKK/NF-kappaB signaling. BMC Neurosci 7:64
Bargou RC, Emmerich F, Krappmann D et al (1997) Constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB-RelA activation is required for proliferation and survival of Hodgkin’s disease tumor cells. J Clin Invest 100:2961–2969
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY et al (1999) NF-kappaB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cell Biol 19:5785–5799
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A et al (1999) NF-kappaB function in growth control: regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0/G1-to-S-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 19:2690–2698
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734
Ghosh S, Karin M (2002) Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 109(Suppl):S81–S96
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3:221–227
Sen R, Baltimore D (1986) Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell 47:921–928
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D (1988) I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science 242:540–546
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D (1996) NF-kappa B: ten years after. Cell 87:13–20
Chen Z, Hagler J, Palombella VJ et al (1995) Signal-induced site-specific phosphorylation targets I kappa B alpha to the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. Genes Dev 9:1586–1597
Böcker W, Rossmann O, Docheva D et al (2007) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction as a reliable method to determine functional lentiviral titer after ex vivo gene transfer in human mesenchymal stem cells. J Gene Med 9:585–595
Neth P, Ciccarella M, Egea V et al (2006) Wnt signaling regulates the invasion capacity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 24:1892–1903
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I et al (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317
Fahim MR, Halim SM, Kamel I (2004) Tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Egypt J Immunol 11:31–37
Jiang J, Tian K, Chen H et al (1997) Kinetics of plasma cytokines and its clinical significance in patients with severe trauma. Chin Med J (Engl) 110:923–926
Gerstenfeld LC, Cho TJ, Kon T et al (2003) Impaired fracture healing in the absence of TNF-alpha signaling: the role of TNF-alpha in endochondral cartilage resorption. J Bone Miner Res 18:1584–1592
Kon T, Cho TJ, Aizawa T et al (2001) Expression of osteoprotegerin, receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (osteoprotegerin ligand) and related proinflammatory cytokines during fracture healing. J Bone Miner Res 16:1004–1014
Einhorn TA, Majeska RJ, Rush EB et al (1995) The expression of cytokine activity by fracture callus. J Bone Miner Res 10:1272–1281
Ruster B, Gottig S, Ludwig RJ et al (2006) Mesenchymal stem cells display coordinated rolling and adhesion behavior on endothelial cells. Blood 108:3938–3944
Kang YJ, Jeon ES, Song HY et al (2005) Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem 95:1135–1145
Schmal H, Niemeyer P, Roesslein M et al (2007) Comparison of cellular functionality of human mesenchymal stromal cells and PBMC. Cytotherapy 9:69–79
Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM (2004) The IKK NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:17–26
Kalluri R (2003) Basement membranes: structure, assembly and role in tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 3:422–433
Visse R, Nagase H (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res 92:827–839
Egeblad M, Werb Z (2002) New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:161–174
Lee HY, Park KS, Kim MK et al (2005) A small compound that inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 upregulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:716–722
Lee SO, Jeong YJ, Yu MH et al (2006) Wogonin suppresses TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9 expression by blocking the NF-kappaB activation via MAPK signaling pathways in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:118–125
Isacke CM, Yarwood H (2002) The hyaluronan receptor, CD44. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34:718–721
Peng ST, Su CH, Kuo CC et al (2007) CD44 crosslinking-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 relocation in breast tumor cells leads to enhanced metastasis. Int J Oncol 31:1119–1126
Bourguignon LY, Gunja-Smith Z, Iida N et al (1998) CD44v(3,8-10) is involved in cytoskeleton-mediated tumor cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) association in metastatic breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 176:206–215
Alaniz L, Garcia M, Cabrera P et al (2004) Modulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity by hyaluronan is dependent on NF-kappaB activity in lymphoma cell lines with dissimilar invasive behavior. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324:736–743
Zhu H, Mitsuhashi N, Klein A et al (2006) The role of the hyaluronan receptor CD44 in mesenchymal stem cell migration in the extracellular matrix. Stem Cells 24:928–935
Meiler SE, Hung RR, Gerszten RE et al (2002) Endothelial IKK beta signaling is required for monocyte adhesion under laminar flow conditions. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:349–359
Theiss AL, Simmons JG, Jobin C et al (2005) Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha increases collagen accumulation and proliferation in intestinal myofibroblasts via TNF receptor 2. J Biol Chem 280:36099–36109
Mehrhof FB, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Dietz R et al (2005) Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation: role of NF-kappaB revisited. Circ Res 96:958–964
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Prof. Dr. Med. Ulrich Koszinowski and Priv. Doz. Dr. med. Dr. rer. nat. Jürgen Haas (Max-von-Pettenkofer-Institute, Virology Section, University of Munich) for providing us the S2 laboratory and the intense discussion on lentiviral gene transfer and Martina Burggraf for PCR technical help and Dr. Eduard Fellows for assistance in the apoptosis assay. This project was supported by the AO Research Fund of the AO Foundation, Davos-Platz, Switzerland (AO grants: 05-B42 and 05-D83). We also appreciate the financial support of the Friedrich-Baur-Foundation (University of Munich) on lentiviral gene transfer in hMSCs, and Denitsa Docheva and Cvetan Popov acknowledge the financial support of the Bavarian Research Foundation (grant DPA-51/05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böcker, W., Docheva, D., Prall, W.C. et al. IKK-2 is required for TNF-α-induced invasion and proliferation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Mol Med 86, 1183–1192 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-008-0378-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-008-0378-3