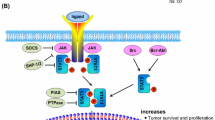
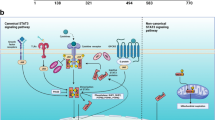
Abstract
The signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins are a family of latent cytoplasmic transcription factors, which form dimers when activated by cytokine receptors, tyrosine kinase growth factor receptors as well as non-receptor tyrosine kinases. Dimeric STATs translocate to the nucleus, where they bind to specific DNA-response elements in the promoters of target genes, thereby inducing unique gene expression programs often in association with other transcription regulatory proteins. The functional consequence of different STAT proteins activation varies, as their target genes play diverse roles in normal cellular/tissue functions, including growth, apoptosis, differentiation and angiogenesis. Certain activated STATs have been implicated in human carcinogenesis, albeit only few studies have focused into their role in lung tumours. Converging evidence unravels their molecular interplays and complex multipartite regulation, rendering some of them appealing targets for lung cancer treatment with new developing strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stahl N, Farruggella TJ, Boulton TG, Zhong Z, Darnell JE Jr, Yancopoulos GD (2002) Choice of STATs and other substrates specified by modular tyrosine-based motifs in cytokine receptors. Science 267:1349–1353
Khwaja A (2006) The role of Janus kinases in haemopoiesis and haematological malignancy. Br J Haematol 134:366–384
Leeman RJ, Lui VW, Grandis JR (2006) STAT3 as a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther 6:231–241
Arredondo J, Chernyavsky AI, Jolkovsky DL, Pinkerton KE, Grando SA (2006) Receptor-mediated tobacco toxicity: cooperation of the Ras/Raf-1/MEK1/ERK and JAK-2/STAT-3 pathways downstream of alpha7 nicotinic receptor in oral keratinocytes. FASEB J 20:2093–3101
Xi S, Zhang Q, Dyer KF, Lerner EC, Smithgall TE, Gooding WE, Kamens J, Grandis JR (2003) Src kinases mediate STAT growth pathways in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Biol Chem 278:31574–31583
Zhang X, Wrzeszczynska MH, Horvath CM, Darnell JE Jr (1999) Interacting regions in Stat3 and c-Jun that participate in cooperative transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 19:7138–7146
Liu L, McBride KM, Reich NC (2005) STAT3 nuclear import is independent of tyrosine phosphorylation and mediated by importin-alpha3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8150–8155
Wang R, Cherukuri P, Luo J (2005) Activation of Stat3 sequence-specific DNA binding and transcription by p300/CREB-binding protein-mediated acetylation. J Biol Chem 280:11528–11534
Komyod W, Bauer UM, Heinrich PC, Haan S, Behrmann I (2005) Are STATS arginine-methylated? J Biol Chem 280:21700–21705
Siavash H, Nikitakis NG, Sauk JJ (2004) Signal transducers and activators of transcription: insights into the molecular basis of oral cancer. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 15:298–307
Arnaud M, Crouin C, Deon C, Loyaux D, Bertoglio J (2004) Phosphorylation of Grb2-associated binder 2 on serine 623 by ERK MAPK regulates its association with the phosphatase SHP-2 and decreases STAT5 activation. J Immunol 173:3962–3971
Gate L, Majumdar RS, Lunk A, Tew KD (2004) Increased myeloproliferation in glutathione S-transferase pi-deficient mice is associated with a deregulation of JNK and Janus kinase/STAT pathways. J Biol Chem 279:8608–8616
Yu H, Jove R (2004) The STATs of cancer—new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer 4:97–105
Haura EB, Turkson J, Jove R (2005) Mechanisms of disease: insights into the emerging role of signal transducers and activators of transcription in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2:315–324
Sharrocks AD (2006) PIAS proteins and transcriptional regulation—more than just SUMO E3 ligases? Genes Dev 20:754–758
Yoshimura A (2005) Negative regulation of cytokine signaling. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 28:205–220
Piessevaux J, Lavens D, Montoye T, Wauman J, Catteeuw D, Vandekerckhove J, Belsham D, Peelman F, Tavernier J (2006) Functional cross-modulation between SOCS proteins can stimulate cytokine signalling. J Biol Chem 281:32953–32966
Song L, Bhattacharya S, Yunus AA, Lima CD, Schindler C (2006). Stat1 and SUMO modification. Blood DOI 10.1182/blood2006-04-020271
Shuai K (2006) Regulation of cytokine signaling pathways by PIAS proteins. Cell Res 16:196–202
Yang SH, Sharrocks AD (2006) PIASxalpha differentially regulates the amplitudes of transcriptional responses following activation of the ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. Mol Cell 22:477–487
Ungureanu D, Vanhatupa S, Gronholm J, Palvimo JJ, Silvennoinen O (2005) SUMO-1 conjugation selectively modulates STAT1-mediated gene responses. Blood 106:224–226
Tanaka T, Soriano MA, Grusby MJ (2005) SLIM is a nuclear ubiquitin E3 ligase that negatively regulates STAT signaling. Immunity 22:729–736
Wormald S, Hilton DJ (2004) Inhibitors of cytokine signal transduction. J Biol Chem 279:821–824
Fang P, Kofoed EM, Little BM, Wang X, Ross RJM, Frank SJ, Hwa V, Rosenfeld RG (2006) A mutant signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b, associated with growth hormone insensitivity and insulin-like growth factor-I deficiency, cannot function as a signal transducer or transcription factor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:1526–1534
Karamouzis MV, Papavassiliou AG (2006) The IGF-1 network in lung carcinoma therapeutics. Trends Mol Med DOI 10.1016/j.molmed.2006.10.003
Yeh HH, Lai WW, Chen HH, Liu HS, Su WC (2006) Autocrine IL-6-induced Stat3 activation contributes to the pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma and malignant pleural effusion. Oncogene 25:4300–4309
He B, You L, Xu Z, Mazieres J, Lee AY, Jablons DM (2004) Activity of the suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 promoter in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 5:366–370
Sanchez-Ceja SG, Reyes-Maldonado E, Vazquez-Manriquez ME, Lopez-Luna JJ, Belmont A, Gutierrez-Castellanos S (2006) Differential expression of STAT5 and Bcl-x(L), and high expression of Neu and STAT3 in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 54:163–168
Wikman H, Kettunen E (2006) Regulation of the G1/S phase of the cell cycle and alterations in the RB pathway in human lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 6:515–530
Vincenzi B, Schiavon G, Silletta M, Santini D, Perrone G, Di Marino M, Angeletti S, Baldi A, Tonini G (2006) Cell cycle alterations and lung cancer. Histol Histopathol 21:423–435
Arredondo J, Chernyavsky AI, Grando SA (2006) The nicotinic receptor antagonists abolish pathobiologic effects of tobacco-derived nitrosamines on BEP2D cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132:653–663
Arany I, Chen SH, Megyesi JK, Adler-Storthz K, Chen Z, Rajaraman S, Ember IA, Tyring SK, Brysk MM (2003) Differentiation-dependent expression of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) might modify responses to growth factors in the cancers of the head and neck. Cancer Lett 199:83–89
Adjei AA (2005) Targeting multiple signal transduction pathways in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 7(Suppl 1):S39–S44
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin Oncol 33:369–385
Liu J, Kern JA (2002) Neuregulin-1 activates the JAK–STAT pathway and regulates lung epithelial cell proliferation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 27:306–313
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139
Pao W, Miller VA (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations, small-molecule kinase inhibitors, and non-small-cell lung cancer: current knowledge and future directions. J Clin Oncol 23:2556–2568
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J (2004) Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science 305:1163–1167
Alvarez JV, Greulich H, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Frank DA (2006) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for the oncogenic effects of non-small-cell lung cancer-associated mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 66:3162–3168
Haura EB, Zheng Z, Song L, Cantor A, Bepler G (2005) Activated epidermal growth factor receptor-Stat-3 signaling promotes tumor survival in vivo in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:8288–8294
Lee D, Gautschi O (2006) Clinical development of SRC tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 7:381–384
Carelli S, Zadra G, Vaira V, Falleni M, Bottiglieri L, Nosotti M, Di Giulio AM, Gorio A, Bosari S (2006) Up-regulation of focal adhesion kinase in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 53:263–271
Xie B, Zhao J, Kitagawa M, Durbin J, Madri JA, Guan JL, Fu XY (2001) Focal adhesion kinase activates Stat1 in integrin-mediated cell migration and adhesion. J Biol Chem 276:19512–19523
Silver DL, Naora H, Liu J, Cheng W, Montell DJ (2004) Activated signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3: localization in focal adhesions and function in ovarian cancer cell motility. Cancer Res 64:3550–3558
He B, You L, Uematsu K, Zang K, Xu Z, Lee AY, Costello JF, McCormick F, Jablons SM (2003) SOCS-3 is frequently silenced by hypermethylation and suppresses cell growth in human lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14133–14138
Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, Saiura A, Matsubara K, Kitagawa T, Yamamoto J, Kubo T, Yoshikawa H (2005) Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration by enhancing JAK/STAT and FAK signalings in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 24:6406–6417
Bayle J, Letard S, Frank R, Dubreuil P, De Sepulveda P (2004) Suppressor of cytokine signaling 6 associates with KIT and regulates KIT receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 279:12249–12259
Ogata Y, Osaki T, Naka T, Iwahori K, Furukawa M, Nagatomo I, Kijima T, Kumagai T, Yoshida M, Tachibana I, Kawase I (2006) Overexpression of PIAS3 suppresses cell growth and restores the drug sensitivity of human lung cancer cells in association with PI3-K/Akt inactivation. Neoplasia 8:817–825
Johnson FM, Krug LM, Tran HT, Shoaf S, Prieto VG, Tamboli P, Peeples B, Patel J, Glisson BS (2006) Phase I studies of Imatinib Mesylate combined with cisplatin and irinotecan in patients with small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 106:366–374
Vlahovic G, Rabbani ZN, Herndon JE II, Dewhirst MW, Vujaskovic Z (2006) Treatment with Imatinib in NSCLC is associated with decrease of phosphorylated PDGFR-beta and VEGF expression, decrease in interstitial fluid pressure and improvement of oxygenation. Br J Cancer 95:1013–1019
Song L, Morris M, Bagui T, Lee FY, Jove R, Haura EB (2006) Dasatinib (BMS-354825) selectively induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells dependent on epidermal growth factor receptor signaling for survival. Cancer Res 66:5542–5548
Blaskovich MA, Sun J, Cantor A, Turkson J, Jove R, Sebti SM (2003) Discovery of JSI-124 (cucurbitacin I), a selective Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway inhibitor with potent antitumor activity against human and murine cancer cells in mice. Cancer Res 63:1270–1279
Lee YK, Isham CR, Kaufman SH, Bible KC (2006) Flavopiridol disrupts STAT3/DNA interactions, attenuates STAT3-directed transcription, and combines with the JAK kinase inhibitor AG490 to achieve cytotoxic synergy. Mol Cancer Ther 5:138–148
Buerger C, Groner B (2003) Bifunctional recombinant proteins in cancer therapy: cell penetrating peptide aptamers as inhibitors of growth factor signaling. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 129:669–675
Campo S, Serlupi-Crescenzi O, Arseni B, Rossi S, Saggio I, Salone B, Cherubini G, Carminati P, De Santis R (2005) Comparative activity of Sant7 and anti-IL-6, IL-6R monoclonal antibodies in a murine model of B-cell lymphoma. Cytokine 31:368–374
Yamaji H, Iizasa T, Koh E, Suzuki M, Otsuji M, Chang H, Motohashi S, Yokoi S, Hiroshima K, Tagawa M, Nakayama T, Fujisawa T (2004) Correlation between interleukin 6 production and tumor proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 53:786–792
Washio K, Aoe M, Toyooka S, Mushiake H, Tsukuda K, Shimizu N (2003) The effect of epidermal growth factor receptor antisense morpholino oligomer on non-small cell lung cancer cell line. Oncol Rep 10:1967–1971
Liby K, Voong N, Williams CR, Risingsong R, Royce DB, Honda T, Gribble GW, Sporn MB, Letterio JJ (2006) The synthetic triterpenoid CDDO-Imidazolide suppresses STAT phosphorylation and induces apoptosis in myeloma and lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 12:4288–4293
Turkson J, Kim JS, Zhang S, Yuan J, Huang M, Glenn M, Haura E, Sebti S, Hamilton AD, Jove R (2004) Novel peptidomimetic inhibitors of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 dimerization and biological activity. Mol Cancer Ther 3:261–269
Karamouzis MV, Gorgoulis VG, Papavassiliou AG (2002) Transcription factors and neoplasia: vistas in novel drug design. Clin Cancer Res 8:949–961
Nagel-Wolfrum K, Buerger C, Wittig I, Butz K, Hoppe-Seyler F, Groner B (2004) The interaction of specific peptide aptamers with the DNA binding domain and the dimerization domain of the transcription factor Stat3 inhibits transactivation and induces apoptosis in tumor cells. Mol Cancer Res 2:170–182
Shapiro GI (2006) Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol 24:1770–1783
Leong PL, Andrews GA, Johnson DE, Dyer KF, Xi S, Mai JC, Robbins PD, Gadipathi S, Burke NA, Watkins SF, Grandis JR (2003) Targeted inhibition of Stat3 with a decoy oligonucleotide abrogates head and neck cancer cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4138–4143
Xi S, Gooding WE, Grandis JR (2005) In vivo antitumor efficacy of STAT3 blockade using a transcription factor decoy approach: implications for cancer therapy. Oncogene 24:970–979
Barton BE, Murphy TF, Shu P, Huang HF, Meyenhofer M, Barton A (2004) Novel single-stranded oligonucleotides that inhibit signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 induce apoptosis in vitro and in vivo in prostate cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther 3:1183–1191
Wang LH, Yang XY, Zhang X, Farrar WL (2005) Nuclear receptors as negative modulators of STAT3 in multiple myeloma. Cell Cycle 4:242–245
Litterst CM, Kliem S, Lodrini M, Pfitzner E (2005) Coactivators in gene regulation by STAT5. Vitam Horm 70:359–386
Bali P, Pranpat M, Swaby R, Fiskus W, Yamaguchi H, Balasis M, Rocha K, Wang HG, Richon V, Bhalla K (2005) Activity of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid against human breast cancer cells with amplification of her-2. Clin Cancer Res 11:6382–6389
Coppelli FM, Grandis JR (2005) Oligonucleotides as anticancer agents: from the benchside to the clinic and beyond. Curr Pharm Des 11:2825–2840
Gao LF, Xu DQ, Wen LJ, Zhang XY, Shao YT, Zhao XJ (2005) Inhibition of STAT3 expression by siRNA suppresses growth and induces apoptosis in laryngeal cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:377–383
Lee TL, Yeh J, Van Waes C, Chen Z (2006) Epigenetic modification of SOCS-1 differentially regulates STAT3 activation in response to interleukin-6 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling through JAK and/or MEK in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Cancer Ther 5:8–19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karamouzis, M.V., Konstantinopoulos, P.A. & Papavassiliou, A.G. The role of STATs in lung carcinogenesis: an emerging target for novel therapeutics. J Mol Med 85, 427–436 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0152-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0152-3