Abstract
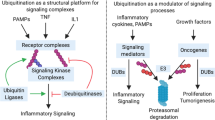
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway has a central role in the selective degradation of intracellular proteins. Among the key proteins modulated by the proteasome are those involved in the control of inflammatory processes, cell cycle regulation, and gene expression. Consequently proteasome inhibition is a potential treatment option for cancer and inflammatory conditions. Thus far, proof of principle has been obtained from studies in numerous animal models for a variety of human diseases including cancer, reperfusion injury, and inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis. Two proteasome inhibitors, each representing a unique chemical class, are currently under clinical evaluation. Velcade (PS-341) is currently being evaluated in multiple phase II clinical trials for several solid tumor indications and has just entered a phase III trial for multiple myeloma. PS-519, representing another class of inhibitors, focuses on the inflammatory events following ischemia and reperfusion injury. Since proteasome inhibitors exhibit anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative effects, diseases characterized by both of these processes simultaneously, as is the case in rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis, might also represent clinical opportunities for such drugs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CLA :
-
Cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen
- EAE :
-
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- IκB :
-
Nuclear factor κB inhibitor
- IL :
-
Interleukin
- NF-κB :
-
Nuclear factor κB
- TNF :
-
Tumor necrosis factor
References
Ciechanover A (1998) The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway: on protein death and cell life. EMBO J 24:7151–7160
Peters JM, Harris JR, Finley D (eds) (1998) Ubiquitin and the biology of the cell. Plenum, New York
Rivett AJ (1993) Proteasomes: multicatalytic proteinase complexes. Biochem J 291:1–10
Goldberg AL, Stein R, Adams J (1995) New insights into proteasome function: from archaebacteria to drug development. Chem Biol 2:503–508
Hershko A (1997) Roles of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis in cell cycle control Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:788–799
Epinat JC, Gilmore TD (1999) Diverse agents act at multiple levels to inhibit the Rel/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. Oncogene 18:6896–6909
Myung J, Kim KB, Crews CM (2001) The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and proteasome inhibitors. Med Res Rev 21:245–273
Kisselev AF, Goldberg AL (2001) Proteasome inhibitors: from research tools to drug candidates. Chem Biol 8:739–758
Bogyo M, Wang EW (2002) Proteasome inhibitors: complex tools for a complex enzyme. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 268:185–208
Vinitsky A, Michaud C, Powers JC, Orlowski M (1992) Inhibition of the chymotrypsin-like activity of the pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Biochemistry 31:9421–9428
Palombella VJ, Rando OJ, Goldberg AL, Maniatis T (1994) The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-kappa B1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-kappa B. Cell 78:773–785
Rock KL, Gramm C, Rothstein L, Clark K, Stein R, Dick L, Hwang D, Goldberg AL (1994) Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell 78:761–771
Tsubuki S, Saito Y, Tomioka M, Ito H, Kawashima S (1996) Differential inhibition of calpain and proteasome activities by peptidyl aldehydes of di-leucine and tri-leucine. J Biochem (Tokyo) 119:572–576
Adams J, Behnke M, Chen S, Cruickshank AA, Dick LR, Grenier L, Klunder JM, Ma YT, Plamondon L, Stein RL (1998) Potent and selective inhibitors of the proteasome: dipeptidyl boronic acids. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8:333–338
Elliott PJ, Ross JS (2001) The proteasome: a new target for novel drug therapies. Am J Clin Pathol 116:637–646
Adams J (2002) Development of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341. Oncologist 7:9–16
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, Johnson J, Destree A, Lazarus DD, Maas J, Pien CS, Prakash S, Elliott PJ (1999) Proteasome inhibitors: a novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res 59:2615–2622
Hideshima T, Richardson P, Chauhan D, Palombella VJ, Elliott PJ, Adams J, Anderson KC (2001) The Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis, and overcomes drug resistance in human multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res 61:3071–3076
Aghajanian C, Soignet S, Dizon DS, PienCS, AdamsJ, Elliott PJ, Sabbattini P, Miller V, Hensley ML, Pezzulli S, Canales CA, Dauda A, Spriggs DR (2002) A phase I trial of the novel proteasome inhibitor PS-341 in advanced solid tumor malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 8:2505–2011
Orlowski RZ, Stinchcombe TE, Mitchell BS, Shea TC, Baldwin AS, Stahl S, Adams J, Esseltine D-L, Elliott PJ, Pien CS, Guerciolini R, Depcik-Smith ND, Bhagat R, Lehman MJ, Novick SC, O'Connor OA, Soignet SL (2002) Phase I trial of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 in patients with refractory hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol 20:4420–4427
Fenteany G, Standaert RF, Lane WS, Choi S, Corey EJ, Schreiber SL (1995) Inhibition of proteasome activities and subunit-specific amino-terminal threonine modification by lactacystin. Science 268:726–731
Dick LR, Cruikshank AA, Grenier L, Melandri FD, Nunes SL, Stein RL (1996) Mechanistic studies on the inactivation of the proteasome by lactacystin. J Biol Chem 271:7273–7276
Dick LR, Cruikshank AA, Destree AT, Grenier L, McCormack TA, Melandri FD, Nunes SL, Palombella VJ, Parent LA, Plamondon L, Stein RL (1997) Mechanistic studies on the inactivation of the proteasome by lactacystin in cultured cells. J Biol Chem 272:182–188
Ostrowska H, Wojcik C, Omura S, Worowski K (1997) Lactacystin, a specific inhibitor of the proteasome, inhibits human platelet lysosomal cathepsin A-like enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 234:729–732
Geier E, Pfeifer G, Wilm M, Lucchiari-Hartz M, Baumeister W, Eichmann K, Niedermann G (1999) A giant protease with potential to substitute for some functions of the proteasome. Science 283:978–981
Soucy F, Grenier L, Behnke ML, Destree AT, McCormack TA, Adams J, Plamondon L (1999) A novel and efficient synthesis of a highly active analogue of clasto-lactacystin b-lactone. J Am Chem Soc 121:9967–9976
Groll M, Kim KB, Kairies N, Huber R, Crews CM (2000) Crystal structure of epoxomicin: 20S proteasome reveals a molecular basis for selectivity of a',b'-epoxoketone proteasome inhibitors. J Am Chem Soc 122:1237–1238
Meng L, Mohan R, Kwok BHB, Elofsson M, Sin N, Crews CM (1999) Epoxomicin, a potent and selective proteasome inhibitor, exhibits in vivo antiinflammatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10403–10408
Furet P, Imbach P, Furst P, Lang M, Noorani M, Zimmermann J, Garcia-Echeverria C (2001) Modeling of the binding mode of a non-covalent inhibitor of the 20S proteasome. Application to structure-based analogue design. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:1321–1324
Furet P, Imbach P, Fuerst P, Lang M, Noorani M, Zimmermann J, Garcia-Echeverria C (2002) Structure-based optimisation of 2-aminobenzylstatine derivatives: potent and selective inhibitors of the chymotrypsin-Like activity of the human 20S proteasome. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12:1331–1334
Garcia-Echeverria C, Imbach P, France D, Furst P, Lang M, Noorani AM, Scholz D, Zimmermann J, Furet P (2001) A new structural class of selective and non-covalent inhibitors of the chymotrypsin-like activity of the 20S proteasome. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:1317–1319
Lin ZP, Boller YC, Am SM, et al (1998) Prevention of brefeldin A-induced resistance to teniposide by the proteasome inhibitor MG-132: involvement of NF-kappa B activation in drug resistance. Cancer Res 58:3059–3065
Wang C-Y, Cusack JC, Liu R, et al (1999) Control of inducible chemoresistance: enhanced antitumor therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappa B. Nat Med 5:412–417
Lawrence T, Gilroy DW, Colville-Nash PR, Willoughby DA (2001) Possible role of NF-kappa B in the resolution of inflammation. Nat Med 7:1291–1297
Cheason BD (2002) Hematologic malignancies: new developments and future treatments. Semin Oncol 29:33–45
Almond JB, Cohen GM (2002) The proteasome: a novel target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 16:433–443
Jain KK (2000) Neuroprotection in cerebrovascular disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9:695–711
White BC, Sullivan JM, DeGracia DJ, O'Neil BJ, Neumar RW, Grossman LI, Rafols JA, Krause GS (2000) Brain ischemia and reperfusion: molecular mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurol Sci 179–:1–33
Carroll JE, Hess DC, Howard EF, Hill WD (2000) Is nuclear factor-kappaB a good treatment target in brain ischemia/reperfusion injury? Neuroreport 11:R1–R4
Phillips JB, Williams AJ, Adams J, Elliott PJ, Tortella FC (2000) Proteasome inhibitor PS-519 reduces infarction and attenuates leukocyte infiltration in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 31:1686–1693
Berti R, Williams AJ, Moffett JR, Hale SL, Velarde LC, Elliott PJ, Yao C, Dave JR, Tortella FC (2002) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory gene expression associated with ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:1068–1079
Buchan AM, Li H, Blackburn B (1999) Neuroprotection achieved with a novel proteasome inhibitor which blocks NF-κB activation. Neuroreport 11:427–430
Zhang L, Zhang ZG, Zhang RL, Chopp M, Adams J, Elliott PJ (2001) Postischemic (6 h) treatment with rht-PA and proteasome inhibitor PS-519 reduces infarction in a rat model of embolic focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 32:2926–2931
Campbell B, Adams J, Shin YK, Lever AM (1999) Cardioprotective effects of a novel proteasome inhibitor following ischemia and reperfusion in the isolated perfused rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:467–476
Pye JP, Ardeshirpour F, McCain A, Bellinger DD, Merricks E, Adams J, Elliott PJ, Pien C, Fischer TH, Baldwin AS, Nichols TC (2002) Proteasome inhibition ablates activation of NF-kappaB induced during myocardial reperfusion and reduces reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol (in press)
Bao J, Sato K, Li M, Gao Y, Abid R, Aird W, Simons M, Post MJ (2001) PR-39 and PR-11 peptides inhibit ischemia-reperfusion injury by blocking proteasome-mediated I kappa B alpha degradation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H2612–H2618
Baldwin AS (1996) The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–683
Palombella VJ, Conner EM, Fuseler JW, Destree A, Davis JM, Laroux FS, Wolf RE, Huang J, Brand S, Elliott PJ, Lazarus D, McCormack T, Parent L, Stein R, Adams J, Grisham MB (1998) Role of the proteasome and NF-kappaB in streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15671–15676
Cromartie WJ, Craddock JC, Schwab JH, Anderie SK, Yang CH (1977) Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J Exp Med 146:1585–1602
Migita K, Tanaka F, Yamasaki S, Shibatomi K, Ida H, Kawakami A, Aoyagi T, Kawabe Y, Eguchi K (2001) Regulation of rheumatoid synoviocyte proliferation by endogenous p53 induction. Clin Exp Immunol 126:334–338
Busse WW (1998) Inflammation in asthma: the cornerstone of the disease and target of therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 102:S17–S22
Montefort S, Holgate ST, Howarth PH (1993) Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules and their role in bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis. Eur Respir J 6:1044–1054
Fujihara S, Ward C, Dransfield I, Hay RT, Uings IJ, Hayes B, Farrow SN, Haslett C, Rossi AG (2002) Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activation un-masks the ability of TNF-alpha to induce human eosinophil apoptosis. Eur J Immunol 32:457–466
Elliott PJ, Pien CS, McCormack TA, Chapman ID, Adams J (1999) Proteasome inhibition: a novel mechanism to combat asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 104:294–300
Paterson PY, Swanborg RH (1988) Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous systems. In: Sampter M, Talmage DW, Frank MM, Austen KF, Claman HN (eds) Immunological diseases. Little Brown, Boston, pp 1877–1916
Vanderlugt CL, Rahbe SM, Elliott PJ, Dal Cano MC, Miller SD (2000) Treatment of established relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with the proteasome inhibitor PS-519. J Autoimmunol 14:205–211
McRea BL, Vanderlugt CL, Dal Canto MC, Miller SD (1995) Functional evidence for epitope spreading in the relapsing pathology of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med 182:75–85
Hosseini H, Andre P, Lefevre N, Viala L, Walzer T, Peschanski M, Lotteau V (2001) Protection against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a proteasome modulator. J Neuroimmunol 30:233–244
Valdimarsson H, Baker BS, Jonsdottir I, Powles A, Fry L (1996) Psoriasis: a T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease induced by streptococcal superantigens? Immunol Today 16:145–149
Boehncke W-H (1996) Psoriasis and bacterial superantigens: formal or causal correlation? Trends Microbiol 4:485–48968
Robert C, Kupper TS (1999) Inflammatory skin diseases, T cells, and immune surveillance. N Engl J Med 341:1817–1828
Zollner TM, Podda M, Pien C, Elliott PJ, Kaufmann R, Boehncke W-H (2002) Proteasome inhibition reduces superantigen-mediated T cell activation and the severity of psoriasis in a SCID-hu model. J Clin Invest 109:671–679
Boehncke W-H, Sterry W, Hainzl A, Scheffold W, Kaufmann R (1994) Psoriasiform architecture of murine epidermis overlying human psoriatic dermis transplanted onto SCID mice. Arch Dermatol Res 286:325–330
Nickoloff BJ, Kunkel SL, Burdick M, Strieter RM (1995) Severe combined immunodeficiency mouse and human psoriatic skin chimeras. Validation of a new animal model. Am J Pathol 146:580–588
Boehncke W-H, Kock M, Hardt-Weinelt K, Wolter M, Kaufmann R (1999) The SCID-hu xenogeneic transplantation model allows screening of anti-psoriatic drugs. Arch Dermatol Res 291:104–106
Dam TM, Kang S, Nickoloff BJ, Voorhees JJ (1999) 1a,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol and cyclosporine suppress induction and promote resolution of psoriasis in human skin grafts transplanted onto SCID mice. J Invest Dermatol 113:1082–1089
Goldberg AL, Rock K (2002) Not just research tools—proteasome inhibitors offer therapeutic promise. Nat Med 8:338–340
Honda T, Yasutake K, Nihonmatsu N, Mercken M, Takahashi H, Murayama O, Murayama M, Sato K, Omori A, Tsubuki S, Saido TC, Takashima A (1999) Dual roles of proteasome in the metabolism of presenilin 1. J Neurochem 72:255–261
Hoffman EK, Wilcox HM, Scott RW, Siman R (1996) Proteasome inhibition enhances the stability of mouse Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase with mutations linked to familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sc 139:15–20
Vives-Pi M, Vargas F, James RFL, Trowsdale J, Costa M, Sospedra M, Somoza N, Obiols G, Tampe R, Pujol-Borelli R (1997) Proteasome subunits, low-molecular-mass polypeptides 2 and 7 are hyperexpressed by target cells in autoimmune thyroid disease but not in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: implications for autoimmunity. Tissue Antigens 50:153–163
Lazarus DD, Destree AT, Mazzola LM, McCormack TA, Dick LR, Xu B, Huang JQ, Pierce JW, Read MA, Coggins MB, Solomon V, Goldberg AL, Brand SJ, Elliott PJ (1999) A new model of cancer cachexia: contribution of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Am J Physiol 277:332–341
Whitehouse AS, Smith HJ, Drake JL, Tisdale MJ (2001) Mechanism of attenuation of skeletal muscle protein catabolism in cancer cachexia by eicosapentaenoic acid. Cancer Res 61:3604–3609
Groettrup M, Schmidtke G (1999) Selective proteasome inhibitors: modulators of antigen presentation? DDT 4:63–70
Sirma H, Weil R, Rosmorduc O, Urban S, Israel A, Kremsdorf D, Brechot C (1998) Cytosol is the prime compartment of hepatitis B virus X protein where it colocalizes with the proteasome. Oncogene 16:2051–2063
Robek MD, Wieland SF, Chisari FV (2002) Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by interferon requires proteasome activity. J Virol 76:3570–3574
Conner EM, Brand SJ, Davis JM, Kang DY, Grisham MB (1996) Role of reactive metabolites of oxygen and nitrogen in inflammatory bowel disease: toxins, mediators, and modulators of gene expression. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2:133–147
Conner EM, Brand S, Davis JM, Laroux FS, Palombella VJ, Fuseler JW, Kang DY, Wolf RE, Grisham MB (1997) Proteasome inhibition attenuates nitric oxide synthase expression, VCAM-1 transcription and the development of chronic colitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:1615–1622
Dijkstra G, Moshage H, Jansen PL (2002) Blockade of NF-kappaB activation and donation of nitric oxide: new treatment options in inflammatory bowel disease? Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl 236:37–41
Hasselgren PO, Fischer JE (1997) The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway: review of a novel intracellular mechanism of muscle protein breakdown during sepsis and other catabolic conditions. Ann Surg 225:307–316
Snyder JG, Prewitt R, Campsen J, Britt LD (2002) PDTC and MG-132, inhibitors of NF-kappaB, block endotoxin induced vasodilatation of isolated rat skeletal muscle arterioles. Shock 17:304–307
Feist E, Dorner T, Kuckelkorn U, Schmidtke G, Micheel B, Hiepe F, Burmester GR, Kloetzel PM (1996) Proteasome a-type subunit C9 is a primary target of autoantibodies in sera of patients with myositis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med 10:1313–1318
Elofsson M, Splittgerber U, Myung J, Mohan R, Crews CM (1999) Towards subunit-specific proteasome inhibitors: synthesis and evaluation of peptide alpha, "beta"-epoxyketones. Chem Biol 6:811–822
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
All authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elliott, P.J., Zollner, T.M. & Boehncke, WH. Proteasome inhibition: a new anti-inflammatory strategy. J Mol Med 81, 235–245 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-003-0422-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-003-0422-2