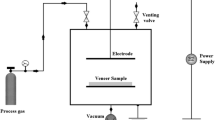
Abstract
In this study the effect of plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure of wood veneers on the curing behaviour of a PVAc adhesive was investigated. Time-dependent shear bond strength tests on untreated and plasma-treated maple (Acer pseudoplanatus), oak (Quercus sp.), beech (Fagus sylvatica) and teak (Tectona grandis) veneers were carried out. The results confirm that plasma treatment accelerated curing of the PVAc adhesive on the wood veneers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avramidis G, Hauswald E, Lyapin A, Militz H, Viöl W, Wolkenhauer A (2009) Plasma treatment of wood and wood-based materials to generate hydrophilic or hydrophobic surface characteristics. Wood Mater Sci Eng 4(12):52–60
Belgacem MN, Czeremuszkin G, Sapieha S, Gandini A (1995) Surface, characterization of cellulose fibres by XPS and inverse gas chromatography. Cellulose 2:145–157
Custódio J, Broughton J, Cruz H, Winfield P (2008) Activation of timber surfaces by flame and corona treatments to improve adhesion. Int J Adhes Adhes 29(2):167–172
Evans PD, Ramos M, Senden T (2007) Modification of wood using a glow-discharge plasma derived from water. In: Hill CAS, Jones D, Militz H, Ormondroyd GA (eds) The third European conference on wood modification (ECWM3), Biocomposites Centre, University of Wales, Bangor, pp 123–132
Klarhöfer L, Frerichs M, Maus-Friedrichs M, Kempter V, Viöl W (2005) Investigation of pure and plasma treated spruce with surface analytical techniques. In: Militz H, Hill CAS (eds) The second European conference on wood modification (ECWM2). University of Göttingen, Göttingen, pp 339–345
Kogelschatz U (2003) Dielectric-barrier discharges: their history, discharge physics, and industrial applications. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 23:1–46
Lecoq E, Clément F, Panousis E, Loiseau JF, Held B, Castetbon A, Guimon C (2008) Pinus pinaster surface treatment realized in spatial and temporal afterglow DBD conditions. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 42:47–53
Mantanis GI, Young RA (1997) Wetting of wood. Wood Sci Technol 31:339–353
Nguyen T, Johns WE (1979) The effects of aging and extraction on the surface free energy of Douglas fir and redwood. Wood Sci Technol 13:29–40
Nussbaum RM (1993) Oxidative activation of wood surfaces by flame treatment. Wood Sci Technol 27:183–193
Odrásková M, Ráhel J, Zahoranová A, Tino R, Cernák M (2008) Plasma activation of wood surface by diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28:203–211
Sakata I, Morita M, Tsuruta N, Morita K (1993) Activation of wood surfaces by corona treatment to improve adhesive bonding. J Appl Polym Sci 49:1251–1258
Topala I, Dumitrascu N (2007) Dynamics of the wetting process on dielectric barrier discharge (DBD)-treated wood surfaces. J Adhes Sci Technol 21:1089–1096
Uehara T, Sakata I (1990) Effect of corona discharge treatment on cellulose prepared from beech wood. J Appl Polym Sci 41:1695–1706
Vander Wielen LC, Östenson M, Gatenholm P, Ragauskas AJ (2006) Surface modification of cellulosic fibers using dielectric-barrier discharge. Carbohydr Polym 65:179–184
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Cai Y, Militz H, Viöl W (2007a) Investigation of wood and timber surface modification by dielectric barrier discharge at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Process Polym 4:470–474
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Militz H, Viöl W (2007b) Wood modification by atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. In: Hill CAS, Jones D, Militz H, Ormondroyd GA (eds) The third European conference on wood modification (ECWM3). Biocomposites Centre, University of Wales, Bangor, pp 271–274
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Hauswald E, Militz H, Viöl W (2009) Sanding vs. plasma treatment of aged wood: a comparison with respect to surface energy. Int J Adhes Adhes 29:18–22
Zeppenfeld G, Grunwald D (2005) Klebstoffe in der Holz- und Möbelindustrie. DRW, Leinfelden-Echterdingen
Acknowledgement
Financial support from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, 1708X08) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avramidis, G., Nothnick, E., Militz, H. et al. Accelerated curing of PVAc adhesive on plasma-treated wood veneers. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 69, 329–332 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-010-0429-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-010-0429-7