Abstract
The physical and mechanical properties (density, bending strength and stiffness) of 82 sawn pieces of Tali wood (Erythrophleum ivorense A. Chev., Erythrophleum suaveolens Brenan.) from Guinea and Cameroon were estimated using the EN 408 (2003) test standard. Timber pieces had a cross section of 80 mm×80 mm and 200 mm×250 mm and were visuallygraded according to British Standard BS 5756 (1997) in a single HS grade. The efficacy of this test was analyzed. The velocity of propagation of ultrasound waves had previously been measured by means of equipment specially designed for structural timber (Sylvatest Duo).
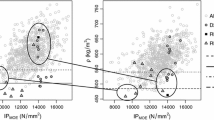
The results of visual grading according to BS 5756 (1997) show very low output with an excessive percentage of rejected pieces. Due to this, modifications are proposed to some of the specifications with the aim of reducing this percentage. Furthermore, visual grading does not facilitate to clearly separate the mechanical properties of HS grade and rejected pieces. The use of ultrasonic measurements shows good accuracy for the evaluation of stiffness properties, but not for strength. Visual grading makes it possible to reach a strength class of D50, while ultrasonic method could be used as an added parameter for grading.
Zusammenfassung
Die physikalischen und mechanischen Eigenschaften (Dichte, Biegefestigkeit und Steifigkeit) von 82 Tali-Kantholzstücken (Erythrophleum ivorense A. Chev., Erythrophleum suaveolens Brenan.) aus Guinea und Kamerun wurden nach der Prüfnorm EN 408 (2003) bestimmt. Die Holzstücke hatten einen Querschnitt von 80 mm×80 mm sowie 200 mm×250 mm und wurden nach der britischen Norm BS 5756 (1997) visuell in eine einzige HS-Klasse sortiert. Die Effizienz dieses Versuches wurde analysiert. Die Ausbreitungsgeschwindigkeit der Ultraschallwellen wurde vorher mittels einer speziell für Kantholz entworfenen Vorrichtung gemessen (Sylvatest Duo).
Die visuelle Sortierung nach BS 5756 (1997) ergab eine sehr geringe Ausbeute mit einem übermässig hohen Ausschussanteil. Um den Ausschussanteil zu reduzieren, wurden Veränderungen an der Spezifikation vorgeschlagen. Mit visueller Sortierung ist eine Trennung der mechanischen Eigenschaften der HS-Klasse und der Ausschussteile nicht eindeutig möglich. Mit Ultraschallmessungen können zwar die Steifigkeitseigenschaften präzise bestimmt werden, nicht aber die Festigkeitseigenschaften. Die Festigkeitsklasse D50 kann mit visueller Sortierung erreicht werden. Die Ultraschallmessung kann als zusätzlicher Sortierparameter eingesetzt werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekhta P, Niemz P, Kucera L (2000) The study of sound propagation in the wood-based composite materials. 12th International Symposium on Non-Destructive Testing of Wood, pp 33–42
Böstrom L (1994) Machine strength grading: comparison of four different systems. Swedish National Testing and Research Institute, Building Technology SP Report 49, pp 57
BS 5756 (1997) Specification for visual strength grading of hardwood
Bucur V, Archer RR (1984) Elastic constants for wood by an ultrasonic method. Wood Sci Technol 18:225–265
Centre Technique Forestier Tropical (1977) Fiche botanique et forestiére, industrielle et comerciale: Tali. Bois Forêts Trop 176:17–31
EN 384 (2004) Structural timber. Determination of characteristic values of mechanical properties and density
EN 408 (2003) Timber structures. Sawn timber and glued laminated timber for structural use. Determination of some physical and mechanical properties
EN 13183-1 (2002) Moisture content of a piece of sawn timber. Part 1: Determination by oven dry method
EN 13183-2 (2002) Moisture content of a piece of sawn timber. Part 2: Estimation by electrical resistance method
Guindeo A, García L, Peraza F, Arriaga F, Kasner C, Medina G, Palacios P, Touza M (1997) Especies de maderas para carpintería, construcción y mobiliario. AITIM, Madrid, Spain
Hermoso E, Fernández-Golfín JI, Díez MR (2003) Evaluación de la clasificación resistente de la madera estructural mediante ultrasonidos. 10o Congreso Nacional de Ensayos No Destructivos. Asociación Española de Ensayos No Destructivos, pp 187–195
Ross RJ, Hunt MO (2000) Stress wave timing non-destructive evaluation tools for inspecting historic structures. A guide for use and interpretation. Gen. Tech. Rep. FPL-GTR-119. Madison, WI: US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Product Laboratory, p 15
Sandoz JL (1989) Grading of construction timber by ultrasound. Wood Sci Technol 2:95–108
Van de Kuilen J-WG, Ravenshorst GJP (2002) Bending strength and stress wave grading of (tropical) hardwoods. Workshop: Probabilistic Modelling in Reliability Analysis of Timber Structures. Cost E24. ETH Zürich, Switzerland
Wang X, Ross RJ, Mattson JA, Erickson JR, Forsman JW, Geske EA, Wehr MA (2001) Several non-destructive evaluation techniques for assessing stiffness and moe of small-diameter logs. Res. Paper FPL-RP-600. Madison, WI: US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory, p 12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arriaga, F., Íñiguez, G., Esteban, M. et al. Structural Tali timber (Erythrophleum ivorense A. Chev., Erythrophleum suaveolens Brenan.): Assessment of strength and stiffness properties using visual and ultrasonic methods. Holz Roh Werkst 64, 357–362 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-006-0100-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-006-0100-5