Abstract
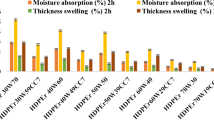
The main goal of this research is to innovate wood-plastic composites by using various wood particle sizes and different mixture ratios (weight ratio) of HDPE (High Density Polyethylene). After mixing the wood particles (recycled wood waste) and the plastic powder, we use a molding and pressing process to make composites with a thickness of 12 mm. By doing so, the wood particle content can be increased to 75%. This kind of composite provides excellent dimensional stability, its moisture content is under 2.5%, and the thickness swelling rate after 24 hr water absorption is under 7.5%. The maximum static bending strength of this composite reaches 20.7 N/mm2, and is better than that of general commercial particleboards. The composite made of larger sized wood particles has better strength properties. In addition, when the plastic content ratio increases, the dimensional stability of the composite will increase as well. After the soaking process in boiling water, the static bending strength of wet composite remained at 50%; this shows the good weather resistance of the composite. The surface veneer overlaid peeling strength of the composite showed 1.02–1.63 N/mm. After the evaluation of processing, cost of material and strength properties of the composite, we would suggest that the use of 70% of wood particles and 30% of plastic powder is practical to produce proper sized composites.
Zusammenfassung
Ziel dieser Untersuchung ist die Herstellung neuartiger Holz-Kunststoff-Verbundplatten durch Verwendung verschieden grosser Holzspäne und HDPE (Polyethylen – hoher Dichte) mit unterschiedlichen Mischungsverhältnissen (Masseanteilen). Nach dem Mischen der Holzspäne (recyceltes Holz) und des Kunststoffpulvers wurden durch Formen und Pressen 12 mm dicke Verbundplatten hergestellt. Dabei kann der Anteil der Holzpartikel auf 75% erhöht werden. Diese Verbundplatten verfügen über ausgezeichnete Dimensionsstabilität und einer Holzfeuchte unter 2,5%. Die Dickenquellung nach 24-stündiger Wasseraufnahme blieb unter 7,5%. Die maximale Biegefestigkeit dieser Verbundplatten betrug 20,7 N/mm2 und ist somit höher als diejenige handelsüblicher Spanplatten. Die aus grösseren Holzpartikeln hergestellten Verbundplatten weisen bessere Festigkeitseigenschaften auf. Die Dimensionsstabilität nimmt mit steigendem Kunststoffanteil zu. Nach Lagerung in kochendem Wasser betrug die Biegefestigkeit der nassen Verbundplatten noch 50%, was deren gute Wetterbeständigkeit verdeutlicht. Die Abhebefestigkeit der aufgeklebten Furniere lag zwischen 1.02–1.63 N/mm2. Nach Überprüfung des Herstellverfahrens, der Materialkosten sowie der Festigkeitseigenschaften der Verbundplatten hat sich ein Holzpartikelanteil von 70% und ein Kunststoffpulveranteil von 30% als für die Herstellung von Verbundplatten herkömmlicher Grösse praktikabel erwiesen.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Clemons CM, Ibach RE (2002) Laboratory Tests on Fungal Resistance of Wood Filled Polyethylene Composites. In: Annual Technical Conference, San Francisco, USA, pp 2219–2222
Clemons CM (2002) Wood-Plastic composites in the United States – The Interfacing of Two Industries. Forest Prod J 52(6):10–18
Nicole MS, Mark JB (1999) Effect of Particle Size on Properties of Wood-Flour Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. In: Fourth International conference on Wood fiber-Plastic composites, USA, pp 134–143
Peng WT, Hwang GS (1996) Research and Development of Wood/Plastic Composite Materials (V) Manufacturing and Property Comparisons of Waste Bamboo, Gum wood, and Palm Particles/PP Composite Boards. Taiwan Forest Research Institute. New Series 11(3):245–260
Shiue CY, Chen TY, Chen HC, Hsu CH (2001) Effect of LLDPE-MA Addition on the Properties of Wood Particle-LDPE Composites and Rice Hull-LDPE Composites. Forest Prod Ind 20(4):295–302
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Chen, T. & Hsu, C. Effects of Wood Particle Size and Mixing Ratios of HDPE on the Properties of the Composites. Holz Roh Werkst 64, 172–177 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-005-0072-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-005-0072-x