Pinus pinaster
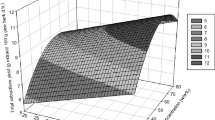
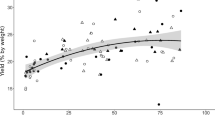
bark extracts obtained by lixiviation with water or alkaline solutions followed by spray drying. Extract yield was 2.5- to 6-fold higher with alkaline extractant solutions than with water. Within the ranges of temperature (T), NaOH dose (NaOH) and solid/liquid ratio (S/L) that were studied, the formaldehyde-condensable polyphenols content of spray-dried extracts obtained with NaOH as extractant was highest (27.3%) at T=90 °C, NaOH=5%, S/L=1/6. Polyphenols content fell with increasing particle size due to both diffusion limitations and the variation of particle composition with size, which is attributable to the dependence of both the chemical composition of the bark and its response to grinding on its anatomical origin. All the spray-dried extracts had Stiasny numbers high enough to allow their use in adhesives, although this application may require prior chemical modification to reduce the rapid rise in the viscosity of their aqueous solutions with increasing solids content. The reactivity of the extracts with formaldehyde is readily controlled by varying pH.
P. pinaster
wurden durch Auslaugen mit Wasser und Alkalien gewonnen. Nach Sprühtrocknen wurden ihre Eigenschaften bestimmt. Mit Alkalien ergaben sich 2,5- bis 6-fach höhere Ausbeuten als mit Wasser. Der Einfluß der Temperatur, des NaOH-Anteils und des Verhältnisses Festkörper zur Flüssigkeit (S/L) wurde untersucht. Der Anteil an Polyphenolen, die mit Formaldehyd kondensierbar sind, war am höchsten (27,3%) 90 °C, 5% NaOH und S/L=1/6. Der Polyphenolanteil wird niedriger mit steigender Partikelgröße. Die Gründe dafür sind die Begrenzung der Diffusion sowie die Variation der chemischen Zusammensetzung der Partikel, die sich entsprechend der anatomischen Herkunft beim Zerkleinern bilden. Die Stiasyn-Zahlen aller Extrakte waren ausreichend hoch für ihre Verwendung als Klebstoffe. Allerdings ist dafür eine chemische Modifizierung nötig, um den starken Anstieg der Viskosität der wässrigen Lösungen bei erhöhtem Feststoffgehalt zu verhindern. Die Reaktivität gegenüber Formaldehyd ist über den pH-Wert leicht einstellbar.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vázquez, G., González-Alvarez, J., Freire, S. et al. Characteristics of Pinus pinaster bark extracts obtained under various extraction conditions. Holz als Roh- und Werkstoff 59, 451–456 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-001-0246-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-001-0246-0