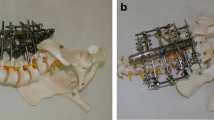
Summary.
Thirty-eight patients with 40 fractures of the thoracic spine and the thoracolumbar junction were treated by a minimally invasive procedure, which includes partial corporectomy, the interposition of a tricortical bone graft and anterior stabilization by plate spondylodesis under thoracosopic control. For 36 patients the operation was successfully performed in a complete thoracoscopic way; in 2 patients conversion to an open technique was necessary. Two postoperative complications such as a reversible lesion of the thoracodorsalis nerve and a transient irritation of nerve root L1 on the approach side were encountered. Postoperative control by X-ray and CT scan showed correct positioning of the bone graft, as well as the fixation device in all patients. Our experience with this minimally invasive stabilizing procedure for injuries of the thoracic spine and the thoracolumbar junction demonstrated the feasibility of the method. Compared to the open method the benefit of minimally invasive surgery included postoperative pain reduction, shorter hospitalization, early recovery of function and reduced mobidity of the operative approach.
Zusammenfassung.
Bei 38 Patienten mit insgesamt 40 Frakturen der Brustwirbelsäule und des thoracolumbalen Übergangs wurde die ventrale Fusion und Stabilisierung auf minimal-invasivem Weg vorgenommen. Das thoracoskopische Verfahren beinhaltet die Teilkorporektomie des verletzten Wirbelkörpers, die Interposition eines Knochenspans sowie die ventrale Stabilisierung mittels Plattenspondylodese. Bei 36 Patienten konnte die Operation auf minimal-invasivem Weg erfolgreich zu Ende geführt werden, 2malig erfolgte die Konversion zum offenen Verfahren. An postoperativen verfahrensbedingten Komplikationen wurde ein reversibler lagerungsbedingter Druckschaden des N. thoracodorsalis sowie eine vorübergehende Wurzelirritation auf der Zugangsseite verzeichnet. Die postoperative Röntgen- und CT-Kontrolle zeigte in allen Fällen eine regelrechte Span- und Implantatlage. Revisionsbedürftige Blutungen oder Infekte wurden nicht beobachtet. Unsere Erfahrungen mit der minimal-invasiven Methode zur Frakturenversorgung der Brustwirbelsäule und des thoracolumbalen Übergangs belegen zunächst die prinzipielle Machbarkeit der Methode. Gegenüber dem offenen Verfahren bestehen die wesentlichen Vorteile in der Reduktion des postoperativen Schmerzes, der raschen Erholung des Patienten, einer verkürzten Hospitalisierung und der reduzierten Zugangsmorbidität.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bühren, V., Beisse, R. & Potulski, M. Minimal-invasive ventrale Spondylodesen bei Verletzungen der Brust- und Lendenwirbelsäule. Chirurg 68, 1076–1084 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001040050326
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001040050326