Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to identify the incidence and risk factors of hardware-related complications in patients treated with anatomical locking plate fixation for extra-articular distal humerus fractures.
Methods
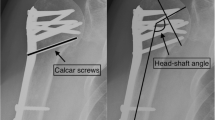
From 2013 to 2020, patients with extra-articular distal humerus fractures who underwent open reduction and internal fixation with an extra-articular distal humerus locking plate (EADHP) were retrospectively reviewed and categorized according to the presence/absence of hardware-related complications. Hardware-related complications were defined as the occurrence of skin prominence on the plate and discomfort in activities of daily living. Patient demographics, the lateral condylar angle, lateral body length, shaft-condylar angle of the humerus, and plate length were analyzed.
Results
Of the 29 patients, 10 (34%) did not develop hardware-related complications (group A), whereas 19 (66%) did (group B). Patient demographics did not differ between the groups. However, the number of patients who underwent hardware removal was significantly greater in group B (16/19) than in group A (4/10; p = 0.032). Radiologic assessment revealed no significant difference in the lateral condylar or shaft-condylar angle. However, the lateral body length was greater in group A than in group B (44.5 ± 4.8 vs. 39.5 ± 3.7, p = 0.007). The plate length significantly differed between the groups. Twelve of 19 (63%) patients in group B received short-hole plates (six holes), while nine of ten (90%) patients in group A received long-hole plates (eight holes). In the multivariable analysis, the lateral body length of the distal humerus (p = 0.047, odds ratio = 0.734, 95% confidence interval: 0.542–0.996) and plate length (p = 0.036, odds ratio = 0.076, 95% confidence interval: 0.542–0.996) were associated with hardware-related complications.
Conclusions
Most patients developed hardware-related complications, particularly with short plates, mainly because of the narrow lateral body length of the distal humerus. Surgeons should be careful to secure EADHP in the appropriate position, especially when short plates are used in patients with narrow lateral body length.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekholm R, Adami J, Tidermark J, Hansson K, Törnkvist H, Ponzer S. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus an epidemiological study of 401 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(11):1469–73.
Jain D, Goyal GS, Garg R, Mahindra P, Yamin M, Selhi HS. Outcome of anatomic locking plate in extraarticular distal humeral shaft fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2017;51(1):86–92. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.197554.
Scolaro JA, Voleti P, Makani A, Namdari S, Mirza A, Mehta S. Surgical fixation of extra-articular distal humerus fractures with a posterolateral plate through a triceps-reflecting technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(2):251–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2013.09.020.
Scolaro JA, Hsu JE, Svach DJ, Mehta S. Plate selection for fixation of extra-articular distal humerus fractures: a biomechanical comparison of three different implants. Injury. 2014;45(12):2040–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2014.08.036.
Meloy GM, Mormino MA, Siska PA, Tarkin IS. A paradigm shift in the surgical reconstruction of extra-articular distal humeral fractures: single-column plating. Injury. 2013;44(11):1620–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2013.07.005.
Yang KH, Park HW, Park SJ, Jung SH. Lateral J-plate fixation in comminuted intercondylar fracture of the humerus. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123(5):234–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-003-0508-x.
Capo JT, Debkowska MP, Liporace F, Beutel BG, Melamed E. Outcomes of distal humerus diaphyseal injuries fixed with a single-column anatomic plate. Int Orthop. 2014;38(5):1037–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-2213-x.
Matsunaga FT, Tamaoki MJ, Matsumoto MH, Netto NA, Faloppa F, Belloti JC. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis with a bridge plate versus a functional brace for humeral shaft fractures: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(7):583–92. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.16.00628.
Tejwani NC, Murthy A, Park J, McLaurin TM, Egol KA, Kummer FJ. Fixation of extra-articular distal humerus fractures using one locking plate versus two reconstruction plates: a laboratory study. J Trauma. 2009;66(3):795–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318181e53c.
Trikha V, Agrawal P, Das S, Gaba S, Kumar A. Functional outcome of extra-articular distal humerus fracture fixation using a single locking plate: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(3):2309499017727948. https://doi.org/10.1177/2309499017727948.
Zhou Z, Tang Z, Zhao X, Chen W, Chen X, Mu M, et al. Mismatch of AO anatomically shaped distal humeral plate with humeral shaft forward flexion angulation in adult Chinese population. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(7):1145–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-014-1431-2.
Lim JR, Yoon TH, Lee HM, Chun YM. Anatomic fit of precontoured extra-articular distal humeral locking plates: a cadaveric study. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2021;24(2):66–71. https://doi.org/10.5397/cise.2021.00227.
Goldfarb CA, Patterson JM, Sutter M, Krauss M, Steffen JA, Galatz L. Elbow radiographic anatomy: measurement techniques and normative data. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(9):1236–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2011.10.026.
Hanson B, van der Werken C, Stengel D. Surgeons’ beliefs and perceptions about removal of orthopaedic implants. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008;9:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-9-73.
Lovald S, Mercer D, Hanson J, Cowgill I, Erdman M, Robinson P, et al. Complications and hardware removal after open reduction and internal fixation of humeral fractures. J Trauma. 2011;70(5):1273–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318215bedd (discussion 7-8).
Lim JR, Yoon TH, Choi YR, Lee HM, Chun YM. Biomechanical evaluation of a modified proximal humeral locking plate application for distal extra-articular diaphyseal humeral fractures. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(9):1877–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.24925.
Sohn HS, Shin SJ. Modified use of a proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) plate in extra-articular distal-third diaphyseal humeral fractures. Injury. 2019;50(7):1300–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2019.05.030.
Saracco M, Smimmo A, De Marco D, Palmacci O, Malerba G, Vitiello R, et al. Surgical approach for fracture of distal humerus: Posterior vs lateral. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2020;12(Suppl 1):8664. https://doi.org/10.4081/or.2020.8664.
Lauder A, Richard MJ. Management of distal humerus fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(5):745–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-020-02626-1.
Lotzien S, Hoberg C, Rausch V, Rosteius T, Schildhauer TA, Gessmann J. Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral midshaft fractures: anterior versus posterior plate fixation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):527. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2888-2.
Zhiquan A, Bingfang Z, Yeming W, Chi Z, Peiyan H. Minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis (MIPO) of middle and distal third humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(9):628–33. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e31815928c2.
Levy JC, Kalandiak SP, Hutson JJ, Zych G. An alternative method of osteosynthesis for distal humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19(1):43–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-200501000-00008.
Ali N, Ahmad Mir N, Ahmad Dar T, Nawaz Rather M, Ahmad Mir W, S S, et al. Outcome of extra-articular distal humerus fractures fixed by single column extra-articular distal humerus locking compression plate using triceps sparing postero-lateral approach. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2018;6(4):306–12.
Conaway WK, Hennrikus WL, Ravanbakhsh S, Winthrop Z, Mahajan J. Surgical treatment of displaced pediatric lateral condyle fractures of the humerus by the posterior approach. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2018;27(2):128–33. https://doi.org/10.1097/bpb.0000000000000481.
Aktekin CN, Toprak A, Ozturk AM, Altay M, Ozkurt B, Tabak AY. Open reduction via posterior triceps sparing approach in comparison with closed treatment of posteromedial displaced Gartland type III supracondylar humerus fractures. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2008;17(4):171–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0b013e3283046530.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest related to this study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Owing to the retrospective study design using existing data from medical records, informed consent was not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, HS., Won, YS., Choi, YS. et al. Risk factors for hardware-related complications after extra-articular distal humerus fracture fixation using an anatomical locking plate. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 49, 125–131 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-022-02064-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-022-02064-0