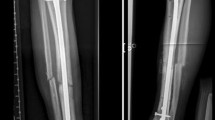
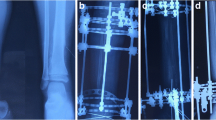
Abstract
Post-traumatic segmental bone defects of the femur and the tibia above the critical size require special attention because conventional bone grafts result in high rates of nonunion. The biological and biomechanical aspects of this challenging surgery, as well as ongoing refinements to achieve mechanically stable bone healing with correct bone alignment are reviewed. Choosing the best appropriate method is mainly dependent on both the location and etiology of the bone defect. Three patients with successful bone reconstruction using two-stage reconstruction with cancellous bone graft, double-barrel free vascularized fibula transfer and distraction osteogenesis are described. Advantages and disadvantages of these methods are discussed in accordance with recent literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evrard, J. Role of tibial-fibular grafting in the treatment of infected pseudarthrosis of the tibia. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 1992;78:389–98.
Osterman, AL, Bora, FW. Free vascularized bone grafting for large-gap nonunion of long bones. Orthop Clin North Am 1984;15:131–142.
DeCoster, TA, Gehlert, RJ, Mikola, EA, Pirela-Cruz, MA. Management of posttraumatic segmental bone defects. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2004;12:28–38.
Talbot, M, Zdero, R, Garneau, D, Cole, PA, Schemitsch, EH. Fixation of long bone segmental defects: a biomechanical study. Injury 2008;39:181–6.
Uhthoff, HK, Poitras, P, Backman, DS. Internal plate fixation of fractures: short history and recent developments. J Orthop Sci 2006;11:118–26.
Betz, AM, Hierner, R, Baumgart, R, Stock, W, Sebisch, E, Kettler, M, Schweiberer, L. Primary shortening-secondary lengthening. A new treatment concept for reconstruction of extensive soft tissue and bone injuries after 3rd degree open fracture and amputation of the lower leg. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 1998;30:30–9.
Pu, LL. Soft-tissue reconstruction of an open tibial wound in the distal third of the leg: a new treatment algorithm. Ann Plast Surg 2007;58:78–83.
Fischer, MD, Gustilo, RB, Varecka, TF. The timing of flap coverage, bone-grafting, and intramedullary nailing in patients who have a fracture of the tibial shaft with extensive soft-tissue injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1991;73:1316–22.
Cierny G 3rd, Byrd HS, Jones RE. Primary versus delayed soft tissue coverage for severe open tibial fractures. A comparison of results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1983;178:54–63.
Dedmond BT, Kortesis B, Punger K, Simpson J, Argenta J, Kulp B, Morykwas M, Webb LX. The use of negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT) in the temporary treatment of soft-tissue injuries associated with high-energy open tibial shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2007;21:11–17.
Parrett BM, Matros E, Pribaz JJ, Orgill DP. Lower extremity trauma: trends in the management of soft-tissue reconstruction of open tibia-fibula fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006;117:1315–1322 discussion 23-4.
Wu CC, Shih CH. Treatment of open femoral and tibial shaft fractures preliminary report on external fixation and secondary intramedullary nailing. J Formos Med Assoc 1991;90:1179–85.
McGraw JM, Lim EV. Treatment of open tibial-shaft fractures. External fixation and secondary intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1988;70:900–911.
Harwood PJ, Giannoudis PV, Probst C, Krettek C, Pape HC. The risk of local infective complications after damage control procedures for femoral shaft fracture. J Orthop Trauma 2006;20:181–9.
Magyar G, Toksvig-Larsen S, Moroni A. Hydroxyapatite coating of threaded pins enhances fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1997;79:487–9.
Zachee B, Roosen P, Mc Aechern AG. The dynamic axial fixator in fractures of the tibia and femur. A retrospective study in 98 patients. Acta Orthop Belg 1991;57:266–71.
Pape HC, Hildebrand F, Pertschy S, Zelle B, Garapati R, Grimme K, Krettek C, Reed RL 2nd. Changes in the management of femoral shaft fractures in polytrauma patients: from early total care to damage control orthopedic surgery. J Trauma 2002;53:452–461, discussion 61-2.
Keating JF, Simpson AH, Robinson CM. The management of fractures with bone loss. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2005;87: 142–150.
Papineau LJ. Excision-graft with deliberately delayed closing in chronic osteomyelitis. Nouv Presse Med 1973;2:2753–5.
Patzakis MJ, Greene N, Holtom P, Shepherd L, Bravos P, Sherman R. Culture results in open wound treatmentwith muscle transfer for tibial osteomyelitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;360:66–70.
Pelissier P, Martin D, Baudet J, Lepreux S, Masquelet AC. Behaviour of cancellous bone graft placed in induced membranes. Br J Plast Surg 2002;55:596–8.
Musharafieh R, Osmani O, Musharafieh U, Saghieh S, Atiyeh B. Efficacy of microsurgical free-tissue transfer in chronic osteomyelitis of the leg and foot: review of 22 cases. J Reconstr Microsurg 1999;15:239–244.
Weiland AJ, Phillips TW, Randolph MA. Bone grafts: a radiologic, histologic, and biomechanical model comparing autografts, allografts, and free vascularized bone grafts. Plast Reconstr Surg 1984;74:368–79.
Pelissier P, Boireau P, Martin D, Baudet J. Bone reconstruction of the lower extremity: complications and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 2003;111:2223–9.
Harding AK, Aspenberg P, Kataoka M, Bylski D, Tagil M. Manipulating the anabolic and catabolic response in bone graft remodeling: synergism by a combination of local BMP-7 and a single systemic dosis of zoledronate. J Orthop Res 2008;26:1245–9.
Little DG, Ramachandran M, Schindeler A. The anabolic and catabolic responses in bone repair. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2007;89:425–33.
Lieberman JR, Daluiski A, Einhorn TA. The role of growth factors in the repair of bone. Biology and clinical applications. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2002;84-A:1032–44.
Novicoff WM, Manaswi A, Hogan MV, Brubaker SM, Mihalko WM, Saleh KJ. Critical analysis of the evidence for current technologies in bone-healing and repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90:85–91.
Masquelet AC, Augereau B, Apoil A, Nordin JY. Treatment of compound fractures of the leg using pedicled or free muscle flaps and supplemental bone grafts. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 1987;73:118–21.
Pelissier P, Masquelet AC, Bareille R, Pelissier SM, Amedee J. Induced membranes secrete growth factors including vascular and osteoinductive factors and could stimulate bone regeneration. J Orthop Res 2004;22:73–9.
Gazdag A, Lane J, Glaser D, Forster R. Alternatives to autogenous bone graft: efficacy and indications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 1995;3:1–8.
Richards RR, Schemitsch EH. Effect of muscle flap coverage on bone blood flow following devascularization of a segment of tibia: an experimental investigation in the dog. J Orthop Res 1989;7:550–8.
Watson JT, Anders M, Moed BR. Management strategies for bone loss in tibial shaft fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1995;315:138–52.
Muramatsu K, Ihara K, Shigetomi M, Kawai S. Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts. Br J Plast Surg 2004;57:550–5.
Menezes-Leite MC, Dautel G, Duteille F, Lascombes P. Transplantation of the proximal fibula based on the anterior tibial artery. Anatomical study and clinical application. Surg Radiol Anat 2000;22:235–8.
Innocenti M, Ceruso M, Manfrini M, Angeloni R, Lauri G, Capanna R, Bufalini C. Free vascularized growth-plate transfer after bone tumor resection in children. J Reconstr Microsurg 1998;14:137–43.
Innocenti M, Delcroix L, Romano GF. Epiphyseal transplant: harvesting technique of the proximal fibula based on the anterior tibial artery. Microsurgery 2005;25:284–92.
Pelissier P, Casoli V, Demiri E, Martin D, Baudet J. Soleus-fibula free transfer in lower limb reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2000;105:567–73.
Lin CH, Wei FC, Lin YT, Yeh JT, Rodriguez Ede J, Chen CT. Lateral circumflex femoral artery system: warehouse for functional composite free-tissue reconstruction of the lower leg. J Trauma 2006;60:1032–6.
Weiland AJ. Vascularized bone transfers. Instr Course Lect 1984;33:446–60.
Yazar S, Lin CH, Wei FC. One-stage reconstruction of composite bone and soft-tissue defects in traumatic lower extremities. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004;114:1457–66.
Aronson J. Limb-lengthening, skeletal reconstruction, and bone transport with the Ilizarov method. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1997;79:1243–58.
Dahl MT, Gulli B, Berg T. Complications of limb lengthening. A learning curve. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1994;301:10–8.
Green SA, Harris NL, Wall DM, Ishkanian J, Marinow H. The Rancho mounting technique for the Ilizarov method. A preliminary report. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1992;280:104–16.
Aldegheri R. Distraction osteogenesis for lengthening of the tibia in patients who have limb-length discrepancy or short stature. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1999;81:624–34.
Hofmann GO, Gonschorek O, Buhren V. Segment transport employing intramedullary devices in tibial bone defects following trauma and infection. J Orthop Trauma 1999;13:170–7.
Knothe Tate ML, Ritzman TF, Schneider E, Knothe UR. Testing of a new one-stage bone-transport surgical procedure exploiting the periosteum for the repair of long-bone defects. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89:307–16.
McKee MD, Yoo DJ, Zdero R, Dupere M, Wild L, Schemitsch EH, Mahoney J. Combined single-stage osseous and soft tissue reconstruction of the tibia with the Ilizarov method and tissue transfer. J Orthop Trauma 2008;22:183–9.
Musharafieh RS, Saghieh SS, Nassar H, Hamdan AM, Hashim HA, Atiyeh BS. Microvascular soft-tissue coverage and distraction osteosynthesis for lower-extremity salvage. Microsurgery 1996;17:666–73.
Ring D, Jupiter JB, Gan BS, Israeli R, Yaremchuk MJ. Infected nonunion of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;369:302–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dumont, C.E., Exner, U.G. Reconstruction of Large Diaphyseal Defects of the Femur and the Tibia with Autologous Bone. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 35, 17–25 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-008-8224-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-008-8224-4