Abstract
Purpose
To determine whether rectal displacement devices (RDDs) have a prostate-stabilizing effect during prostate external beam radiotherapy (EBRT).
Methods
A systematic literature search using the PubMed database from January 1, 2000 to December 30th, 2019 was conducted. The effect of RDDs on inter- and intra-fractional prostate displacements was extracted.
Results
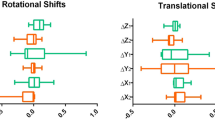
From 356 articles identified via the PubMed database and hand search, 21 articles were included in the systematic review. There was no randomized study. Twelve studies evaluated the role of the endorectal balloon (ERB) in managing prostate motion. Four studies reported the effect of hydrogel spacer on prostate motion. Four studies examined the effect of the rectal retractor (RR) on intra-fractional prostate motion, and only one study assessed the impact of ProSpare (Nottinghamshire, UK) in reducing prostate motion.
Conclusion
Using an ERB significantly reduces intra-fractional prostate motion. This prostate-stabilizing effect of the ERB can translate into reduced planning target volume (PTV) margins and additional rectal dose sparing. Even with an ERB in place, inter-fractional prostate displacements are seen. As a consequence, ERB application does not obviate daily verification; however, this is not a crucial topic because pretreatment imaging is always done nowadays. As compared with ERB, the hydrogel spacer significantly reduces rectal dose and toxicity without influencing prostate immobilization. The RR can increase prostate and rectal inter- and intra-fractional stability without a clear influence on the reduction of rectal toxicity. Finally, it is unclear whether ProSpare is a suitable device reducing prostate motion. Further study will be required to clarify whether the prostate-stabilizing effects of the ERB and RR can result in a safe reduction of PTV margins and further sparing of organs at risks, especially the rectum.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mamgani A, Heemsbergen WD, Peeters ST, Lebesque JV (2009) Role of intensity-modulated radiotherapy in reducing toxicity in dose escalation for localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:685–691
Dearnaley DP, Sydes MR, Graham JD, Aird EG, Bottomley D, Cowan RA et al (2014) Escalated-dose versus standard-dose conformal radiotherapy in prostate cancer: first results from the MRC RT01 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 8:475–487
King CR, Brooks JD, Gill H, Presti JC Jr (2012) Long-term outcomes from a prospective trial of stereotactic body radiotherapy for low-risk prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:877–882
Ruggieri R, Naccarato S, Stavrev P, Stavreva N, Fersino S, Giaj Levra N et al (2015) Volumetric-modulated arc stereotactic body radiotherapy for prostate cancer: dosimetric impact of an increased near-maximum target dose and of a rectal spacer. Br J Radiol 88:20140736
Yu T, Zhang Q, Zheng T, Shi H, Liu Y, Feng S et al (2016) The effectiveness of intensity modulated radiation therapy versus three-dimensional radiation therapy in prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of the literatures. PLoS ONE 11:e154499
Wang KK, Vapiwala N, Bui V, Deville C, Plastaras JP, Bar-Ad V et al (2014) The impact of stool and gas volume on intrafraction prostate motion in patients undergoing radiotherapy with daily endorectal balloon. Radiother Oncol 112:89–94
Yartsev S, Bauman G (2016) Target margins in radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Br J Radiol 89:20160312
Ghadjar P, Fiorino C, Munck Af Rosenschold P, Pinkawa M, Zilli T, van der Heide UA (2019) ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline on the use of image guided radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol 141:5–13
Das S, Liu T, Jani AB, Rossi P, Shelton J, Shi Z et al (2014) Comparison of image-guided radiotherapy technologies for prostate cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 37:616–623
Ghaffari H, Navaser M, Mofid B, Mahdavi SR, Mohammadi R, Tavakol A (2019) Fiducial markers in prostate cancer image-guided radiotherapy. Med J Islam Repub Iran 33:15
van Lin EN, Hoffmann AL, van Kollenburg P, Leer JW, Visser AG (2005) Rectal wall sparing effect of three different endorectal balloons in 3D conformal and IMRT prostate radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:565–576
Mariados N, Sylvester J, Shah D, Karsh L, Hudes R, Beyer D et al (2015) Hydrogel spacer prospective multicenter randomized controlled pivotal trial: dosimetric and clinical effects of perirectal spacer application in men undergoing prostate image guided intensity modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 92:971–977
Pinkawa M, Berneking V, Konig L, Frank D, Bretgeld M, Eble MJ (2017) Hydrogel injection reduces rectal toxicity after radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 193:22–28
Pinkawa M, Piroth MD, Holy R, Escobar-Corral N, Caffaro M, Djukic V et al (2012) Quality of life after intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer with a hydrogel spacer. Matched-pair analysis. Strahlenther Onkol 188:917–925
Pinkawa M, Schubert C, Escobar-Corral N, Holy R, Eble MJ (2015) Application of a hydrogel spacer for postoperative salvage radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 191:375–379
Afkhami Ardekani M, Ghaffari H (2020) Optimization of prostate brachytherapy techniques with polyethylene glycol-based hydrogel spacers: a systematic review. Brachytherapy 19:13–23
Mahdavi SR, Ghaffari H, Mofid B, Rostami A, Reiazi R, Janani L (2019) Rectal retractor application during image-guided dose-escalated prostate radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 195:923–933
Ghaffari H (2019) Rectal wall delineation in patients with a rectal displacement device in place during prostate cancer radiotherapy. J Radiat Oncol 8:103–104
Ghaffari H (2019) Is there a role for hydrogel spacer in post-prostatectomy radiotherapy setting? Radiol Med 124:1062–1063
Ghaffari H, Mahdavi S, Mofid B, Reiazi R (2018) Rectal sparing using a rectal retractor during dose escalated prostate radiotherapy. Med Phys 45:E254
Murray J, Gulliford S, Alexander E, McNair H, Dearnaley D (2014) P028 the effect of ProSpare, a rectal obturator on anorectal doses in prostate radiotherapy. Eur Urol 13:119
Both S, Wang KK, Plastaras JP, Deville C, Bar Ad V, Tochner Z et al (2011) Real-time study of prostate intrafraction motion during external beam radiotherapy with daily endorectal balloon. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:1302–1309
El-Bassiouni M, Davis JB, El-Attar I, Studer GM, Lutolf UM, Ciernik IF (2006) Target motion variability and on-line positioning accuracy during external-beam radiation therapy of prostate cancer with an endorectal balloon device. Strahlenther Onkol 182:531–536
Hung AY, Garzotto M, Kaurin D (2011) Minimal benefit of an endorectal balloon for prostate immobilization as verified by daily localization. Med Dosim 36:195–199
McGary JE, Teh BS, Butler EB, Grant W 3rd (2002) Prostate immobilization using a rectal balloon. J Appl Clin Med Phys 3:6–11
Smeenk RJ, Louwe RJ, Langen KM, Shah AP, Kupelian PA, van Lin EN et al (2012) An endorectal balloon reduces intrafraction prostate motion during radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:661–669
Takayama K, Mizowaki T, Negoro Y, Norihisa Y, Hiraoka M (2011) Impact of double-balloon rectal catheter use in external-beam radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 16:50–56
Teh BS, McGary JE, Dong L, Mai WY, Carpenter LS, Lu HH et al (2002) The use of rectal balloon during the delivery of intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) for prostate cancer: more than just a prostate gland immobilization device? Cancer 8:476–483
van Lin EN, van der Vight LP, Witjes JA, Huisman HJ, Leer JW, Visser AG (2005) The effect of an endorectal balloon and off-line correction on the interfraction systematic and random prostate position variations: a comparative study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 61:278–288
Vargas C, Saito AI, Hsi WC, Indelicato D, Falchook A, Zengm Q et al (2010) Cine-magnetic resonance imaging assessment of intrafraction motion for prostate cancer patients supine or prone with and without a rectal balloon. Am J Clin Oncol 33:11–16
Wachter S, Gerstner N, Dorner D, Goldner G, Colotto A, Wambersie A et al (2002) The influence of a rectal balloon tube as internal immobilization device on variations of volumes and dose-volume histograms during treatment course of conformal radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 52:91–100
Wang KK, Vapiwala N, Deville C, Plastaras JP, Scheuermann R, Lin H et al (2012) A study to quantify the effectiveness of daily endorectal balloon for prostate intrafraction motion management. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:1055–1063
Hedrick SG, Fagundes M, Robison B, Blakey M, Renegar J, Artz M et al (2017) A comparison between hydrogel spacer and endorectal balloon: an analysis of intrafraction prostate motion during proton therapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 18:106–112
Juneja P, Kneebone A, Booth JT, Thwaites DI, Kaur R, Colvill E et al (2015) Prostate motion during radiotherapy of prostate cancer patients with and without application of a hydrogel spacer: a comparative study. Radiat Oncol 10:215
Picardi C, Rouzaud M, Kountouri M, Lestrade L, Vallee JP, Caparrotti F et al (2016) Impact of hydrogel spacer injections on interfraction prostate motion during prostate cancer radiotherapy. Acta Oncol 55:834–838
Pinkawa M, Piroth MD, Holy R, Escobar-Corral N, Caffaro M, Djukic V et al (2013) Spacer stability and prostate position variability during radiotherapy for prostate cancer applying a hydrogel to protect the rectal wall. Radiother Oncol 106:220–224
de Leon J, Jameson MG, Rivest-Henault D, Keats S, Rai R, Arumugam S et al (2019) Reduced motion and improved rectal dosimetry through endorectal immobilization for prostate stereotactic body radiotherapy. Br J Radiol 92:20190056
Legge K, Nguyen D, Ng JA, Wilton L, Richardson M, Booth J et al (2017) Real-time intrafraction prostate motion during linac based stereotactic radiotherapy with rectal displacement. J Appl Clin Med Phys 18:130–136
Nicolae A, Davidson M, Easton H, Helou J, Musunuru H, Loblaw A et al (2015) Clinical evaluation of an endorectal immobilization system for use in prostate hypofractionated stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy (SABR). Radiat Oncol 10:122
Vanhanen A, Kapanen M (2016) The effect of rectal retractor on intrafraction motion of the prostate. Biomed Phys Eng Express 2:35021
Murray J, McNair H, Alexander E, Thomas K, Dearnaley D (2016) ProSpare, a rectal obturator and its effect on prostate and seminal vesicle Interfraction motion. Clin Oncol 28:e13–e4
Hamstra DA, Mariados N, Sylvester J, Shah D, Karsh L, Hudes R et al (2017) Continued benefit to rectal separation for prostate radiation therapy: final results of a phase III trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 97:976–985
Pinkawa M, Bornemann C, Escobar-Corral N, Piroth MD, Holy R, Eble MJ (2013) Treatment planning after hydrogel injection during radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 189:796–800
Ghaffari H (2020) Re: placement of spaceOAR hydrogel spacer for prostate cancer patients treated with iodine-125 low-dose-rate brachytherapy. Int J Urol. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.14209
Ghaffari H, Afkhami Ardekani M, Molana SH, Haghparast M, Sanei M, Mahdavi SR et al (2019) Application of rectal retractor for postprostatectomy salvage radiotherapy of prostate cancer: a case report and literature review. Clin Case Rep 7:2102–2107
Alexander E, McNair H, Landeg S, Hansen V, Dearnaley D (2014) Initial results of a prospective clinical trial examining a novel rectal obturator to localise the prostate and spare the rectum during radical prostate radiotherapy. Clin Oncol 26:e3
Smeenk RJ, Teh BS, Butler EB, van Lin EN, Kaanders JH (2010) Is there a role for endorectal balloons in prostate radiotherapy? A systematic review. Radiother Oncol 95:277–282
Maruoka S, Yoshioka Y, Isohashi F, Suzuki O, Seo Y, Otani Y et al (2015) Correlation between patients’ anatomical characteristics and interfractional internal prostate motion during intensity modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer. SpringerPlus 4:579
Bayley AJ, Catton CN, Haycocks T, Kelly V, Alasti H, Bristow R et al (2004) A randomized trial of supine vs. prone positioning in patients undergoing escalated dose conformal radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol 70:37–44
Wilder RB, Chittenden L, Mesa AV, Bunyapanasarn J, Agustin J, Lizarde J et al (2010) A prospective study of intrafraction prostate motion in the prone vs. supine position. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:165–170
Steenbakkers RJ, Duppen JC, Betgen A, Lotz HT, Remeijer P, Fitton I et al (2004) Impact of knee support and shape of tabletop on rectum and prostate position. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60:1364–1372
Jones BL, Gan G, Kavanagh B, Miften M (2013) Effect of endorectal balloon positioning errors on target deformation and dosimetric quality during prostate SBRT. Phys Med Biol 58:7995–8006
Wang CW, Chong FC, Lai MK, Pu YS, Wu JK, Cheng JC (2007) Set-up errors due to endorectal balloon positioning in intensity modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol 84:177–184
Wootton LS, Kudchadker RJ, Beddar AS, Lee AK (2012) Effectiveness of a novel gas-release endorectal balloon in the removal of rectal gas for prostate proton radiation therapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 13:3945
Benjamin LC, Tree AC, Dearnaley DP (2017) The role of hypofractionated radiotherapy in prostate cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 19:30
Parsai EI, Jahadakbar A, Lavvafi H, Elahinia M (2019) A novel and innovative device to retract rectum during radiation therapy of pelvic tumors. J Appl Clin Med Phys 20:194–199
Isacsson U, Nilsson K, Asplund S, Morhed E, Montelius A, Turesson I (2010) A method to separate the rectum from the prostate during proton beam radiotherapy of prostate cancer patients. Acta Oncol 49:500–505
Dang A, Kupelian PA, Cao M, Agazaryan N, Kishan AU (2018) Image-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Transl Androl Urol 7:308–320
Zelefsky MJ, Kollmeier M, Cox B, Fidaleo A, Sperling D, Pei X et al (2012) Improved clinical outcomes with high-dose image guided radiotherapy compared with non-IGRT for the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 84:125–129
Valeriani M, Bracci S, Osti MF, Falco T, Agolli L, De Sanctis V et al (2013) Intermediate-risk prostate cancer patients treated with androgen deprivation therapy and a hypofractionated radiation regimen with or without image guided radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 8:137
van Lin EN, Kristinsson J, Philippens ME, de Jong DJ, van der Vight LP, Kaanders JH et al (2007) Reduced late rectal mucosal changes after prostate three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy with endorectal balloon as observed in repeated endoscopy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:799–811
Wortel RC, Heemsbergen WD, Smeenk RJ, Witte MG, Krol SDG, Pos FJ et al (2017) Local protocol variations for image guided radiation therapy in the multicenter Dutch hypofractionation (HYPRO) trial: impact of rectal balloon and MRI delineation on anorectal dose and gastrointestinal toxicity levels. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99:1243–1252
Krol R, McColl GM, Hopman WPM, Smeenk RJ (2018) Anal and rectal function after intensity-modulated prostate radiotherapy with endorectal balloon. Radiother Oncol 128:364–368
te Velde BL, Westhuyzen J, Awad N, Wood M, Shakespeare TP (2019) Late toxicities of prostate cancer radiotherapy with and without hydrogel SpaceAOR insertion. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 63:836–841
Dinh TT, Lee HJ Jr., Macomber MW, Apisarnthanarax S, Zeng J, Laramore GE et al (2020) Rectal hydrogel spacer improves late gastrointestinal toxicity compared to rectal balloon immobilization after proton beam radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer: a retrospective observational study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.01.026
Johansson S, Astrom L, Sandin F, Isacsson U, Montelius A, Turesson I (2012) Hypofractionated proton boost combined with external beam radiotherapy for treatment of localized prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer 2012:654861
Schörghofer A, Drerup M, Kunit T, Lusuardi L, Holzinger J, Karner J et al (2019) Rectum-spacer related acute toxicity—endoscopy results of 403 prostate cancer patients after implantation of gel or balloon spacers. Radiat Oncol 14:47
Ghaffari H, Afkhami Ardekani M, Refahi S (2020) In regard to ‘what is the quality of hydrogel spacer insertions? and which patients will benefit? A literature review. J Radiother Pract. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1460396920000035
Goldner G, Tomicek B, Becker G, Geinitz H, Wachter S, Zimmermann F et al (2007) Proctitis after external-beam radiotherapy for prostate cancer classified by Vienna rectoscopy score and correlated with EORTC/RTOG score for late rectal toxicity: results of a prospective multicenter study of 166 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:78–83
Deville C, Both S, Bui V, Hwang WT, Tan KS, Schaer M et al (2012) Acute gastrointestinal and genitourinary toxicity of image-guided intensity modulated radiation therapy for prostate cancer using a daily water-filled endorectal balloon. Radiat Oncol 7:76
Teh BS, Lewis GD, Mai W, Pino R, Ishiyama H, Butler EB (2018) Long-term outcome of a moderately hypofractionated, intensity-modulated radiotherapy approach using an endorectal balloon for patients with localized prostate cancer. Cancer Commun 38:11
Uhl M, van Triest B, Eble MJ, Weber DC, Herfarth K, De Weese TL (2013) Low rectal toxicity after dose escalated IMRT treatment of prostate cancer using an absorbable hydrogel for increasing and maintaining space between the rectum and prostate: results of a multi-institutional phase II trial. Radiother Oncol 106:215–219
Hwang ME, Mayeda M, Liz M, Goode-Marshall B, Gonzalez L, Elliston CD et al (2019) Stereotactic body radiotherapy with periprostatic hydrogel spacer for localized prostate cancer: toxicity profile and early oncologic outcomes. Radiat Oncol 14:136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M.A. Ardekani, H. Ghaffari, M. Navaser, S.H.Z. Moghaddam, and S. Refahi declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afkhami Ardekani, M., Ghaffari, H., Navaser, M. et al. Effectiveness of rectal displacement devices in managing prostate motion: a systematic review. Strahlenther Onkol 197, 97–115 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-020-01633-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-020-01633-9