Purpose:
To evaluate the potential benefit of proton therapy and photon based intensity-modulated radiotherapy in comparison to 3-D conformal photon radiotherapy (3D-CRT) in locally advanced cervix cancer.
Patients and Methods:
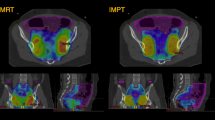
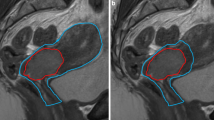
In five patients with advanced cervix cancer 3D-CRT (four-field box) was compared with intensity modulated photon (IMXT) and proton therapy (IMPT) as well as proton beam therapy (PT) based on passive scattering. Planning target volumes (PTVs) included primary tumor and pelvic and para-aortic lymph nodes. Dose-volume histograms (DVHs) were analyzed for the PTV and various organs at risk (OARs) (rectal wall, bladder, small bowel, colon, femoral heads, and kidneys). In addition dose conformity, dose inhomogeneity and overall volumes of 50% isodoses were assessed.
Results:
All plans were comparable concerning PTV parameters. Large differences between photon and proton techniques were seen in volumes of the 50% isodoses and conformity indices. DVH for colon and small bowel were significantly improved with PT and IMPT compared to IMXT, with Dmean reductions of 50–80%. Doses to kidneys and femoral heads could also be substantially reduced with PT and IMPT. Sparing of rectum and bladder was superior with protons as well but less pronounced.
Conclusion:
Proton beam RT has significant potential to improve treatment related side effects in the bowel compared to photon beam RT in patients with advanced cervix carcinoma.
Ziel:
Im Rahmen einer planungstechnischen Studie wurden die potentiellen Vorteile der Protonentherapie und der intensitätsmodulierten Photonentherapie (IMXT) im Vergleich zur konformalen Photontherapie bei der Behandlung des fortgeschrittenen Zervixkarzinoms bewertet.
Patienten und Methodik:
Bei fünf Patientinnen mit fortgeschrittenem Zervixkarzinom wurde eine konformale Vier-Felder-Photonentechnik mit einer Photonen basierten intensitätsmodulierten Radiotherapietechnik sowie Protonentherapie basierend auf Scanning (IMPT) bzw. passiver Aufstreuung (PT) verglichen. Die Planungszielgebiete (PTV) umfassten Lymphknotenstationen im Beckenbereich sowie in der Paraaortalregion. Mittels Dosis-Volumen-Histogramm-(DVH-)Analysen wurde die Belastung der Risikoorgane (Rektumwand, Harnblase, Hüftköpfe und Nieren, Dick- und Dünndarm) sowie die Auslastung des PTV bewertet. Zusätzlich wurden die Gesamtvolumina der 50%-Isodose sowie die Dosiskonformität und Dosishomogenität im PTV bewertet.
Ergebnisse:
Alle Bestrahlungspläne zeigten hinsichtlich der PTV-Auswertungsparameter vergleichbare Werte. Die größten Unterschiede zwischen den Photon- und Protonentechniken ergaben sich für die Volumina der 50%-Isodose und die Konformitätsindices. Im Vergleich zur Photonentherapie ergaben sich für PT und IMPT signifikant niedrigere gemittelte Dosiswerte (~ 50–80%) für den Dickdarm sowie den Dünndarm. Die Dosisbelastung der Nieren und der Hüftköpfe konnte mit Hilfe beider Protonentechniken ebenfalls wesentlich verringert werden. Die Unterschiede zwischen den Photonen- und Protonentechniken waren für die Risikoorgane Rektum und Blase weniger ausgeprägt.
Schlussfolgerung:
Im Vergleich zur Photonentherapie konnte mit Hilfe der Protonentherapie die Dosisbelastung am Darm signifikant reduziert werden. Diese verbesserte Darmschonung könnte zu einer Reduktion therapieassoziierter Nebenwirkungen bei der Behandlung des fortgeschrittenen Zervixkarzinoms führen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georg, D., Georg, P., Hillbrand, M. et al. Assessment of Improved Organ at Risk Sparing for Advanced Cervix Carcinoma Utilizing Precision Radiotherapy Techniques. Strahlenther Onkol 184, 586–591 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-008-1872-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-008-1872-9