Purpose:
It was investigated whether the elementary EORTC/RTOG-CTC score (Common Toxicity Criteria) for radiotherapy skin reactions correlates with spectrophotometric measurements of the skin color.
Patients, Material, and Methods:
In 41 patients irradiated for unilateral breast cancer the regular scoring by CTC was done during radiotherapy. In parallel, a total of 4,920 spectrophotometric measurements to determine the skin color were performed at baseline, at the beginning of radiotherapy, and at 20, 40 and 60 Gy. The nonirradiated contralateral breast was used for control measurements.
Results:
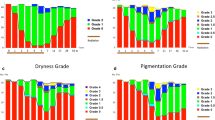
As expected, the skin color (especially red) depended on the radiation dose applied to the skin. The objective spectrophotometric measurements were found to correlate well with the subjective CTC scores.
Conclusion:
For classification of acute radiation toxicity there seems to be no need to replace the common CTC scoring by technical methods.
Ziel:
Es wurde untersucht, ob der einfach zu handhabende EORTC/RTOG-CTC-Score („Common Toxicity Criteria“) zur Bestimmung der Hauttoxizität einer Strahlentherapie mit spektralphotometrischen Messungen der Hautfarbe korreliert.
Patienten, Material und Methodik:
Bei 41 Patientinnen, die wegen eines unilateralen Mammakarzinoms bestrahlt wurden, wurde während der Strahlentherapie regelmäßig der CTC-Score für die Haut im Strahlenfeld erhoben. Parallel dazu wurden insgesamt 4 920 spektralphotometrische Messungen der Hautfarbe bei Studieneinschluss sowie vor Beginn der Bestrahlung und bei 20, 40 und 60 Gy durchgeführt. Die nicht bestrahlte kontralaterale Brust diente als Kontrolle.
Ergebnisse:
Erwartungsgemäß war die Hautfarbe von der Strahlendosis an der Haut abhängig (Abbildung 1). Die Ergebnisse der spektralphotometrischen Messungen korrelierten stark mit den subjektiven Bewertungen anhand der CTC-Klassifikation (Abbildung 2).
Schlussfolgerung:
Bei der Bewertung akuter Strahlennebenwirkungen scheint es keine Notwendigkeit zu geben, die bewährte CTC-Klassifikation durch technische Messmethoden zu ersetzen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
*F.M. and S.B. contributed equally as first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momm*, F., Bartelt*, S., Haigis, K. et al. Spectrophotometric Skin Measurements Correlate with EORTC/RTOG-Common Toxicity Criteria. Strahlenther Onkol 181, 392–395 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-005-1345-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-005-1345-3