Background and Purpose:
The role of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) alone or in combination with whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) in the treatment of cerebral metastases from breast carcinoma is discussed controversially. To elucidate the role of SRS in this context, a retrospective study evaluating the benefit of SRS and prognostic factors for survival was performed.
Patients and Methods:
From 1986 to 2003, 62 patients with cerebral metastases from breast cancer were treated for 103 lesions. Ten patients received SRS alone (group 1), 13 patients were treated with WBRT and SRS as a focal boost (group 2), and 39 patients received WBRT and salvage SRS (group 3) for recurrent metastases at a later time point.
Results:
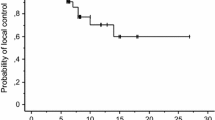
Survival was increased in patients receiving SRS only compared to WBRT and SRS as a focal boost. Patients < 40 years of age had a favorable outcome (p > 0.04). However, no other prognostic factors could be identified. Overall tolerance of radiation was acceptable. Median local control intervals were 9 months for all patients, 6.5 months in group 1, 4 months in group 2, and 9 months in group 3, respectively. There were no significant intergroup differences.
Conclusion:
SRS alone is an effective treatment for patients with one to three brain metastases from breast cancer. A randomized trial should be performed to evaluate whether WBRT is a necessary component in the primary treatment of these patients. Salvage SRS is an effective therapy option after WBRT.
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Die Behandlung zerebraler Metastasen des Mammakarzinoms mit stereotaktischer Radiochirurgie (SRS) allein oder in Kombination mit einer Ganzhirnbestrahlung (WBRT) wird derzeit kontrovers diskutiert. Um die Vorteile der SRS in diesem Kontext und den Einfluss von prognostischen Faktoren auf das Gesamtüberleben zu evaluieren, wurde eine retrospektive Analyse durchgeführt.
Patienten und Methodik:
Zwischen 1986 und 2003 wurden 62 Patientinnen mit 103 Hirnmetastasen bei Brustkrebs behandelt. Zehn Patientinnen erhielten eine alleinige SRS (Gruppe 1), 13 Patientinnen wurden mit WBRT und SRS (fokaler Boost) behandelt (Gruppe 2), und 39 Patientinnen erhielten eine WBRT und eine Salvage-SRS (Gruppe 3) bei Progredienz der Metastasen zu einem späteren Zeitpunkt.
Ergebnisse:
Das mediane Gesamtüberleben war in der Gruppe, die mit alleiniger SRS behandelt wurde, tendenziell erhöht im Vergleich zu der Gruppe, die eine WBRT mit SRS als fokalem Boost erhalten hatte. Bei Patientinnen < 40 Jahren war das Gesamtüberleben signifikant besser (p > 0,04). Es konnten keine weiteren prognostischen Faktoren identifiziert werden. Die Strahlentherapie wurde von allen Patientinnen gut toleriert. Die mediane lokale Kontrolle lag bei 9 Monaten für alle Patientinnen, 6,5 Monaten in Gruppe 1, 4 Monaten in Gruppe 2 and 9 Monaten in Gruppe 3. Es gab keine signifikanten Unterschiede zwischen den einzelnen Gruppen.
Schlussfolgerung:
Die alleinige SRS ist eine effektive Behandlungsmethode für Patientinnen mit ein bis drei Hirnmetastasen bei Mammakarzinom. Eine randomisierte Studie zur weiteren Evaluation der Notwendigkeit einer WBRT bei diesen Patientinnen sollte durchgeführt werden. Die Salvage-SRS ist eine effektive Therapieoption bei progredienten Hirnmetastasen nach einer WBRT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Combs, S.E., Schulz-Ertner, D., Thilmann, C. et al. Treatment of Cerebral Metastases from Breast Cancer with Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Strahlenther Onkol 180, 590–596 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-004-1299-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-004-1299-x
Key Words:
- Brain metastases
- Breast cancer
- Whole brain radiation therapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Local control
- Overall survival