Background and Purpose:
Precise reproducible patient positioning is a prerequisite for conformal fractionated radiotherapy. A fixation system based on double-vacuum technology is presented which can be used for conventional as well as hypofractionated stereotactic extracranial radiotherapy.
Material and Methods:
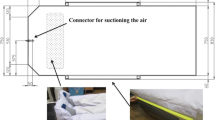
To form the actual vacuum mattress, the patient is pressed into the mattress with a vacuum foil which can also be used for daily repositioning and fixation. A stereotactic frame can be positioned over the region of interest on an indexed base plate. Repositioning accuracy was determined by comparing daily, pretreatment, orthogonal portal images to the respective digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) in ten patients with abdominal and pelvic lesions receiving extracranial fractionated (stereotactic) radiotherapy. The three-dimensional (3-D) vectors and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated from the respective deviations in the three axes. Time required for initial mold production and daily repositioning was also determined.
Results:
The mean 3-D repositioning error (187 fractions) was 2.5 ± 1.1 mm. The largest single deviation (10 mm) was observed in a patient treated in prone position. Mold production took an average of 15 min (10–30 min). Repositioning times are not necessarily longer than using no positioning aid at all.
Conclusion:
The presented fixation system allows reliable, flexible and efficient patient positioning for extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy.
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Voraussetzung für eine konformale fraktionierte Strahlentherapie ist eine präzise reproduzierbare Positionierung des Patienten und des Zielvolumens. Vorgestellt wird ein auf dem Doppelvakuumprinzip basierendes Fixationssystem, das sowohl für konventionelle als auch extrakranielle stereotaktische Bestrahlungen eingesetzt werden kann.
Material und Methodik:
Mittels einer Fixationsfolie, mit der er auch zusätzlich fixiert werden kann, wird der Patient vor der Abformung in die Vakuummatratze hineingepresst. Eine exakt auf einer indexierten Bodenplatte positionierbare Plexiglashaube dient als stereotaktischer Rahmen. Bei zehn Patienten mit Zielvolumina im Abdomen und Becken wurden vor jeder Bestrahlung orthogonale digitale Verifikationsaufnahmen angefertigt. Diese wurden mit den digital rekonstruierten Röntgenbildern (DRRs) des dreidimensionalen (3-D) Planungssystems verglichen. Aus den Abweichungen der drei Raumrichtungen wurden die 3-D-Vektoren als Maß für die Repositionierungsgenauigkeit errechnet.
Ergebnisse:
Der Mittelwert der für alle Patienten errechneten 3-D-Vektoren (187 Fraktionen) betrug 2,5 ± 1,1 mm. Der mit 10 mm größte 3-D-Vektor wurde bei einem in Bauchlage bestrahlten Patienten beobachtet. Die initiale Abformung dauerte im Durchschnitt 15 min (10–30 min). Der tägliche zeitliche Lagerungsaufwand am Bestrahlungsgerät ist nur unwesentlich länger als ohne Fixationshilfe.
Schlussfolgerung:
Das vorgestellte Fixierungssystem ermöglicht eine zuverlässige, flexible und effiziente Patientenpositionierung für die stereotaktische Bestrahlung extrakranieller Tumoren.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nevinny-Stickel, M., Sweeney, R.A., Bale, R.J. et al. Reproducibility of Patient Positioning for Fractionated Extracranial Stereotactic Radiotherapy Using a Double-Vacuum Technique. Strahlenther Onkol 180, 117–122 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-004-1146-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-004-1146-0