Abstract
Objective
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of proximal humerus fractures via an anterolateral delta split approach.
Indications
All proximal humerus fractures classified as 11-A1-3, 11-B1-2 (B3), and 11-C1-2 (C3) according to the AO/OTA system.
Contraindications
Head split and closed irreducible dislocation type fractures, fractures with primary neurovascular impairment, and fractures in children with open growth plate.
Surgical technique
Beach chair position. Anterolateral delta split approach. Maintain rotator cuff insertions with nonabsorbable sutures. Reduction and K-wire retention of the tuberosities to the head fragment. Establish a tunnel along the anterolateral aspect of the proximal humerus with a blunt instrument (e.g., elevatorium). Attachment of the rotator cuff sutures to the corresponding plate holes of a 5-hole PHILOS® plate. Insertion of the plate underneath the deltoid muscle along the prepared tunnel. Preliminary fixation of the plate to the humerus head. Distal alignment of the plate and preliminary fixation. Reduction of the fracture onto the plate with a cortical screw in the shaft segment. Definitive plate fixation in the shaft and head segment. The nonabsorbable sutures are then tightened onto the plate.
Postoperative management
Immediate guided active exercise is encouraged. Weight bearing is increased according to radiological signs of consolidation.
Results
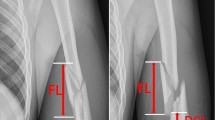
In a prospective evaluation from 2003–2006, 29 patients (8 male and 21 female) with a mean age of 64 years (16–91 years) were analyzed. The mean follow-up time was 12 months (6–32 months). The operation was accomplished in 75 min (55–155 min) with an image intensifier time of 160 s (48–807 s). All fractures healed in a timely manner. The median Constant score reached 78 points (28–93 points). In one case (3%), clinical evidence of a lesion of the anterior branch of the axillary nerve was found.
Zusammenfassung
Operationsziel
Stabilisierung von proximalen Humerusfrakturen über einen minimalinvasiven anterolateralen Deltasplit-Zugang.
Indikationen
Proximale Humerusfrakturen entsprechend der AO/OTA-Klassifikation 11-A1-3, 11-B1-2 (B3), 11-C1-2 (C3).
Kontraindikationen
Head-split-Frakturen und geschlossene irreponible Luxationsfrakturen, Frakturen mit primärer Gefäss- und Nervenläsion sowie Frakturen bei offenen Epiphysenfugen.
Operationstechnik
Halbsitzende „beach chair“-Lagerung. Anterolateraler Deltasplit-Zugang. Anschlingen der Tuberkula mit nicht-resorbierbaren Fäden. Reposition und präliminäre K-Draht-Retention der Tuberkula gegenüber der Kopfkalotte. Submuskuläres Tunnelieren des Plattenlagers z. B. mit einem Elevatorium. Einfädeln der Fäden in die entsprechenden peripheren Löcher einer 5-Loch-PHILOS®-Platte und Einschieben der Platte entlang dem präparierten Tunnel unter dem Delta-Muskel. Präliminäre Fixation im Kopfbereich mit einer winkelstabilen Schraube. Ausrichtung der Platte distal und ebenfalls präliminäre Fixation im untersten Plattenloch. Überprüfen und ggf. Korrektur der Achsenstellung im seitlichen Strahlengang. Die Reposition des Humerusschaftes gegen die Platte erfolgt nun mit einer Kortikalisschraube im proximalen Schaft. Definitive Fixation der Platte im Kopf und Schaft. Verknoten der vorgelegten Fäden.
Weiterbehandlung
Sofortige aktiv-assistierte Mobilisation und Belastungssteigerung je nach radiologischer Konsolidation.
Ergebnisse
Von 2003 bis 2006 wurden 29 Patienten (8 Männer, 21 Frauen) mit einem mittleren Alter von 64 Jahren(19–91 Jahre) in einer prospektiven Studie untersucht. Das durchschnittliche Follow-up betrug 12 Monate (6–32 Monate). Die mittlere Operationsdauer lag bei 75 min (55–155 min), die mittlere Durchleuchtungszeit bei 160 s (48–807 s). Alle Frakturen heilten zeitgerecht. Funktionell erreichten die Patienten durchschnittlich einen Constant-Score von 78 Punkten (28–93 Punkte). Ein Patient (3%) wies klinische Anzeichen für einen Ausfall des anterioren Astes des N. axillaris auf.































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acklin YP, Jenni R, Walliser M, Sommer C (2009) Minimal invasive PHILOS®-plate osteosynthesis in proximal humeral fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 35:35–39
Blevins FT, Warren RF, Cavo C et al (1996) Arthroscopic assisted rotator cuff repair: results using a mini-open deltoid splitting approach. Arthroscopy 12(1):50–59
Brunner F, Sommer C, Bahrs C et al (2009) Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using a proximal humeral locked plate: a prospective multicenter analysis. J Orthop Trauma 23(3):163–172
Bono CM, Grossman MG, Hochwald N, Tornetta P 3rd (2000) Radial and axillary nerves. Anatomic considerations for humeral fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 373:259–264
Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Dines JS, Lorich DG (2004) A minimally invasive approach for plate fixation of the proximal humerus. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 62(1–2):18–23
Gardner MJ, Boraiah S, Helfet DL, Lorich DG (2008) The anterolateral acromial approach for fractures of the proximal humerus. J Orthop Trauma 22(2):132–137
Hertel R, Hempfing A, Stiehler M, Leunig M (2004) Predictors of humeral head ischemia after intracapsular fracture of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 13(4):427–433
Laflamme GY, Rouleau DM, Berry GK et al (2008) Percutaneous humeral plating of fractures of the proximal humerus: results of a prospective multicenter clinical trial. J Orthop Trauma 22(3):153–158
Mackenzie DB (1993) The anterior-superior exposure for total shoulder replacement. Orthop Traumatol 2(2):71–77
Röderer G, Erhardt J, Graf M et al (2010) Clinical results for minimally invasive locked plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma 24(7):400–406
Smith J, Berry G, Laflamme Y et al (2007) Percutaneous insertion of a proximal humeral locking plate: an anatomic study. Injury 38(2):206–211
Sommer C (2006) Four case presentations of humerus fractures. In: Wagner M, Frigg R (eds) AO Manual of Fracture Management. Internal Fixators. Concepts and Cases using LCP and LISS. Thieme, Davos-Stuttgart, pp 293–316
Thanasas C, Kontakis G, Angoules A et al (2009) Treatment of proximal humerus fractures with locking plates: a systematic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 18(6):837–844
Conflict of interest
The corresponding author states the following: no benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acklin, Y., Sommer, C. Plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the minimally invasive anterolateral delta split approach. Oper Orthop Traumatol 24, 61–73 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00064-011-0051-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00064-011-0051-9
Keywords
- Osteosynthesis, fracture
- Minimally invasive surgical procedures
- Humerus fractures, proximal
- Anterolateral delta split approach
- PHILOS aiming device